Lack of estrogen
introduction
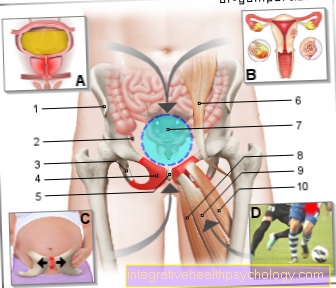
Estrogens, like progestins, are the sex hormones (reproductive hormones) of women. They are mainly formed in the ovaries, but to a lesser extent also in the adrenal cortex, in connective tissue and in adipose tissue. The production of sex hormones is subject to a control loop between structures in the brain (pituitary gland and hypothalamus) and the ovaries.

Estrogens influence the sexual organs (structure of the uterine lining, growth of the uterine muscles, amount and texture of vaginal discharge) and the development of secondary sexual characteristics (growth of the mammary gland during puberty, high voice, female body appearance with broad hips, narrow waist and narrow shoulders). During puberty, the estrogens also cause the growth spurt.
A lack of estrogens can have many different causes and effects.
causes
An estrogen deficiency or a lowered estrogen level is common in women Menopause (climacteric) or after menopause physiologically - that is, completely naturally. During menopause, which usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, the ovaries stop producing estrogens. There is a lack of estrogens with a variety of symptoms.
In women who are still before menopause, an estrogen deficiency can result from impaired function and / or malformation of the ovaries.
The dysfunction of the ovaries is divided into primary and secondary forms.
In the primary dysfunction the problem lies with the ovaries themselves. They can no longer fulfill their tasks (egg cell maturation and hormone production) due to malformations or functional disorders. Premature "fatigue" of the ovaries before menopause can occur, for example, after autoimmune processes (in the ovaries themselves), after chemotherapy or radiation therapy or metabolic diseases such as diabetes mellitus. If the primary dysfunction of the ovaries occurs before the age of 40, this is referred to as "Climacteric praecox“(Premature menopause).
The woman becomes infertile prematurely because the egg cells no longer mature and ovulation cannot occur. This phenomenon occurs family-run on. If the mother entered menopause early, it could be important not to start family planning too late if the daughter wishes to have children.
In the case of secondary dysfunction of the ovaries, the problem lies at the level of the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland (pituitary gland) in the brain, but the ovaries themselves are actually functional. If the impulses to the ovaries are missing due to a disturbance in the brain, they do not produce any hormones.
The causes of the disturbances in the corresponding areas can be inflammatory processes, trauma, tumors, stress, excessive physical activity, severe underweight (anorexia nervosa: anorexia nervosa: anorexia nervosa: anorexia nervosa: anorexia nervosa: anorexia patients often miss their periods because the regulating cycle no longer works properly and accordingly does not lead to one regular cycle comes), depression and endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism.
A so-called gonadal dysgenesis describes the congenital, genetically determined absence of the ovaries. Since no estrogens are produced here, the sexual organs do not mature during puberty. The affected women do not get their period (primary amenorrhea) and remain sterile. Gonadal dysgenesis occurs in the context of rare genetic syndromes such as Turner syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome.
Of course, estrogen production is also reduced after surgical removal of one or both ovaries (oophorectomy). An oophorectomy can be part of the therapy for the following diseases, for example: ovarian tumors, ovarian endometriosis, breast cancer, fallopian tube cancer.
Lack of estrogen during menopause
Menopause (climacteric) form the transition phase from a woman's reproductive time (the time when the woman is fertile) to the absence of a menstrual period. During this time, the ovaries gradually cease to function. Menopause usually begins between the ages of 40 and 50. The production of estrogens decreases, the cycle becomes irregular and the period becomes less and less frequent.
Menopause is the time of the last menstruation, an average of 52 years of age.
The hormonal change can be asymptomatic, but unfortunately some women experience the typical "menopausal symptoms".
The symptoms of the failure of sex hormones can be diverse:
Count among them Sweats, Hot flashes, dizziness, a headache, sleep disordersSkin changes, urinary tract problems, cardiac arrhythmias, nervousness, irritability and depressed mood. In addition, a Vaginal dryness occur, which on the one hand leads to pain during sexual intercourse, on the other hand favors infections with bacteria or fungi.
In the long term, the lack of estrogen can osteoporosis (Bone loss) and arteriosclerosis (Deposit in the vessel walls). These diseases are associated with an increased risk of bone fractures and circulatory disorders, for example in the legs or heart.
If the unpleasant symptoms during the menopause are pronounced, you can do one Hormone replacement therapy contemplate. Here, the woman's sex hormones (estrogens and gestagens) are replaced by drugs in the form of tablets, patches or creams. Creams, vaginal rings or pessaries (hard plastic pieces that hold the uterus in place) are also available for local treatment.
Hormone substitution can improve the symptoms mentioned above and reduce the long-term consequences such as osteoporosis.
One disadvantage of hormone replacement therapy with estrogens is that it can increase the risk of breast cancer and uterine cancer.
