scabies
introduction
In scabies (medical: scabies, acarodermatitis) is a skin disease that is caused by certain parasites (itch mites). It is a highly contagious disease that often occurs in places with poor hygiene and many people.

An infection is often noticeable by severe itching, which occurs mainly at night. Changes in the skin are another indication of an infection with the mites. Treatment can be carried out with the help of specific medication and meticulous hygiene and is usually successful.
Read more on the topic Rash from mites
Causes of Scabies
The clinical picture of scabies is caused by so-called itch mites. These parasites burrow through the skin, form ducts, and lay their eggs under the skin. The excretions of the mites are responsible for the typical, itchy rashes of scabies.
Especially in places where many people live and sleep in one place, perfect conditions are created for the itch mites to spread. Kindergartens and old people's homes are typical. Poor hygiene intensifies this effect, which is why the occurrence of scabies is often associated with poor hygienic conditions and a low social status. However, these risk factors do not necessarily have to be present in every disease. Especially people with a weak immune system often suffer from the symptoms of scabies. Your immune system is no longer able to fight off the parasites.
Symptoms of scabies
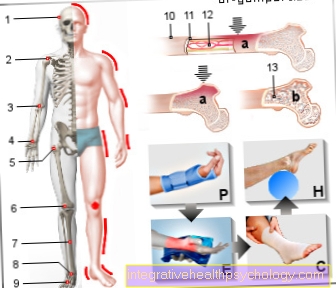
The symptoms of scabies are mostly limited to the skin. They appear at the earliest 2 weeks and at the latest within 6 weeks after infection with the mite and severely impair the quality of life of those affected. Although the symptoms can be extremely uncomfortable, scabies does not pose a threat to life.
Read more about the topic here: What are the symptoms of scabies?
First of all, the itching sensation occurs when the scabies is present. Shortly afterwards, skin symptoms appear, which are noticeable in rashes and eczema. Depending on the extent of the infestation and the individual course of the disease, redness, flaking and blisters can appear on the skin. Typical parts of the body are warm localizations such as in the genital area, anal area, on the groin or between the fingers and toes.
What might also interest you: Itching in the vagina
In addition to the symptoms that are triggered directly by the parasites and their excretions, additional infections on the skin can lead to problems. Particularly due to the pronounced itchiness, scratching causes small wounds on the skin, which can easily become inflamed.
Read more under
- Itchy rash
- Rash causes
Is Scabies Contagious?
Scabies is a contagious disease. Contact with people who carry the parasites that cause the disease on and under the skin can lead to infection and thus the outbreak of scabies.
For a long time it was assumed that only prolonged contact with infected people could lead to transmission and infection. Today it seems to be proven that even brief contact with people suffering from scabies can lead to an outbreak of the disease.
The mites can survive for a few days without skin contact with humans. Contact with the clothes or bed linen of infected people can also lead to an infection with the parasites. The first symptoms usually appear between 2 and 6 weeks after infection.
After starting treatment, there is usually no longer any risk of infection for other people within 12 hours.
Read more on the topic: How contagious is scabies?
Treatment of scabies
The aim and principle of the treatment of scabies is that Elimination of the parasites responsible for scabies. To achieve this, drugs can be taken, which are called so-called Anti-scratch preparations are designated. Overall, the scabies can treated very well become. It must be noted, however, that the drugs used strong side effects and therefore, especially in risk groups such as pregnant women and small children, it should be considered which drug is suitable.
The drugs available can be applied directly to the skin or taken as tablets. The side effects of the tablets, which are rarely used in Germany, are usually stronger than the ointments applied directly to the skin. The most common active ingredient used in scabies is what is known as permethrin. The duration of use can vary, although the parasites can often be eliminated after 2 weeks. However, symptoms may persist for a few weeks after the parasites have been eliminated. As a rule, there is no longer any risk of infection for other people as early as 12 hours after starting treatment with permethrin.
Home remedies for scabies
In addition to applying anti-itch preparations as part of medical treatment, there are some home remedies that can also help cure the disease in the case of scabies.
Since the mites are also on the clothes and bed linen of those affected, should all textiles first either washed at 60 ° or stowed in a sealed plastic bag for 4 days the mites will die. General Hygiene measures can also help to suppress the multiplication of mites.
Using Oilwhich should be applied to the skin to kill the mites not recommended as the effectiveness of these agents is doubtful.
Do you have to report scabies?
There is no general reporting requirement for scabies. This means that if a person, regardless of age, is diagnosed with scabies, the attending physician does not have to provide the health department with any information. It should be noted, however, that managers of community facilities are obliged to inform the health department if infections become known or if an infection with scabies is suspected within these facilities. These community facilities include, for example, kindergartens, schools, old people's homes and asylum shelters.
Scabies in children
Basically all age groups can be affected by scabies. All in all pile up the cases of scabies however with children towards adults. This is mainly due to the fact that children in crawling groups, kindergartens or schools have much more intensive contact with other children than is usually the case with adults. The transmission in these facilities is much easier and epidemics often occur in which children in an entire facility are infected by the parasites.
The course of the disease in children does not differ much from that in adults. In addition to the typical sites of infection in adults, children often have symptoms of scabies on the scalp and neck. Itching can be difficult to control in children. However, to avoid infection of the wounds, it is extremely important to refrain from scratching. The normal anti-scratch preparations can also be used on children. The application of these preparations may have to be carried out by an educator with gloves.



.jpg)