flu
Synonyms
Medical: Influenza
In a broader sense: real flu, viral flu
introduction

The disease known as “flu” is an infection that occurs suddenly during the cold season and is triggered by viruses.
Depending on the immune situation of the individual, an infection with the flu virus can proceed differently. While some people affected only develop mild symptoms, other people react to the virus infection with severe malaise and severe symptoms. Due to the fact that the classic flu is rather mild within the first few days, it is often mistakenly mistaken for a common cold.
Only when the clinical picture is fully developed does the severity of the course of the clear difference between cold and flu virus. In addition, just the sudden onset of discomfort for the presence of flu.Flu infections or simple colds usually creep in slowly. The incubation period (Time from infection to the development of the first symptoms) can take a period of a few hours up to dthree to four days accept.
Infected people are already during the incubation period, i.e. before they become sick themselves, highly contagious. After the onset of the first symptoms, there is still approximately three to five days a high risk of infection.
Causes of the flu
The cause of infection with the classic flu is this Infection with a certain viral pathogen. The so-called influenza viruses (flu viruses) are generally divided into three groups. According to this classification, a distinction is made between types A, B and C flu viruses Type A or B can become severe after successful transmission in humans Respiratory infections and lead to the appearance of the flu.
Type C influenza viruses, on the other hand, are only able to do this in the rarest of cases in adults serious symptoms trigger. Even children suffer only mild symptoms, if at all, after being infected with type C flu viruses. For this reason, types A and B influenza viruses in particular are among the types in Central Europe main causes of the occurrence of the flu.
Flu symptoms
The symptoms of the flu can very different be. Just that Type and intensity of manifestation of symptoms depends a lot on Age and immune status of the affected patient. Basically, weak courses with few symptoms up to a strong impairment of the body are possible. In rare cases can even have the effects of a flu lead to death. It can usually be seen that especially children, old people and immunocompromised patients show severe symptoms after infection with the influenza virus. Nevertheless, the flu can also otherwise clearly add to perfectly healthy people.
Another problem with distinguishing between real flu and other infectious diseases is the fact that the most symptoms relatively unspecific and could speak for a variety of underlying diseases. However, this is characteristic of the flu acute, sudden onset of illness. Many of the affected patients report that they still felt perfectly healthy in the morning and became increasingly sicker during the day. In addition, when compared to other acute respiratory diseases, real flu is characterized by the symptoms persist over a long period of time (remain).
In most cases it comes after 7 to 14 days to a complete resolution of the complaints. Some symptoms, such as a general feeling of weakness and loss of appetite, may even occur persist for weeks after the flu broke out. The main symptoms of the flu include pronounced feeling of illness, which in most cases is not limited locally to one body region, but rather the raids whole body.
Also read: Pain all over the body and Eye pain
In addition, almost all those affected develop pronounced fever attacks. Usually body temperatures of up to 40 ° C are measured. These attacks of fever are usually accompanied by severe chills. Furthermore, most patients complain of severe headaches and pain in their limbs, especially at the beginning of the flu. In general, flu sufferers feel exhausted, tired, and limp. The normal daily routine can no longer be completed during the acute phase of illness.
Learn more about Fever with aching limbs.
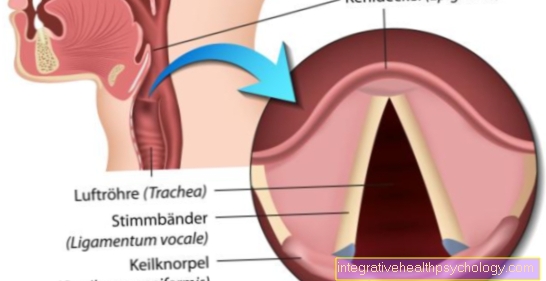
In the respiratory tract, the viral infection manifests itself in the appearance of dry, irritable cough (i.e. without sputum), a dry throat and swollen nasal mucous membranes. In addition, many of the affected patients report allergy-like swelling and irritation in the area of the eyes.
Furthermore, it can become in the course of a flu
- increased loss of appetite
- nausea
- Vomiting and
- severe diarrhea
come.
In general, these symptoms are similar to symptoms of a simple cold. However, when looking closely at the symptoms, a clear distinction can be drawn between a simple cold and the real flu.
To make it easier to differentiate between a cold and the flu outside of a flu wave, a so-called flu rapid test is suitable, which can detect the pathogens causing the flu after a few minutes.
Read more on the topic: Flu symptoms
Diagnosis of the flu
The flu is usually diagnosed based on the symptoms of the patient concerned. For this purpose stands above all one detailed doctor-patient discussion (anamnese) in the foreground. During this conversation the doctor asks the patient about it possible previous illnesses and the type and severity of the current symptoms. Also play Allergies, medication taken regularly and various Habits plays a vital role in this conversation.
