Diastole Too High - Is It Dangerous?
definition
The heart's action is divided into two phases, an expulsion phase, in which the blood is pumped from the chambers into the blood vessels, and a filling phase, in which the pumped heart fills itself with blood again. The heart works like a suction-pressure pump, so to speak. The expulsion phase is known as systole, the filling phase as diastole.

introduction
What do these phases of the heart's action have to do with blood pressure? There is a certain pressure in the vessels, the diastolic blood pressurecaused by the blood in the vessels during the filling phase. This depends on which one Amount per time the heart is pumping and how large the vessel diameter is. The diastolic blood pressure should be around 80mmHg (say: Millimeters of mercury) lie.
In the expulsion phase, however, the heart has to generate a higher pressure than the diastolic pressure so that the blood can be pumped into the vessels. Because the blood is always flowing from higher to lower pressure. During systole, the heart generates a pressure of approx. 120 mmHg, which is pumped into the vessels and from there passed through the body's circulation.
During the Filling phase of the heart if the blood pressure falls back to the diastolic "Low point“From. With that the Blood pressure from two values together, one systolic and one diastolic: 120/80.
These two values can pathologically increased or decreased be. Most of them are with one arterial hypertension, the common high blood pressure, both values increased. But it can also isolated the systolic or the diastolic is too high.
Both values depend on the one hand on the blood volume and on the other hand on the vascular resistance, because the smaller the diameter, the higher the pressure. Thus there is high volume pressure (too much volume), which can be distinguished from high resistance pressure (too small vessel diameter).
Symptoms of excessive diastole
High blood pressure goes unnoticed for a very long time and is symptomatically inconspicuous, that is, if symptoms are noticed, the hypertension has been present for a long time with a high degree of probability.
Typical are early morning headaches, sleep disorders, dizziness, ringing in the ears, nervousness, palpitations, shortness of breath during exercise and nosebleeds.
Which diastolic values are classified as dangerous?
Values between 70 and 90mmHg apply as a reference value for a normal diastolic blood pressure value. If the diastolic value exceeds the limit of 90mmHg, it is called diastolic high blood pressure. But values below 70mmHg can also be classified as dangerous.
In the case of known pre-existing conditions, the normal values of the diastolic blood pressure can deviate. With known diabetes mellitus, for example, values above 85mmHg are classified as dangerous. Even with known heart or circulatory diseases, even lower diastolic values are rated as dangerous and harmful to health.
The dangerous thing about high blood pressure are the secondary diseases that are favored by the high blood pressure. For example, high blood pressure increases the risk of a heart attack or stroke. Therefore, the increased blood pressure should be treated early. It is important not only to treat with medication. You should also pay attention to a healthy diet and enough exercise and sport.
Diagnosis
The simplest and safest means for diagnosis is one Blood pressure measurement.
To check the blood pressure permanently increased is, often becomes a 24h blood pressure measurement carried out.
The Standard value for diastolic blood pressure is attached <85 to a maximum of 90mmHg, optimal are <80mmHg.
A mild hypertension is present when blood pressure increases between 90-99mmHg is located. At 100-109mmHg there is already one moderate hypertension before and with severe high blood pressure values above 110mmHg are measured.
At > 120mmHg one speaks of one malignant hypertension, a acutely derailed blood pressure, the one with a Brain and retinal damage as well as heart failure.
What to do if the diastole is too high
You can do a lot yourself, starting with taking the medication your doctor prescribes. Theoretically, high blood pressure can be treated well, but it requires that the patient participate. Unfortunately, it is frighteningly often the case that drugs are not taken or not taken regularly. In addition, weight loss is recommended because the blood pressure drops 2 mmHg per kg.
Physical activity is also an excellent way of permanently lowering blood pressure and also makes weight loss easier. Here you kill two birds with one stone. During exercise, the diastolic blood pressure in particular falls because the blood vessels in the working muscles expand and this leads to a decrease in peripheral resistance, which, as mentioned above, plays an important role in the development of high blood pressure.
In addition to weight loss, it is of course also useful to eliminate other risk factors. These include smoking, alcohol consumption (more than ¼ liter of wine per day or <30g per day) and stress, be it professional or private. If you make the diagnosis yourself or if you suspect that hypertension is present, you should definitely consult a doctor and have the suspicion further clarified and arrange therapy.
