Splenic abscess
Introduction - the splenic abscess
The splenic abscess is relatively rare. As with liver abscesses, the causes are usually pathogens that have entered the bloodstream. Sources of bacteria in the body that cause a spleen abscess can result from endocarditis, chronic tonsillitis, or other chronic bacterial infections in the body. Another way of inflammation of a spleen abscess is the penetration of the pathogen from outside, e.g. after abdominal injuries as a result of an accident.

diagnosis
In addition to the patient interview and the physical examination, the ultrasound examination, which can show the sonographic signs typical of abscesses, is also very important here.
Symptoms
As with the other abscesses, the inflammatory picture is in the foreground with a spleen abscess, which consists of chills, fever, and an increase in the signs of inflammation in the blood count. In the further course it can lead to a full septic picture, which can be life-threatening. This occurs especially when the abscess is seen and treated too late.
complication
The abscess can break through with the pus flowing into the abdominal cavity, which is known as an acute abdomen and is a life-threatening condition that must be treated immediately. The spleen is well supplied with blood and so there is also the risk of life-threatening bleeding in the event of a perforation but also after surgical abscess treatment of the spleen.
Patients who have already suffered endocarditis should be given a prophylactic antibiotic cover to prevent the development of an abscess.
Therapy and Treatment
A splenic abscess is a serious disease that, if left untreated, leads to death within a very short time. For this reason, a quick diagnosis and a quick start of treatment are crucial for the positive outcome of the disease.
First, the patient is given antibiotic therapy to combat the infection underlying the spleen abscess. In addition, the splenic abscess can be pricked (punctured) and the purulent secretion can be drained away. The drainage is inserted either surgically or, nowadays, mainly CT-guided. In severe cases, parts of the spleen or the entire spleen may need to be surgically removed (partial splenectomy or splenectomy).
Life without a spleen is entirely possible, as the spleen is not an essential organ. However, since the spleen is an important organ of the immune system, patients who have had a splenectomy have an increased risk of developing sepsis (blood poisoning). This clinical picture is called OPSI syndrome (overwhelming post-splenectomy infection).
At first it can also be tried to treat conservatively with antibiotics. If this does not work, surgical drainage with wound irrigation of the abscess cavity is necessary. In severe cases, the spleen must be completely removed (splenectomy).
Sonography
One of the things the doctor can do to make the diagnosis of a spleen abscess is an ultrasound scan. This is a non-invasive method in which the spleen located in the upper abdomen can be scanned over the abdominal wall with the help of an ultrasound device and displayed in a 2D image.
The abscess can be clearly distinguished from the healthy spleen tissue by means of its capsule made of connective tissue, which appears as a white structure on ultrasound, and the dark cavity below. Sonography can determine the location of the abscess in the spleen. In addition, the size can be measured precisely with the aid of the device.
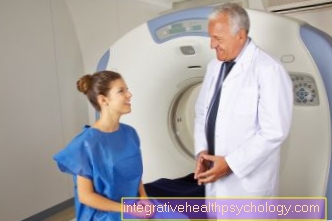
Computed tomography (CT)
A spleen abscess can be visualized by computed tomography (CT) scan. The advantages of CT are that the examination has a high contrast, which means that the internal organs can be displayed very well.
The CT is done within a few minutes, but the examination is associated with a certain radiation exposure for the patient. A CT can also be used to puncture and drain the abscess from the spleen in a controlled manner. This method reduces possible complications, such as incorrect puncture of neighboring organs, and enables successful treatment.
drainage
As an alternative to surgical removal of the entire spleen, the doctor may consider puncturing the abscess and then draining the secretion.In the past, the spleen abscess was drained as part of a surgical procedure. Today, the CT-guided percutaneous drainage of the abscess cavity is considered the standard therapy. The spleen abscess is punctured through the skin and the purulent secretion is drained away. The simultaneous control by means of CT enables the exact localization of the abscess and reduces the risk of a faulty puncture.