Bradycardia
What is bradycardia?
Bradycardia is a heart rate that is below the expected normal range. For an adult, a frequency of 60 to 100 beats per minute is usually assumed. Bradycardia would therefore be present if this value was not reached.
The age and the level of training of a person must be taken into account.
For babies and children, the fundamental frequencies of the heart are generally higher than natural. The values of bradycardia would therefore be located higher up.
In very sporty people, very low frequencies can occur without showing any disease value.
At this point you can read general information about cardiac arrhythmias and how they are classified: Classification of cardiac arrhythmias

Cardiac arrhythmias - what's behind it?
The heart usually beats at a rate of 60-100 beats / min. If there is a change in the sequence of the heartbeat, this is known as an arrhythmia. The disturbance can be shown with the help of an EKG.
Normally, the heart beats at a certain frequency and with the rhythm set by the sinus node, i.e. in the so-called sinus rhythm.
This natural rhythm can be disturbed, for example, if it occurs irregularly or arrythmically, too quickly or much too slowly. A heart action that is too fast is called tachycardia and too slow is called bradycardia.
Cardiac arrhythmias do not always require treatment. When symptoms occur, however, it is often the case that therapy for the arrhythmia or its cause is necessary.
It is important that you get an overview of cardiac arrhythmias. The following article is recommended: What are arrhythmias?
Causes of Bradycardia
One of the possible causes of a heart rate that is too low is a disorder in the sinus node. The sinus node is naturally the "clock" of the heart. Here the electrical excitation in the heart arises more precisely in the atrium and from there it spreads over the whole heart. If the sinus node is defective or disturbed, it cannot function as a clock, which is then expressed in a low heartbeat.
Furthermore, so-called conduction disorders can lead to bradycardia. The electrical excitation that originates in the sinus node cannot properly be passed on. There is a blockage, so to speak, and the electrical excitation is interrupted.
One of the more common places where blockage occurs is the AV node. This is normally supposed to carry the electrical excitation away from the sinus node. In the event of a defect, the transmission is irregular or even interrupted and the associated bradycardia occurs.
Furthermore, bradycardia can also manifest itself with atrial fibrillation, i.e. with bradycardiac atrial fibrillation. This is characterized by rapid and irregular excitation of the atria, which are only partially transmitted and ultimately result in a low heart rate.
An underactive thyroid can also lead to a slow heartbeat. In addition to bradycardia, other symptoms of hypofunction such as weight gain, brittle hair and fingernails can also appear here.
Bradycardia can also occur in the event of a disturbance in the electrolyte balance, especially the potassium in the blood plays a role here.
In athletes, bradycardia may be without disease. Here the heart muscle is able to transport the same amount of blood with fewer beats due to its strong expansion. The heart can therefore literally fulfill its function despite the reduced number of beats.
Drugs can also cause bradycardia. The most important representatives here are the beta blockers, the so-called calcium antagonists and cardiac glycosides. In the case of known and pronounced bradycardia, these preparations are usually not recommended. Only in certain cases and under medical supervision should the above medication be administered in the presence of bradycardia.
The following articles can also give you a clear overview of the causes mentioned:
- Atrial fibrillation - what are the causes?
- Hypothyroidism - The most important things in summary
- Heart rhythm disorder - that's behind it
Sick sinus syndrome as a cause of bradycardia
Sick sinus syndrome comprises a number of cardiac arrhythmias that arise from a defective or malfunctioning sinus node. If, for example, the sinus node cannot generate electrical excitation in the correct cycle or if the transmission of electrical excitation is disrupted, this is summarized under the term sick sinus syndrome. The malfunction can have different causes.
Would you like to find out more about sick sinus syndrome? At this point, read the main page on the topic for the most important details: Sick sinus syndrome - that's behind it
Beta blockers as a cause of bradycardia
The so-called beta blockers are drugs that are preferably used in the treatment of high blood pressure. Among other things, they lower the heart rate and the conduction of excitation in the heart.In the case of high blood pressure, this reduces the undesirable "high pressure" in the blood vessels.
Beta blockers, however, are contraindicated in people who have significant bradycardia, i.e. a heart rate of less than 50 beats per minute. The already low heartbeat would be further reduced by the administration of medication. As a result, severe side effects such as fainting and dizziness could occur.
What are the exact effects and side effects to be expected from the administration of beta blockers? You can find out more at: Effect of beta blockers
Can a thyroid disorder lead to bradycardia?
The thyroid gland and its hormones influence a number of organs and body functions, including the heart. If there is a malfunction of the thyroid gland, it can have decisive effects on the heart.
In the case of an underactive thyroid, known as hypothyroidism, bradycardia can result in addition to other symptoms. As part of a diagnostic investigation, the thyroid value or the blood values of the thyroid hormones in the but are also determined on the basis of this. If an underactive thyroid is the cause of bradycardia, certain thyroid drugs usually help to normalize the function again and thus also to remedy the bradycardia.
