Knee prosthesis
Synonyms in a broader sense
Knee joint prosthesis, knee joint endoprosthesis, total knee prosthesis, knee TEP, total endoprosthesis (TEP), artificial knee joint
definition
A Knee prosthesis replaces the worn part of the joint Knee joint through an artificial surface. The worn ones cartilage- and Layers of bone are removed as part of an operation and replaced by two artificial parts, namely the thigh bone shield and the metallic tibia plateau. In order to avoid that these two joint surfaces rub against each other and thus metal parts get into the joint are stored, a so-called plastic sliding surface is inserted between the two components. This plastic sliding surface is thus stored between the Thigh and the Tibia.

Structure of a knee prosthesis
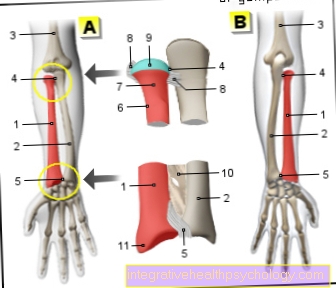
As you can see from the illustration below, there is a Knee prosthesis at least two different components: the Thigh- and the Shin portion. While these two components always have to be exchanged, an exchange of the posterior kneecap is not absolutely necessary.
- Of the Thigh portion of the knee prosthesis (= Femoral component), usually consists of one Cobalt - chrome alloy
- Of the Shin portion the knee prosthesis (= Tibial plateau) consists of a metal component on which an inlay, the plastic layer (=Sliding surface) rests.
- Of the Kneecap portion the knee prosthesis consists of very hard plastic (Polyethylene). The exchange of this surface is not absolutely necessary.
Figure knee prosthesis

- Thigh bone (femur)
- Thigh (femur) component
- Lower leg (tibia) component
- Shinbone (tibia)
- Calf bone (fibula)
Material of the prosthesis
Since the first knee prosthesis, both the surgical methods and the materials used have changed and developed. Depending on the manufacturer, different materials are used in a knee prosthesis today. Become common different materials within a prosthesis used to achieve the optimal result. In the so-called "bicondylar knee TEP", one of the most common prostheses, high-quality metals such as Stainless steel or oxinium and titanium, as well as a special plastic (Polyethylene) is used. The metal is attached to the thigh and the lower leg bone. A plastic disc is then placed on the lower part on which the upper part can slide.
So-called alloys are used to make the stainless steel hard enough for use as a prosthesis. This will be special Chromium-cobalt alloys used. There Allergies to these alloys implants can also be known in individual cases Ceramics or so-called Allergy implants where particularly low-allergen alloys are used.
You can find more information on this topic here: Knee prosthesis material
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Installation of the knee prosthesis
A knee prosthesis can be made of different materials and can be attached using different surgical methods. Which surgical method is used in the individual case depends on the Condition of the joint, the resilience of the patient, as well as of Surgeon from.
The procedure is usually done by Specialists in orthopedics carried out, the specialists in this field. The operation is always performed under anesthesia. The attending surgeon can use the X-ray images to do this Operation plan design. The size and type of the prosthesis as well as the surgical method can thus be determined before the operation begins. The Total duration the surgery usually amounts to under 2 hours.
At the beginning of the operation, the attending surgeon procures himself with a running centrally over the knee joint Skin incision an access to the joint. With the help of special surgical tools, the Joint surface adapted to the required prosthesis become. The prosthesis parts are now attached to the previously processed joint surfaces fixed to the bone. After all parts of the prosthesis are in the desired location and are fixed, the joint is moved through again and it is checked whether all movements can be carried out. After that, the previously severed Fabric with seams sewn again.
In order for blood and fluid to drain away, thin plastic tubes are often placed in the wound, which look out of the wound (a so-called drainage). Then a bandage is applied, which can reduce the swelling somewhat.
It can generally be between a one-sided (i.e. only on the upper or Lower leg bones restricted) and one bilateral (Upper and Lower leg bone) prosthesis, as well as the axle-guided Prosthesis can be distinguished. In most cases, a two-sided prosthesis will be used, too Total knee prosthesis (total knee replacement), built-in.
The prosthesis parts can both with cement, cementless, as well as being fixed to the bone using a combination of both methods.
You can find more information on this topic here: Operation of a knee prosthesis
When is a knee prosthesis implanted?