Causes of increased diastole
The diastolic blood pressure, like the systolic, increases continuously up to the age of 60. The systolic continues to increase with age, the diastolic decreases again. It follows from this that the blood pressure amplitude, i.e. the pulse pressure, increases. This means that the difference between the systolic and diastolic values increases.
For this reason, diastolic hypertension is very rare in old age, but occurs mainly in the 4th and 5th decades of life. Primary hypertension often begins at this age, the genesis (development) of which has not yet been fully elucidated. This usually begins with diastolic hypertension, but in the further course systolic hypertension also develops, so that both values are increased and are worthy of treatment.
The cause is usually an increase in peripheral resistance. This resistance arises from the vessels, which in simplified terms can be imagined as pipes. If liquid now flows through these “pipes”, friction and thus resistance arise. This resistance is higher, the smaller the vessel radius is. Furthermore, it can be deduced from this that a higher pressure must be generated in order to overcome the high resistance. This means that the smaller the radius, the higher the pressure. If someone suffers from a diastolic blood pressure that is too high, one can conclude that the blood vessels are narrowing.
This is the case, for example, in a state of shock or if there is a lack of fluid / volume. However, there are also a number of other causes for constriction of the vessels, e.g. the vegetative nervous system, which causes the muscles of the vessels to contract, or a disruption in the release of hormones in the kidneys.
Over time, the high pressure, especially in the large arteries, leads to calcification of the vessels, which in turn reduces the radius of the vessel - a vicious circle.
In the case of severe diastolic high blood pressure, a secondary form of hypertension must be considered. In this case, the cause lies primarily in another organ, the damage of which results in high blood pressure. The underlying disease can be an endocrine disorder, i.e. affect the hormonal balance, e.g. hyperthyroidism or hormone-producing tumors (e.g. pheochromocytoma). Psychiatric diseases can also play a role as well as certain vascular diseases, e.g. renal artery stenosis.
Kidney function as a possible cause
In addition to the detoxification function, the kidneys have another, essential function - the regulation of blood pressure.
The level of blood pressure is closely related to the total amount of blood that circulates in our body. The kidney has a special influence on this, because it is the decisive organ for regulating the amount of fluid. Closely regulated mechanisms inside and outside the kidney lead to the narrowing or widening of the kidney vessels, which subsequently allows a larger or smaller part of the blood to be filtered. The amount of blood in the circulatory system is increased or decreased accordingly and thus has a decisive influence on the blood pressure values.
If, for example, renal artery stenosis occurs, i.e. an occlusion of one of the renal arteries, this can result in the kidney's filtration being severely restricted and consequently more blood volume remaining in the circulatory system. As a result, blood pressure rises.
The therapy
Since arterial high blood pressure is a widespread disease, there are now numerous drug targets.
Diuretics can be combined well with other medications. These increase the excretion of water and thereby reduce the blood volume.
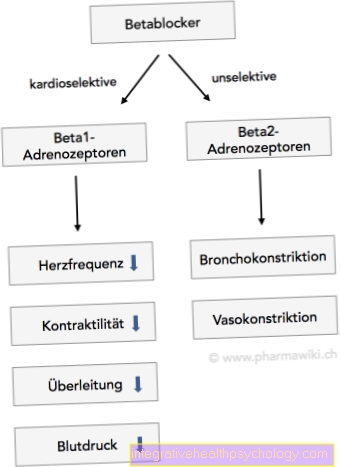
Beta-blockers are also used, which ensure that less blood is pumped from the heart per unit of time. This can also effectively lower blood pressure.
The third large group of drugs are inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system. This is a system of enzymes in our body that naturally increases blood pressure. If this is inhibited, it can no longer increase the blood pressure, the pressure decreases accordingly, which in this case is the desired effect.
Read extensive information under: How I can best lower my diastole
Home remedies as a therapy option
In the case of permanently elevated diastolic, but also systolic blood pressure values, action should be taken as soon as possible. Medication does not always have to be used directly. There are various home remedies that can help quickly and effectively against high blood pressure values. However, if these show no effect, a specialist medical assessment should be carried out in any case.
To treat diastolic high blood pressure primarily, home remedies such as peppermint or chamomile tea can be used. These have a known antihypertensive effect. In addition to chamomile and peppermint, mistletoe also has an antihypertensive effect. However, this only achieves the desired effect in the correct dosage, which is why this must be discussed with the family doctor or other specialist medical staff. In addition to herbs and preparations that can be consumed, sporting activities can also help lower blood pressure. Endurance sports are particularly beneficial.