Which values speak exactly for an underactive thyroid? This and much more can be found at: Hypothyroidism values
These symptoms indicate bradycardia
The heart's real pumping function is used to supply the rest of the body with blood and the oxygen it contains. In bradycardia, the heart beats too slowly.
As a result, less blood is often pumped into the body's circulation. The organs and tissues are thus supplied with less blood overall than would be usual for people with a normal heart rate.
An exception are (competitive) athletes, in whom the trained state of the heart ensures an adequate supply of blood to the body's circulation even at a low frequency.
A variety of symptoms can occur with bradycardia. Among other things, a decrease in performance, tiredness and a feeling of weakness can show. In addition to the rather unspecific symptoms, dizziness and visual impairment are also common symptoms of a reduced heart rate.
Furthermore, those affected may experience difficulty breathing, which may also be accompanied by nervousness and feelings of fear.
If the brain is not supplied with sufficient oxygen or blood due to the heart's low beating frequency, it can lead to fainting attacks.
Not all of these symptoms have to be present to diagnose bradycardia. Some people even perceive only very slight complaints or even no symptoms at all.
Course of the disease in bradycardia
The course of the disease depends, among other things, on the therapy. When therapy is initiated, most people can expect symptoms to decrease.
Of course, it is always important to consider which other diseases are still present that may affect the heart.
All in all, bradycardia can be treated with adequate therapy.
If no therapeutic measures are initiated, heart failure, known as heart failure, can develop over time. This can lead to an insufficient supply of oxygen to the other organs. Depending on which organ is affected by the undersupply, different symptoms then occur.
How can so-called cardiac insufficiency be recognized and, if necessary, treated? This information and much more can be found in the following articles:
- Symptoms of heart failure
- Therapy for heart failure
Which bradycardia should be treated?
It is not necessary to treat bradycardia. Very sporty people, for example, can have a low heartbeat, but this has no disease value and therefore does not require treatment.
Therapy should be initiated especially in people who show symptoms such as weakness, dizziness, and fainting.
Furthermore, treatment should be given to those whose heart rate is already particularly low, since the supply of the body or organs with blood is no longer sufficiently guaranteed.
Therapy of bradycardia
There are several therapeutic options that can be used for bradycardia. As a rule, the treatment depends on the triggering cause.
In the case of bradycardia caused by drugs such as beta blockers, alternative preparations are looked for.
In the context of an underactive thyroid, the administration of certain thyroid medications is necessary to put an end to bradycardia as a side effect.
If the disorder is in the sinus node or in a pronounced conduction disorder, the insertion of a pacemaker is usually necessary. This is a small probe that can be inserted into the heart using a cardiac catheter. The pacemaker is able to generate its own impulses, which then lead to an electrical excitation of the heart. The pacemaker takes over the function of the sinus node.
In the case of minor disturbances in the electrical transmission, only regular checks with an EKG may be necessary.
The exact therapeutic procedure is of course also related to other diseases, especially of the heart. Consultation with a doctor is therefore essential in order to adequately treat bradycardia.
Are you interested in how a pacemaker works and are you about to have a pacemaker implanted? So it is advantageous that you also deal with the following article: Pacemaker - What is its job?
Duration and prognosis of bradycardia
In the case of bradycardia caused by a defective sinus node or a pronounced conduction disorder, the implantation of a pacemaker can usually achieve good therapeutic results. Those affected are usually free of complaints after the procedure.
Bradycardia caused by medication can be resolved by changing medication. Depending on the preparation, normalization of the heart rate can usually be expected after a short time.
In very trained people, bradycardia is usually a natural condition that persists as long as the training condition is maintained, but does not require any treatment.
At this point, the following article could also be of interest to you: Can you do sports if you have an arrhythmia?
What could be the long-term consequences of bradycardia?
Long-term consequences can occur, especially in people who do not want treatment or do not have it carried out.
On the one hand, the symptoms are maintained by the lack of treatment or worsen over time.
On the other hand, the heart becomes weaker and weaker as a result of the bradycardia and ultimately heads towards heart failure, i.e. a state in which it is no longer able to supply the body with sufficient blood. The organs and tissues in the body are affected because they are not adequately supplied with blood or oxygen.
The consequences of bradycardia that is adequately treated depend both on the treatment itself and on the general condition of the person affected and cannot be described in general terms.
Also read the general consequences of an arrhythmia to get a precise overview of these: Consequences of cardiac arrhythmias
Which bradycardia is dangerous?
Bradycardia, which is associated with insufficient supply of the brain and other organs, can be dangerous for those affected. The brain in particular is dependent on a continuous supply of oxygen. Inadequate oxygen supply can lead to fainting, for example.
