The lower ankle
synonym
USG, articulatio talotarsalis
definition
The lower ankle joint, in combination with the upper ankle joint, is the articulated connection between
- Lower leg and
- Foot,
which enables optimal stability with great mobility.
In contrast to the ankle joint, it has no direct contact with one of the lower leg bones; the joint surfaces are formed by three of the tarsal bones.

Hocks in general
The Ankle joint is not really a joint, but consists of two separate joints, but one functional unit form.
Together they enable an optimal agility, but are at the same time stable enough to withstand the great forces exerted on them by body weight and the complexity of human movements.
Lower ankle - anatomy
The USG is below the upper ankle. Three of the Tarsus participate in its formation with their joint surfaces.
- The talus (Talus) forms the upper (proximal) Joint body,
- the calcaneus (Calcaneus) and
- the scaphoid (Os naviculare) the lower (distal).
Divided by two Bone grooves, the so-called Sinus tarsi, the lower ankle is divided into two joint cavities. The back lies Articulatio subtalaris (Subtalar joint). This is where the posterior articular surface of the talus and the calcaneus articulate. Before that lies the Articulatio talocalcaneonavicularis, Here the talar head articulates not only with one joint surface, but with three structures. He has an articulated connection to the
- Calcaneus, to the
- Navicular bone and the so-called
- Pan band (Plantar calcaneonavicular ligamente).
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
Athletes (joggers, soccer players, etc.) are particularly often affected by diseases of the foot. In some cases, the cause of the foot discomfort cannot be identified at first.
Therefore, the treatment of the foot (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, heel spurs, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of foot diseases.
The aim of every treatment is treatment without surgery with a complete recovery of performance.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
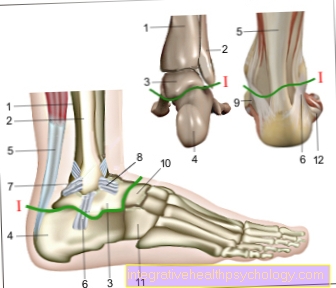
Lower ankle illustration

I - Lower ankle
(Joint line green) -
Articulatio talocalcaneonavicularis
- Shin - Tibia
- Fibula - Fibula
- Ankle bone - Talus
- Heel bone - Calcaneus
- Achilles tendon -
Tendo calcaneus - Fibula-calcaneus tape -
Calcaneofibular ligament - Hint. Shin-fibula
Tape-
Posterior tibiofibular ligament - Front Fibula ankle
Tape-
Lig fibulotalare anterius - Delta band - Deltoid ligament
- Scaphoid bone - Navicular bone
- Cuboid bone -Os cuboideum
- Fibula short muscle -
Musculus fibularis brevis
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Tape apparatus
That too lower ankle is reinforced in its basic bony structure by ligaments. However, two of these ligaments do not have the typical ligament function in terms of inhibition or stabilization, but are parts of the lower joint body.
The Pan band lies on the sole of the foot (plantar) and serves the purpose the Calcaneus and the Navicular bone, the essential articular surfaces of the anterior portion of the USGto brace together. In addition, the acetabular ligament is assigned a role in shaping the arch of the foot.
A portion of the also serves to connect the calcaneus and the navicular bone Fork belt (Ligamentum bifurcate). This firm connection between the calcaneus and the navicular bone is important because they have no bony connection to one another.
In addition to these tapes, there is also the USG Bands that are used to inhibit unwanted movements. Some of the tapes of the upper ankle also act on the lower one. So form two parts
- Pars tibiocalcanea and
- Pars tibionavicularis
of Deltoid ligament, i.e. the inner band of the OSG.
You hold that Pronation, i.e. the lifting of the lateral edge of the foot, within limits. The Ligament calcaneofibularthat goes to the outer band of the OSG belongs restricts movement in the opposite direction, the Supination, so the lifting of the inner edge of the foot.
In addition to these tapes, the USG is also secured by its own tapes. The Interosseous talocalcaneum ligament lies in the bone groove that divides the USG into two joint cavities. It connects the calcaneus with the talus and inhibits both pronation and supination of the foot. The Ligemantum talocalcaneum laterale serves to inhibit supination.
Function of the lower ankle

The USG is - analogous to that OSG - a Hinge joint.
However, its axis is different, so that it supports other movements. As a result, the combination of both joints enables a large range of motion.
in the USG two movements take place.
- The Eversion (Lifting the side of the foot) and the
- inversion (Lifting the inner edge of the foot).
An eversion of around 10 degrees and an inversion of around 20 degrees are possible. Strictly speaking, these two movements cannot be equated with the designation of Pronation or. Supination, since these are movements that are not performed in the USG alone, but rather result from a combination of the movements of the USG and the Joints between Tarsus.
Clinical evidence:
The USG is much less affected by injuries than the ankle.