Stress in everyday life and at work is considered to be one of the most common causes of high blood pressure. In order to reduce high blood pressure, stress reduction through targeted relaxation measures can already be successful.
How can you successfully reduce stress? Find out more about this here.
Medicines as a therapy option
If non-drug therapy in the form of exercise, stress avoidance and lifestyle changes when attempting to lower blood pressure is not sufficient, medication must be resorted to. There are different drugs that trigger their effects in different ways. Drug treatment tries to achieve a slow and careful lowering of blood pressure in order to avoid possible side effects.
There are four different subclasses of drugs used to lower diastolic blood pressure. The best known drug is the beta blocker. This reduces the effect of the hormone adrenaline on the heart. As a result, the heart's pumping capacity is reduced and thus the pressure with which the heart is pushed into the body's circulation is reduced. In addition to the diastolic blood pressure, the systolic blood pressure is also lowered at the same time.
Another drug that is used to lower diastolic blood pressure is the calcium antagonist. This acts as an antagonist to calcium in the muscles by blocking the calcium channels and thereby expanding the blood vessels.
So-called ACE inhibitors work by interfering with the hormonal system to lower blood pressure. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which has an effect not only on the kidneys but also in the heart and lungs, is particularly influenced.
A final drug used to lower diastolic blood pressure is a diuretic. This kindles its special effect in the kidneys, where it has a diuretic function. As a result, there is an increased excretion of water and thus a reduction in the volume of blood in the body's circulation. Thus, it has an indirect effect as an antihypertensive drug. However, diuretics should only be taken under strict control, because in addition to the increased excretion of water with the urine, important electrolytes can also be lost.
Find out all about the topic here: How can I lower my diastole?
Homeopathy as a therapy option
The homeopathic remedies for lowering blood pressure are generally considered controversial. Despite everything, there are some homeopathic remedies that have ameliorating effects on patients. They mainly treat the symptoms that are caused by diastolic high blood pressure.
For example, symptoms of fatigue caused by Baryta carbonica or Plumbum can be treated. Cardiovascular complaints, on the other hand, are specifically treated with baryta and spigelia. But also malaise and nausea are treated by the specifically adapted homeopathic remedies Aconit and Sulfur.
Therapy treatments in the form of homeopathic remedies prove to be non-invasive and generally do not have any side effects. Whether or not they work in a patient differs from person to person.
The long-term consequences of a permanently increased diastole
The consequence of a permanently increased diastole, i.e. diastolic high blood pressure, should by no means be underestimated. Even if the lower, diastolic blood pressure value is usually classified as a minor matter among laypeople, it can cause enormous damage.
If the diastolic blood pressure value is permanently increased, the heart can no longer relax in its actual diastolic relaxation phase. In addition, a permanently high diastolic blood pressure value leads to hardening of the arteries at some point. Connected with many other consequences, the blood flow is disturbed. This includes, for example, the reduced blood supply to organs. In addition to this reduced blood flow, increased diastolic blood pressure also has considerable effects on the kidneys, which can only keep their function constant within a certain range. In addition, increased blood pressure leads to damage to the kidneys, as this results in vascular changes within the kidneys, which can ultimately be accompanied by a severe loss of function.
In addition to the effects on the abdominal organs, the increased blood pressure can also have enormous effects on the heart and brain. The restricted blood flow but at the same time increased pressure within the blood vessels can lead to damage, which in the worst case can lead to aortic and brain aneurysms. In addition, the disturbed blood flow leads to an insufficient supply of oxygen to the organs, which of course also includes the heart. The heart is more and more stressed in the diastole, which ultimately leads to a revision of it. A heart attack can occur at an increased risk.
Depending on the age, the symptoms of diastolic high blood pressure can increase even further. Women of the menopausal age, but also men of the corresponding age, are particularly at risk of suffering a consequence of diastolic high blood pressure.
Read more about the topic here: Aortic aneurysm.
The prognosis of a too high diastole
If the diastole is too high, the prognosis is not bad if it is discovered and if the attending physician adjusts it well.
Frequent checks are necessary, especially at the beginning, which you can carry out yourself at home. There are many medications that can help in this area, but they will only work to their full potential if taken regularly and correctly.
In addition, exercise and a healthy diet can do a lot, influence the prognosis and thus significantly reduce the risk of secondary diseases in the cardiovascular system.