In a second step, the doctor gets an initial overview of the constitution (General condition) of the patient. He succeeds in doing this by performing a extensive physical examination. The doctor checks it all organ systems relevant for flu:
- Auscultation (Wiretapping) the lungs and heart
- Palpation (Scan) of the abdomen.
In this way, the suspected diagnosis of "flu" can already be confirmed in most cases. In addition, there is usually a Nasal swab from the posterior nasal cavity taken. Alternatively, a deep throat swab can be done. That too Tracheal secretions (Secretion from the windpipe) or Secretions of the bronchial system can be used to detect the influenza virus.
In addition, many doctors use the to diagnose flu Collection of patient blood back. In a special laboratory, the submitted material is examined in various ways for the influenza virus or metabolic products of the pathogen.
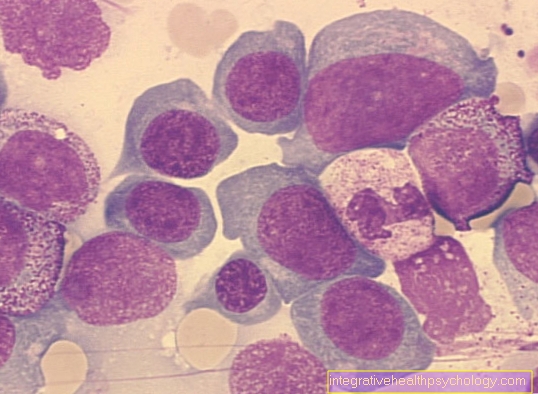
The most important method of detecting the flu virus is the so-called Influenza PCR (Polymerase chain reaction) in which the Genome of the pathogen duplicated and can then be assigned to the influenza virus. In many cases, pathogens can also be found in the Electron microscopy or one Cell culture prove.
From the second week after the outbreak the flu can also Influenza-specific antibodies detect in the blood. At the start the affected organism usually indicates the disease phase not enough antibodies to guarantee perfect evidence. The delayed validity of the antibody test is based on this fact.
In addition, other parameters that can be measured in the blood also indicate a viral infection. Usually the so-called Sedimentation rate if you have a viral infection such as the flu clearly increased. A measurement of the white blood cells (if suspected Leukocytosis), on the other hand, is not very meaningful, since they can behave quite variably in the case of viral infections. Both an increase and a decrease in white blood cells are possible.
Meanwhile exist various rapid testshaving the flu within a few minutes can be diagnosed. These rapid tests have color-coded antibodies which on different Influenza virus proteins react. That way you can Influenza virus metabolic products shown in color become. A result can be obtained from these tests after about 15 minutes can be read.
Therapy of the flu

Therapy at Presence of real flu can on two different types respectively. On the one hand there is the Relief of symptoms in the foreground, on the other hand, in individual cases, however, a direct Combating the causative agent be necessary.
1. Antiviral Therapy
There are now a number of ways to treat the flu antiviral drugs to disposal. At early start of intake can the Duration of illness significantly shortened become. In addition, there is evidence that patients who contract flu treated with antivirals at an early stage become clear less often life-threatening complications develop. Generally will two different substance classes used to treat the flu. Besides the Inhibiting a specific membrane protein (M2), which acts as a proton pump on the viral shell, are mainly found nowadays by the so-called Neuraminidase inhibitors frequently used.
Taking neuraminidase inhibitors increases the activity of the viral surface enzyme Neuraminidase throttled and in this way the Detachment of the virus in the Blocked release from a host cell. Neuraminidase inhibitors prevent consequently the infection further, so far uninvolved cells. It should be noted, however, that both substance classes are only the Prevent the flu virus from multiplying. Viruses already in the organism can not inactivated by these drugs or be eliminated. For this reason, the time also coincides with the Taking antiviral drugs is started, a crucial one Influence on the success of the treatment. Experts consider flu treatment with antiviral drugs only useful when the first symptoms appear no longer than 48 hours lies back. Failure to do so also shows up when taking the medicine no positive influence on the course of the disease.
Also read: Grippostad® and general information about Antiviral drugs.
2. Symptomatic therapy
Since an immunocompetent organism is in most cases able to cope with an infection with the flu virus itself, in many cases the symptomatic therapy in the foreground. The aim of this treatment strategy is Relief of typical symptoms with a flu and the Increase in wellbeing of the affected patient.
With a high fever and against Headache, muscle aches and pains can medicines like Ibuprofen® or Paracetamol® be taken. Both drugs have both one pain reliever (analgesic), as well as a antipyretic (antipyretic) Active component. For this reason they are particularly suitable for symptomatic treatment of the flu.
