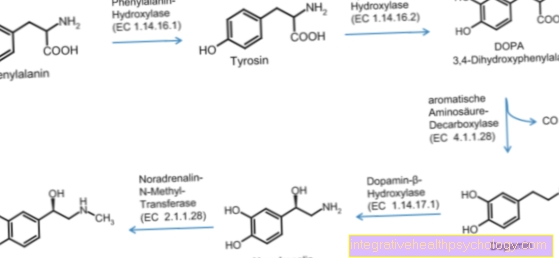
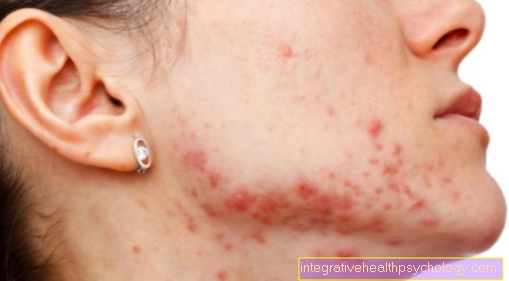
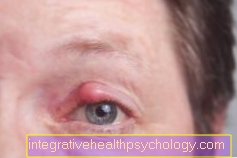
Stress hormones
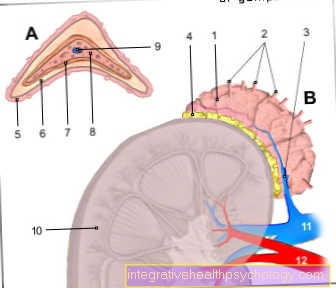
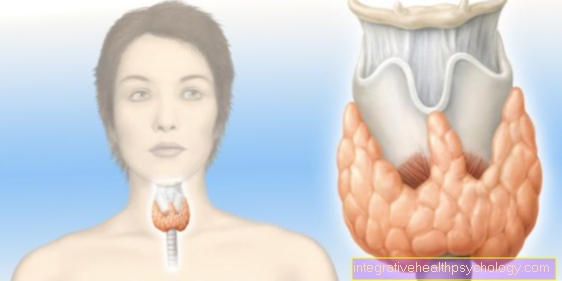
Stress hormones are the messenger substances that trigger a stress reaction in our body. The most important are cortisol, adrenaline and noradrenaline, some of which are acute and others are only released during prolonged stress. There is