Alternative treatment methods come from the field of Naturopathy and include, for example, cupping (using negative pressure through small glasses on the skin to relieve tension and relieve pain), neural therapy (local anesthetics are supposed to influence the vegetative nervous system), bog baths and the ingestion of cimicifuge rootstock (plant extracts that are supposed to develop estrogen-like effects).
Weight gain during menopause
The most frequently lamented Weight gain during menopause is less due to hormonal changes than to the age-related lower basal metabolic rate of the body. The greatest energy expenditure takes place in the muscles. A decrease in muscle mass due to a lack of exercise with unchanged eating habits thus leads to weight gain.
Due to the hormonal change, it can also become a Reconstruction of the fat reserves come. The relative predominance of male sex hormones causes increased fat storage on the trunk, especially on the abdomen and around the internal organs. This can affect your metabolism and the emergence of a Adult diabetes and rising Cholesterol levels favor.
Symptoms
Symptoms of estrogen deficiency in women vary.
If the hormone deficiency already exists in the ChildhoodFor example, if the ovaries are incorrectly positioned as part of a genetic defect, the development of puberty can be delayed, incomplete or even completely absent.
Also Injuries of the ovaries before puberty, for example through radiation and chemotherapy in the pelvic area or changes in the pituitary gland (Pituitary gland) due to inflammatory processes, trauma or tumors can lead to a delayed onset of puberty.
Symptoms in girls who are delayed through puberty may include delayed breast growth, pubic hair, and their first menstrual period. In addition, the growth spurt may not occur. The most common cause of delayed puberty is family conditional, in which the children simply develop a little later, but quite normally.
In adult women, an estrogen deficiency or an imbalance in sex hormones can occur Menstrual cycle disorders lead to infertility. This can lead to intermenstrual bleeding or an increasingly rare occurrence of menstrual bleeding. If the cycle is longer than 35 days (normal: 23 to 35 days), one speaks of an extended cycle.
During menopause, the lack of estrogen is responsible for the typical symptoms during menopause.
Taking the birth control pill
Taking the Birth control pills May be related to conditions such as vaginal dryness, genital tract infections and painful intercourse. When using low-dose contraception Compipreparations its own estrogen production is suppressed, causing it to local Hormone deficiency symptoms can occur in the pelvic floor area. Estrogens normally stimulate the build-up and regeneration of the vaginal skin. If there is a local lack of estrogen, the vaginal skin becomes thinner, drier and more sensitive. The symptoms mentioned above often arise after fungal infections, as the regeneration of the tissue is disturbed.
Deficiency in estrogen in men
Men have estrogens too. They arise from, as in the case of women testosterone. The higher the testosterone level, the more estrogen is formed. Correspondingly, with lower testosterone levels (for example in old age), the estrogen level also decreases.
A lack of estrogen in men is believed to affect the amount of fat in the body. There is probably an increase in fat deposits under the skin and in the abdomen. Also libido and power seem to be dependent on both hormones (testosterone and estrogen).
By taking testosterone, the estrogen level can also be raised back to values in the normal range.
therapy
The therapy of an estrogen deficiency mainly refers to the administration of estrogen. The type of therapy depends on the target group - for example, young girls who are late for puberty or more mature women who want to alleviate their postmenopausal symptoms.
There are various ways to improve or treat symptoms caused by the lack of estrogen.
One possibility is hormone replacement therapy. This is mainly used for postmenopausal complaints. The missing estrogens and possibly also gestagens are administered and the hormone deficiency is compensated for. The aim of treatment is not to restore the original hormone concentration, but to alleviate or prevent the symptoms with a reduced dose.
Before starting hormone replacement therapy, a comprehensive examination by the gynecologist and an explanation of the advantages, disadvantages and risks of long-term treatment are essential. Regular check-ups are recommended during therapy.
It is important to weigh up the benefits and risks on an individual basis. Studies have shown that the risk of breast cancer can increase in women who have received hormone replacement therapy for more than five years (especially with combination preparations with estrogens and gestagens).
In addition to reducing menopausal symptoms, the positive effects of hormone replacement therapy are the prevention of inflammation in the genital area (see also: Vaginal inflammation), depression and osteoporosis in the context of menopause.
The hormones can be administered in a variety of ways: tablets, plasters, creams and gels as well as pessaries and vaginal rings are available for local treatment.
Alternative treatment approaches for a hormone deficiency are offered by natural healing methods. These are particularly useful in the case of milder complaints. They relate to the ingestion of plant-based estrogens. These are obtained from food supplements such as soy, flaxseed, red clover, hops, sage, liquorice or St. John's wort.
Traditional Chinese medicine mainly uses acupuncture and the use of Chinese medicinal herbs. However, the effectiveness and tolerability of long-term use of these naturopathic treatments has not yet been scientifically proven.
Consequences if not treated
The consequences of a lack of estrogen can be far-reaching. A deficiency in the hormone can affect the development of the genital organs, the menstrual cycle, fertility and pregnancy, since the various functions of the estrogen can no longer be fulfilled properly if there is a lack of estrogen.