If necessary, about one tablet every 5-6 hours be taken. In many cases it is also found that the Switch between ibuprofen and paracetamol to one improved antipyretic effect of the preparations leads. This means that affected patients start taking one ibuprofen tablet, for example, if necessary and a dose five to six hours later Paracetamol take in.
Painkillers like Aspirin® (Acetylsalicylic acid; ASS) should be at Children under 12 years of age definitely not be applied. Taking Aspirin® in the presence of a viral infection can be dangerous and too dangerous for children under 12 years of age 25% fatal Reye syndrome to lead. In addition, the affected patients should during the illness phase enough liquid eat and stay in bed if possible. The body needs sufficient rest to contain the virus and promote recovery.
3. Other therapy options
Although the flu is caused by a virus Infectious disease acts, the Use of an antibiotic makes sense be. This fact is due to the fact that a Infection with the influenza virus the immune system so weakens that it often increases at the same time
- bacterial strep throat
- acute bronchitis
- lung infection or
- Meningitis
can come.
Duration
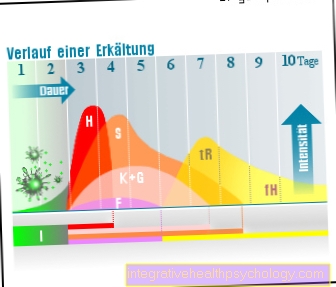
After being infected with an influenza virus, the so-called incubation period the disease. This means that an infection has taken place and the viruses are multiplying in the person's body, but there are still no symptoms. This incubation period usually lasts about 1-2 days.
Typical of the flu is that that of the typical symptoms occur within a few hours can. The average duration of the illness is around 5-7 Days after the onset of symptoms. However, in some cases the disease process can last for weeks.
Depending on the occurrence of possible complications and the presence of specific, individual risk factors, it can take several weeks to recover from the flu and even require admission to a hospital. Patients with risk factors, such as the elderly, usually experience another acute worsening of symptoms about 3-5 days after the onset of symptoms.
As a rule, the symptoms of the disease are not the same every day, but can vary depending on the progression of the disease. Typically the flu starts very sudden and strong and will be in the first days of intermittent fever attacks dominates. As the disease progresses, the symptoms diminish until they disappear completely at the end of the disease.
Complications

For many of those affected, it is not the flu virus itself, but the more easily possible additional bacterial infections (so-called secondary bacterial infections) that pose the greatest risk of flu. The organism, which has already been weakened by fighting the influenza viruses, is in many cases no longer able to deal with bacterial pathogens to meet adequately.
For this reason, bacteria can penetrate the body much more easily and lead to further diseases. Inflammation is one of the most relevant illnesses that can coexist with the flu
- of the brain (encephalitis)
- the skeletal muscles (Myositis) and
- of the heart muscle (myocarditis)
In addition, superinfection in the respiratory tract is often observed in affected patients.
Read more on the topic: Flu complications
Flu prevention
Probably the most effective method of preventing flu is this Performing a Flu vaccination. In contrast to other vaccination methods, however, there is one problem with influenza vaccination that should not be neglected. Influenza viruses, especially those of the Type a, are considered enormously adaptable.
This means that the pathogen that causes the flu outbreak is by mutations are constantly changing within the genome. In terms of effective vaccination, this means that the Immunization only makes sense then is when they refreshed every year becomes. For this reason, large vaccination campaigns take place every year (usually from October to November) in which the strains of influenza viruses circulating at the time is immunized. The cost of a flu shot will be borne by the statutory and private health insurances usually completely taken over. In the end, everyone has to decide for themselves whether a vaccination makes sense.
The preventive vaccination against influenza viruses is particularly recommended for the following groups of people:
- People who older than 60 years are
- Pregnant women from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
- Children and young people
- Adults at increased health risk (due to chronic diseases of the lungs, heart, circulation, liver or kidneys)
- diabetic
- Patient with Multiple sclerosis
- Immunocompromised patients
- HIV infected people
- Residents of retirement and nursing homes
- People with increased risk of infection (medical staff, teachers, educators ...)
In addition, there are also some basic rules regarding hygiene help one To prevent infection with the influenza virus and avoid the flu. If close relatives or people in the area suffer from the flu, the Hands thoroughly washed and disinfected several times a day become.
Risk patients should Keep your distance from the infected or in direct contact one Wear a face mask. In addition, a adequate intake of vitamin D. contribute to that Reduce the risk of infection and to prevent infection. In this context, the one induced by the vitamin plays a role Strengthening the innate immune system a crucial role.The vitamin is able to produce various peptides that lead to Control of pathogens needed be to stimulate.