There are indications that show that it may be necessary to replace the knee joint with an artificial knee joint. In the following, some indications are shown that may also occur in combination and then may even point to the need for a knee prosthesis. A compelling indication to install a Knee prosthesis However, there is no. Ultimately, the decision must be made individually with the patient.
- Significant pain on exercise and / or at rest, with all conservative but also possible surgical therapy options being exhausted.
- Possibly associated increasing restricted mobility (especially: inhibition to straighten the leg)
- Advanced osteoarthritis, such as a Retropatellar arthrosis, the treatment of which both conservatively and surgically-arthroscopically (by a Arthroscopy) brought no improvement.
- Axial misalignment of the leg (If one or Knock knees) if any Corrective osteotomy is not considered. (Particularly with extreme knock knees or bow legs, special stability is required. For this reason, a coupled knee prosthesis is usually necessary).
You can find more information on this topic here: Surgery for knee osteoarthritis
Complications
Of course, there are also states in which a Knee prosthesis does not seem sensible. Just as there are many indications for the possible need to use an artificial joint, there are also so many contraindications. Listed below are some important contraindications that can delay the use of the knee prosthesis. In particular, an artificial knee joint should not be used
- if not all conservative treatment options have been exhausted.
- if the Stretching apparatus is disturbed.
- if there is a danger of Prosthetic infection consists. This is usually the case when there are still physical infections. In addition, small Skin impurities, as a Hair root inflammation or Pimples counting.
- if as a result of a disease such as diabetes mellitus, the arterial Circulation disturbed is.
- if near the joint Paralysis occur or
- extensive Soft tissue damage exist in the operating area.
Pain
Pain can occur both before and after knee prosthesis surgery. Pain before the operation is typically an expression of the broken joint and the most common reason for an operation with a knee prosthesis.
The operation can eliminate the pain in most cases (around 90% depending on the study). Pain that occurs immediately after the operation is normal and can be attributed to the procedure itself. Taking pain medication for the first few days after the operation should improve this pain.
If the pain persists for a long time after the wound has healed, it may be an expression of an infection in the operated joint. A loosened prosthesis can also lead to pain in the knee. If the pain occurs very long (15-20 years) after the operation, the prosthesis may have reached the end of its lifetime and another operation may be necessary to replace the prosthesis.
Pain, which is only noticeable with certain loads, can always occur in everyday life with a knee prosthesis and is a sign of excessive stress on the artificial joint. You are therefore not a cause for alarm. Avoiding these peak loads can reduce pain.
You can read more information on this topic here:
- Pain with a prosthetic knee
- Pain after knee surgery
Aftercare

