Diagnosis of sarcoid
introduction
When diagnosing sarcoid, it is also important to distinguish between the acute and the chronic form of sarcoid. In any case, a comprehensive anamnesis and a physical examination should be carried out by the attending physician.
If there is a suspicion of Löfgren's syndrome, an X-ray of the lungs should be made. A biliary lymphadenopathy can usually be seen very clearly on this. The classification can also be made on the basis of an X-ray image, which is then a good starting point for creating a therapy plan.

What diagnostic tests are there?
Furthermore, a laboratory blood test should be requested. This then results in increased inflammation values as an expression of an inflammatory reaction of the body, a so-called "acute phase reaction" with increased C-reactive protein (CRP value) and increased sedimentation rate.
In 65% of cases, a blood test reveals an increased activity of a certain enzyme, the so-called angiotension-converting enzyme. However, this method has an uncertain specificity, that is, an increase in the angiotension-converting enzyme is also found in other diseases. This parameter is therefore particularly suitable for monitoring the progress.
If there is a chronic form of sarcoid, an X-ray image of the lungs can be very helpful, just as in the acute form; a computed tomogram can usually determine changes in the connective tissue of the lungs and the precise involvement of the lymph nodes earlier. Finally, further information could be obtained through the improvement of the MRI of the lungs.
Furthermore, a biopsy, i.e. a sample of the body's own tissue, should be taken in order to be able to examine the individual granulomas with their cells in detail. In this way, other diseases that are also associated with nodule formation can often be excluded. It is important to know that sarcoid-type granulomas can also occur in tuberculosis and Crohn's disease, an inflammatory bowel disease.
If you suspect that the heart is affected, you should make an EKG to record any cardiac arrhythmias that may be present.
These diagnostic criteria exist
There are different criteria depending on the method used for diagnosis. On the one hand, the question of an acute inflammation and on the other hand the question of the localization of the sarcoid in various organs are in the foreground.
There are also various parameters in the blood, such as calcium, which are also related to the progression and prognosis of the disease. In the x-ray of the lungs, the progress of the lung involvement is primarily assessed based on the lymph nodes and changes in the lung tissue.
It is also important to distinguish the acute form of sarcoid, Löfgren's syndrome, from the chronic form. At this point you can also read our main page on Löfgren Syndrome: Löfgren syndrome - what's behind it?
Laboratory values for sarcoid
An examination of the blood and the evaluation of the laboratory values are standard in a diagnosis of sarcoid.
In the acute form of the disease, various inflammation parameters such as leukocytes, i.e. the white blood cells, can be checked.
In chronic sarcoidosis, certain antibodies and calcium levels are also checked. If the latter is increased, this can have a negative effect on the function of the kidneys and thus the prognosis. Certain receptors are also evaluated in chronic sarcoid to control the course of the disease.
The next article on this topic could also be of interest to you: Blood test
X-ray of the lungs
Probably the best-known means of diagnosing sarcoid is an X-ray of the lungs. This has become particularly prominent, since the chronic form of sarcoid is often diagnosed as an incidental finding.
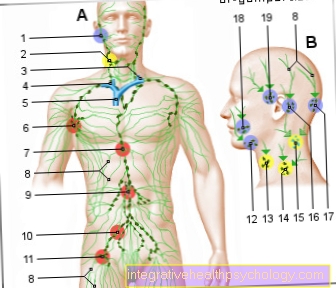
This imaging primarily assesses the lymph nodes located in the area of the lung root. If these are enlarged, this can be a typical indication of the presence of the disease. They are often less swollen in later stages. Instead, there is an infestation of the lung tissue, which can be fibrotic, i.e. scarred, and becomes visible as such in the X-ray image.
Are you more interested in this topic? Read our next article on this below: X-ray of the chest
Sarcoid biopsy
A lung specimen, also known as a bronchoscopy, can perform both a lung lavage and a biopsy of the lymph nodes in the lungs. The latter is usually done with the help of a fine needle. A small piece of tissue is removed from a lymph node under the control of an ultrasound device.
This can then be examined in the laboratory using a microscope and various tests. Above all, the number and type of cells present are evaluated, which can provide information on the stage of the disease. In later stages, tissue samples of the lung tissue can also be taken with a biopsy and examined.
For more detailed information on this diagnostic procedure, see: Biopsy
Scintigraphy for sarcoid
In rare cases, scintigraphy can also be used to diagnose sarcoid. Radiolabelled gallium particles are introduced into the body through the bloodstream. These then accumulate in tissue areas where an active inflammatory process takes place.
These areas of tissue are also known as granulomas. The whole thing can then be measured with the help of the scintigraphy. However, since this method involves risks and is very expensive, it is rarely used these days. In order to check the involvement of various organs, an MRI image of the lungs can be made instead.
You can read more detailed information about this examination procedure here: Scintigraphy
Differential Diagnosis of Sarcoid
Probably the most important differential diagnosis to sarcoid is tuberculosis. It also typically affects the lungs and can have serious consequences if the diagnosis is not made.
Other possible alternative diagnoses are also various cancers of the lymphatic system, such as Hodgkin's disease or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
In addition, a pathological accumulation of foreign particles can lead to similar symptoms. This includes, for example, quartz dust, which can lead to so-called silicosis if inhaled for years, for example during mine work.
Summary
Sarcoid can be diagnosed using a number of different methods. This includes first of all the anamnesis, i.e. the doctor-patient conversation, and a physical examination to determine the exact symptoms. When examining the blood, various parameters can provide clues about the disease.
Probably the best-known diagnostic method for sarcoid is the x-ray of the lungs. In addition, a bronchoscopy, i.e. a lung specimen, a lung function test and a CT scan of the lungs can be helpful. An EKG, an MRI and a PET scan can be used to assess the involvement of organs other than the lungs.
Since sarcoid can affect various organs, including the skin, there are various diagnostic methods to determine this finding. Read more about this in the next article under: Sarcoid of the skin - causes, symptoms and therapy