Typhus
Definition- what is typhus?
Typhus is an infectious disease that is transmitted by bacteria. The type of bacteria is known as rickettsiae and is transmitted by various parasites such as lice, mites, fleas and ticks. Typhus occurs mainly in the Andes in South America, Africa and Southeast Asia. In Germany, typhus is extremely rare. The eponymous symptoms include a sudden high fever and a large patchy rash on the skin all over the body. In addition, there are usually headaches and muscle pain. Treatment consists of giving antibiotics.

Where does typhus occur?
Typhus occurs mainly in regions with a low standard of hygiene and a high population. It occurs in the Andes in South America. Accordingly, the countries Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Argentina and Chile are affected. Typhus also occurs in Central and West Africa, as well as in parts of Southeast Asia. In the past few years, the countries Burundi, Rwanda and Ethiopia have been most severely affected by typhus. In Germany and Europe in general, typhus is extremely rare due to the good hygiene situation.
How contagious is that?
Typhus is triggered by the rickettsial bacteria and is transmitted to humans by various parasites. These include lice, especially clothes lice, mites, ticks and fleas.These mainly occur in environments with many people and poor hygiene conditions. The bacteria are excreted in the parasite's feces. They can get into the body when bitten by a louse and the subsequent scratching or, more rarely, be absorbed through the air.
Accordingly, if the bacteria occur, typhus is very contagious and the disease can spread explosively. In addition, if the sick person is bitten again, the bacteria come back through a parasite during the fever and can thus be passed on to other people.
Also read the article on the topic: Human parasites, how do I know if my fever is contagious?
causes
Typhus is an infectious disease and is therefore caused by a pathogen. This pathogen is the rickettsial bacteria that reproduces in lice, especially clothes lice, mites, ticks and fleas. It is excreted in the excrement of the parasites. For example, if the louse bites and scratches a person, the bacteria in the feces are rubbed off and can enter the body through the wound. Occasionally they can also be inhaled through the air. In the infected person's body, the bacteria spreads through the blood, causing inflammation and various symptoms.
diagnosis
The main way to diagnose typhus is by examining the blood of the potentially infected person. Here, the pathogens can be detected directly using various methods. Alternatively, the antibodies the body made in response to the infection can be detected in the blood.
In addition, a physical examination with a focus on the rash on the body is important for the diagnosis. The anamnesis, i.e. the doctor-patient conversation, can provide important information with regard to the hygienic circumstances and a bite by a parasite.
I recognize typhus by these symptoms
After the transmission of the rickettsial bacteria, it takes about 10 days to 2 weeks for symptoms to appear. This is also known as the incubation period. The disease usually begins with initially unspecific symptoms, which are also referred to as prodromal symptoms. This means that they can be seen as a kind of harbinger of the onset of the disease. This includes feelings of tiredness, exhaustion, coughing and lack of appetite. Then there is a sudden onset of high fever and disturbance of consciousness. People become sleepier and drowsy, which is also known as somnolence.
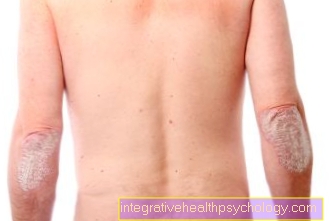
The additional eponymous rash appears on average 5 days after the first symptoms. There are larger spots all over the body. They first appear on the affected person's trunk and spread to the arms and legs. The palms and soles of the feet, as well as the face, are not affected. The color of the spots is usually pale red or slightly bluish. In addition, there are often headaches and myalgias, i.e. pain in the muscles. This further increases the feeling of exhaustion.
Also read the article on the topic: Fever with rash
These are the long-term effects of typhus
Typhus can lead to various long-term effects. These are caused by the irritation or damage to the blood vessels, as well as by the weakened immune system. The long-term effects of typhus include damage to the hearing with hearing loss and chronic tinnitus. The spinal cord can also become inflamed and the function of the nerves disturbed, which can lead to many other diseases. For example, hemiplegia can also occur. If the brain structures are affected, psychological changes or disorders can also occur.
Treatment / therapy
The treatment of spotted fever consists of fighting the bacteria, i.e. the rickettsiae. Antibiotics should therefore be given if the disease is suspected. The first choice antibiotic is doxycycline. Symptoms should improve after just one or two days. If this is not the case, a different antibiotic should be used if the diagnosis is confirmed. This is usually chloramphenicol.
This article might also interest you: Treatment with antibiotics
In addition, various supportive measures should be taken to improve the symptoms. This includes the stabilization of the circulation, the supply of sufficient fluids and electrolytes. The affected person should accordingly be cared for in an intensive care unit. A cortisone supplement, such as prednisolone, may also help to combat inflammation.
Another important aspect is the destruction of the parasites that are responsible for the transmission of the bacteria. There are various means of doing this, such as Lindane. This is a lice killing agent that causes the lice to die.
Typhus complications
The typhus disease can lead to various complications. These occur when treatment is not given in a timely manner. The bacteria spread through the blood and multiply in the vessel walls, which can lead to bleeding and edema, i.e. water retention.
Read more on the topic: Edema
In addition, there is the infestation and the development of inflammation in various organs. If the vessels in the brain are damaged, this can lead to inflammation of the brain, i.e. encephalitis, or the meninges, i.e. meningitis. Pneumonitis, an inflammation of the lungs, can also develop. The kidneys and heart muscle can also be affected. The inflammation can also cause the eventual death of organ tissue. Therefore, in more than half of the cases, the affected person dies without adequate and rapid therapy.
Is there a vaccination against typhus?
There is a vaccination against the typhus disease. This is recommended for particularly vulnerable people. These include, for example, nurses or doctors in risk areas, as well as employees in the corresponding laboratories in which the diagnosis of typhus is made. There are different forms of vaccination against typhus, but not all of them are equally effective. Occasionally the vaccination may not work well enough.
Course of disease
The course of typhus disease depends heavily on the time of diagnosis and the onset of treatment. The symptoms set in 10 to 14 days after infection and are usually relatively severe. With a prompt diagnosis, correct action can be taken to end the disease quickly. Therapy should therefore be initiated even if typhus is suspected. This usually works well and works effectively. Thus the course of the typhus disease is intense, but short-lived.
Duration / forecast
The duration of the typhus disease depends on the time at which the therapy is started. The symptoms appear about 2 weeks after infection. After about 5 days, the strong fever and rash appear at the latest. Treatment is therefore usually started during this period. This usually takes 1 to 2 days and the symptoms subside within a week. Therefore the prognosis of the typhus disease is good with an appropriate therapy. Without treatment, around half of all those affected die from the consequences and complications of typhus.