Patients are now quickly mobilized again after a knee joint prosthesis. The follow-up treatment therefore begins almost immediately after the operation (between the 1st and 3rd day).
Most of the time you start with that Knee joint to move with the help of a motor rail. This bends and stretches the leg in different levels of difficulty. This first one Movement exercises follow physiotherapy exercises.
At least as important as the movement exercises described above is that the patient learns to “stand on their own two feet” again. In the first few days, the patient should only get out of bed with the assistance of the nursing staff. With the help of a walker and / or learning to use crutches, the patient learns to become more independent. This walking has to be learned.
In addition to the movement exercises and thus the physiotherapeutic follow-up treatment, the Removal of Drainages important on the 3rd day after the operation. Physiotherapy will be intensified now at the latest. The aim is to increase the mobility and functionality of the knee joint so that an improved preoperative condition is achieved.
Mobilization in particular requires an increased level of strength, willpower and self-confidence from the patient: an improved preoperative state after the operation is only possible through the cooperation of the patient. From now on, the physiotherapeutic follow-up treatment can be intervened in order to achieve its goal of regaining the mobility and function of the operated knee joint, which was often significantly restricted before the operation. This requires some effort from both the patient and the therapist.
In the further course, regular Wound and laboratory controlsto avoid any malfunction of the Wound healing to recognize as early as possible and to be able to initiate appropriate measures.
As long as the mobilization of the patient could not be fully restored and thus a full load is possible, this is Thrombosis prophylaxis in the form of Antithrombotic stockings and / Heparin syringes of great importance.
Since a thrombosis can have far-reaching consequences, you should watch your body carefully. If calf pain or foot or lower leg swelling (nevertheless) occurs, a doctor should be informed immediately.
You should have one inpatient stay Plan for about two to three weeks after the operation, plus one rehabilitation of about another three weeks, which can take place either as an inpatient (in the form of a cure) or as an outpatient.
Regardless of which measure you choose: As soon as the rehabilitation measures are completed, you will find one radiological control instead of. This x-ray check is usually carried out where the operation took place.
Here it is also decided whether the rehabilitation measures have produced the desired success and whether the knee joint can now be bent beyond the right angle.
In rare cases in which sufficient mobility of the knee joint has not been achieved, a further procedure can be performed in which any adhesions are loosened by moving the knee joint.
As a rule, full mobility is only achieved after a few months. Only then are they Post-op swelling receding and the soft tissues largely healed.
Regular checks are therefore very important for the further course of healing and the improvement of mobility. For this reason, patients with endoprosthetic surgery receive a so-called Endoprosthesis passport. The "control data" of each examination are entered here until the mobility has been satisfactorily restored.
The life after

Life with an artificial knee joint:
The goal that with a Knee prosthesis should be achieved, of course, is the pain-free movement of the knee joint. As a rule, you should have achieved this freedom from pain after the rehabilitation measures.
To achieve this it takes your Help, but also your patience.
Not all movements can be performed again quickly. Climbing stairs is particularly difficult in the first phase after the knee prosthesis operation. Since climbing stairs in particular cannot be avoided in everyday life, you will learn as part of the Rehab know different possibilities.

Walking with walking aids is not easy for every patient either: The so-called “walking school” helps here, it is supposed to prepare you for everyday life.
Avoid if possible Falls! The artificial knee joint is built into your bone and, if you fall, it can break the bones, which means that further operations are necessary.
To lift and to carry never more than a maximum of 20% of your own body weight!
In general, various sports can be combined with a knee prosthesis. At this point, cycling should be briefly discussed, which is basically a cheap sport. A knee flexion ability of at least 90 ° is necessary for cycling, but should not be done in the first few months after the operation.
Exercise with a prosthetic knee
After a knee prosthesis has been inserted, for many people the question arises whether, when and what kind of sporting activity is an option.
Early movement of the operated joint is essential for an optimal result after the operation. The optimal range of motion and sequence can be achieved through special rehabilitation programs and physiotherapy.
In general, the presence of a knee prosthesis is no reason to forego sport. It should be noted, however, that the artificial joint can wear out more quickly through sports that put a lot of strain on the joint, making another operation necessary. Sports that involve punches and rapid turns in the joint should be avoided if possible so as not to risk loosening the prosthesis. Therefore, practicing sports such as skiing, tennis or football is not recommended.
Listed below are some recommendations for various types of sport, which have been classified according to their suitability for knee joint prosthesis wearers.
Sports as suitable can be designated:
- Swimming, best suited: crawl and backstroke.
- Gymnastics, provided that there are no extreme movements of the operated joint.
- Rowing, however: Avoid excessive knee flexion.
- sailing
- Paddle
- hike
- Nordic walking
Sports as conditionally suitable be valid:
- Cross-country skiing (diagonal technique, wide hiking skis are particularly recommended)
- Endurance run (only with good running technique, soft ground and spring-loaded running shoes)
- Golf (only with good technique and little torsion = rotation)
Sports that after fitting a knee joint prosthesis as not suitable must be designated:
- Sports that focus on speed and endurance
- Martial arts
- Any jump discipline
- Backlash games (tennis, squash, ...)
- Most ball games
- Alpine skiing
You can read more about this topic here: Exercise with a prosthetic knee