Depending on the cause, bradycardia can become risky even if it persists for a long time. The heart gradually loses functionality. Ultimately, it comes to heart failure. The heart is then no longer able to supply the body with sufficient amounts of blood without supporting medication.
Bradycardia leads to circulatory disorders in the brain and, accordingly, to an insufficient supply of oxygen, which has numerous consequences. The consequences of this situation and the serious dangers behind it can be found at: Circulatory disorder in the brain
Nocturnal bradycardia
Night-time bradycardia or nocturnal bradycardia usually presents with the same symptoms as during the day. These include tiredness, exhaustion, dizziness, nervousness and also fainting.
Often the bradycardia is not limited to the night, but is only masked by daytime activities. Due to the stress and hectic pace of everyday life, those affected simply do not notice the symptoms. The symptoms are usually noticeable in the resting state.
As with daytime bradycardia, it is important to have a doctor find the cause in order to adequately address the bradycardia. If bradycardia occurs at night, those affected should definitely consult a doctor.
It is also possible that your heart will race at night. You can see the dangers behind this situation at: Palpitations at night - is that dangerous?
What is Bradycardia-Tachycardia Syndrome?
Tachycardia is characterized by a heartbeat that is too fast and is the opposite of bradycardia. As a rule, one speaks of tachycardia when the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute.
Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome involves a sudden change from slow to fast heart rates. Often the rapid heart rate is followed by a short pause, which then turns into bradycardia.
The treatment of bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome usually includes measures that on the one hand contain the tachycardia, e.g. by administering beta blockers, and on the other hand eliminate the bradycardia, as is possible, for example, by implanting a pacemaker.
Since the therapy of bradycardia has now been explained, it is recommended at this point to also deal with the therapy of tachycardia: Therapy of palpitations
What is reflex bradycardia?
Reflective bradycardia is particularly likely to be a side effect of noradrenaline therapy. The north adrenaline is used as a drug for shock states. It has a particularly good effect on the vessels in the body and also on the heart.
The blood vessels are narrowed by the noradrenaline administration and the blood pressure rises again. In the heart, it causes, among other things, an acceleration and strengthening of the heartbeat. As a possible side effect, the body sometimes reacts to the increased heart rate and the increased blood pressure by reducing the heart rate again significantly - this behavior is referred to in medical terminology as reflex bradycardia.
You might also be interested in: Effects of norepinephrine on the body
Diagnosis of bradycardia
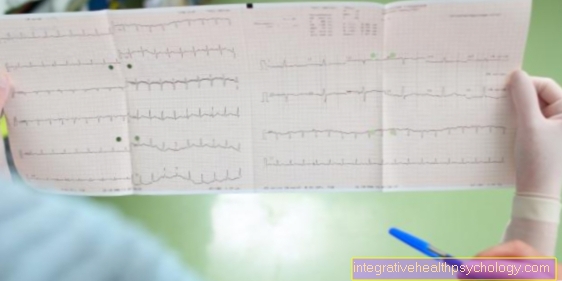
If bradycardia is suspected, a physical exam followed by an EKG measurement is usually done.
The physical examination includes auscultation, i.e. listening to the heart and measuring the pulse. Here the doctor can get the first clues about the presence of bradycardia or its cause.
An EKG, i.e. an electrocardiography, is then performed. With the help of small electrodes that are previously glued to the body, this measures the electrical excitation or its transmission to the heart and also provides information about the heart rate.
In order to see whether the low heart rate is continuously present, a long-term ECG can also be applied to the affected person. This then measures the electrical heart activity at certain intervals, usually over a period of 24 hours. Long-term measurement has the advantage that it also records disturbances that only occur occasionally.
A medical history, i.e. which drugs are taken, is also part of a diagnostic work-up. This is especially important as there are numerous drugs that can affect your heart rate.
Listening to the heart can provide the necessary heart murmurs to suggest brday cardia. To learn more about heart murmurs and what information they reproduce, read also: Heart murmurs - what is their meaning?
Long-term ECG for bradycardia
The long-term ECG can be used as a diagnostic tool if bradycardia is suspected. The EKG measures the electrical currents in the heart and also provides information about the heart rate.
In order to discover irregularities, it makes perfect sense to carry out a long-term EKG, which records the heart's activity over several hours. Usually the EKG is made for 24 hours. The recorded measured values - in conjunction with the physical examination - make a decisive contribution to the diagnosis.
Detailed information on the long-term ECG can be found at: Long-term ECG
Recommendation from the editor
You might also be interested in these topics:
- Cardiac Arrhythmias - How Dangerous Is It?
- What diseases of the heart are there?
- Heartache - what are the causes?
- What does heartache indicate?
- Recognizing arrhythmias













.jpg)