Furthermore, there is a for some groups of people Flu prophylaxis with neuraminidase inhibitors in question. This precautionary option can mainly be used in patients who have a ordinary vaccination because of a Basic illness no longer possible (for example in patients with a severely weakened immune system). Also for Influenza prevention for medical staff the use of neuraminidase inhibitors is now being discussed.
vaccination

Vaccination against influenza viruses is the only reliable way to effectively prevent infection with the virus.
In most cases the vaccination is a so-called "Dead vaccine". This means that the vaccination contains killed viruses that can no longer infect the organism, but efficiently prepare the immune system for infection with the pathogen, so that an illness is efficiently prevented if it comes into contact with the virus. Since the 2012/13 season there has also been a "Live vaccine", which is approved for children between the ages of 2 and 17 inclusive. This is intended to improve the effectiveness of the active ingredient in this age group.
The vaccination is refreshed annually, usually in October and November, as this marks the beginning of the season of infection with the influenza virus. According to data from the Robert Koch Institute, the vaccine protects up to 90% against the disease with the pathogen. The STIKO (Standing Vaccination Commission) recommends the flu vaccination especially for people who fall into one of the following risk groups:
- People over 60 years of age
- Pregnant women from the 2nd trimester
- Children, adolescents and adults with health risks due to an underlying disease
- People at an increased risk of being infected with the virus (e.g. medical staff), as well as people who, if they have the disease, can potentially infect many other people (e.g. teachers)
- People who are in regular contact with poultry or wild birds
Read more on the topic:
- Flu shot
- Flu vaccination during pregnancy
Home remedies
Although home remedies are often recommended for treating the flu, it must be mentioned that real flu, meaning infection with one Influenza virusshould not be confused with a cold, including a flu-like infection. The "real" flu is an illness that can lead to serious complications and even death in some cases, which is why treatment, especially in risk groups, should be discussed with a doctor.
However, there are helpful home remedies that can alleviate some of the symptoms associated with the flu. So can catch the flu by the occurrence of Fever attacks or Diarrhea quickly to a relevant one Dehydration lead that with Soups or teas is easy to get to grips with. These hot liquids can also be pleasant in the case of an accompanying sore throat. By those contained in the soup Electrolytes these are also supplied to the body when ingested. If you have a fever you can Calf wrap be helpful to get the increased temperature under control. With problems like one stuffy nose or one dry nasal mucosa can Nasal rinses or inhalations with salt water Provide relief.
Difference flu / cold
The common cold, often also called "flu-like infection", is a viral disease that is often confused with "real" flu. "Real" flu is an infection with the influenza virus, a disease that in some cases can be very severe. The causative agent of the common cold is also a virus, but a number of different viruses can be held responsible for the development of the common cold. In most cases, the viruses are from the families of adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, coxsackieviruses, parainfluenza viruses or enteroviruses.
The similar symptoms of the two diseases can easily lead to confusion. However, there are some typical differences that can be used to distinguish a "normal" cold from the flu:
For one thing, the sudden onset of the flu is a point that distinguishes flu from the common cold. Within hours, the symptoms of the flu can affect those affected to such an extent that a normal everyday life is no longer possible. Particularly sudden onset of fever and body aches should be mentioned as warning signs. In contrast, a cold usually announces itself a day in advance with weaker symptoms and general malaise. At the same time, attacks of fever, which typically occur with the flu, tend to be the exception with a simple cold.
The duration of the illness is another point that separates the common cold from the flu. The symptoms of a cold usually improve after 3-4 days, although the course of the flu usually lasts at least a week and in some cases can last for several weeks.
If a flu virus is suspected, a doctor should be consulted in any case, who can make the distinction based on a doctor-patient conversation and a physical examination and, if necessary, initiate correct therapy for the respective illness.
Read more on the topic: Difference between flu and cold
forecast

Healthy adults with no chronic diseases of the Cardiovascular system, of immune system or the metabolism can usually be expected to develop without complications. There is complete healing of the flu without consequences.
If the course is complicated, the prognosis depends on the age of the patient, previous illnesses and the state of the immune system. In an elderly patient with known coronary artery disease and a bacterial complication lung infection In addition to the flu, the prognosis is more serious, and in the worst case scenario, the disease can be fatal.
Summary
The flu is a contagious respiratory disease caused by influenza viruses. It is transmitted by droplet infection and is characterized by a very sudden onset of the disease. The most common symptoms are a headache and body aches, high fever over 39 ° C and chills as well as dry cough.
The flu usually lasts a week or two, but many patients still feel weak and less productive for some time.
For high-risk patients such as the chronically ill, people over 65 years of age, infants, young children and Pregnant women can complications like the flu lung infection, Meningitis and Myocarditis cause that can lead to death.
For the named risk groups there is an annual Flu vaccination ponder.