What is tonsillitis?
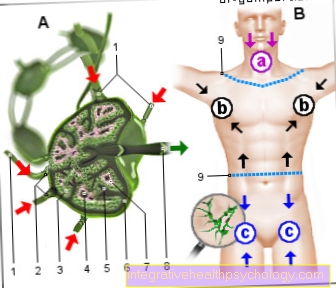
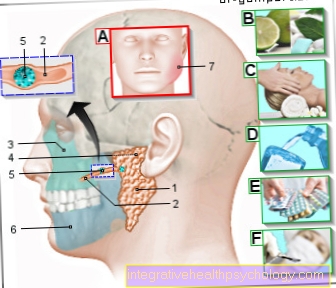
The palatine tonsils, colloquially just called tonsils, are located laterally in the back of the mouth and throat.
They can be seen with your mouth wide open.
In acute tonsillitis, both tonsils are inflamed.
They are painfully swollen, reddened and covered with typical yellow-whitish coatings.
Tonsillitis can affect anyone, but it is most common in children and young adults.
A distinction is made between acute tonsillitis and chronic, which usually causes fewer symptoms.

Causes of tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is caused by infections with bacteria or viruses.
Type A streptococci among the bacteria often cause tonsillitis.
One then speaks of tonsillar angina or streptococcal angina.
The term angina means tightness / tightness. Tonsillar angina is the feeling of tightness in the throat caused by tonsillitis due to the swelling of the tonsils.
More rarely, other bacteria trigger tonsillitis, such as pneumococci, staphylococci or Haemophilus influenzae.
The development of tonsillitis is favored by a weakened immune system. Tonsillitis can also be associated with other diseases.
- Scarlet fever is a disease transmitted by droplet infection and caused by A streptococci. The infection affects the whole body and tonsillitis is a concomitant symptom.
- Diseases that are triggered by viruses, such as Pfeiffer's glandular fever (Epstein-Barr virus) or herpangina (Coxsackie A virus) also cause tonsillitis in the course of the disease.
- Inflammation of the tonsils can also occur in the context of tuberculosis, syphilis, leukemia, diphtheria or in thrush angina caused by fungi (Candida albicans).
Read more on the subject at:
- Scarlet fever
- Angina tonsillaris
- Pfeiffer's glandular fever
diagnosis
A tonsillitis can be recognized very quickly due to the typical symptoms. Swollen and reddened tonsils as well as pus deposits on the tonsils are signs of an acute tonsillitis.
The doctor can confirm the suspicion by looking in the mouth. Occasionally, the palatal arches and the tongue are covered with purulent.
When you palpate the lymph nodes in the neck area, they are often swollen. A tonsillitis is detected early by the family doctor or ear, nose and throat doctor with a few examinations.
These symptoms tell me that I have tonsillitis
Typically, tonsillitis can be recognized by a sudden onset of painful swallowing difficulties and a sore throat.
Frequently there is a high fever and a significantly reduced general condition.
The almonds swell inflammatory, become crimson and usually have a white, grayish or yellowish coating.
The purulent coating of the tonsils can be strip-like, punctiform or completely connected. The lymph nodes on the neck and corner of the jaw are often swollen. The pain can radiate into the ears and a headache can occur.
difficulties swallowing
Difficulty swallowing includes symptoms such as pain when swallowing, a feeling of lump in the throat, lumpy speech and disturbances in the act of swallowing up to the inability to swallow.
"Harmless" swallowing difficulties can occur if pain occurs when swallowing food in the case of tonsillitis.
If an abscess (peritonsillar abscess) develops as part of a tonsillitis, extremely severe pain occurs when swallowing and the mouth is usually difficult and painful to open (jaw clamp).
If you have pronounced swallowing problems, you should consult your doctor or ENT doctor.
Read more on the subject under: Jaw clamp
Sore throat
Characteristic symptoms of tonsillitis are severe sore throats.
The sore throat can radiate into the jaw and ears.
Most of the time, the sore throat lasts longer than two days and is accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, lumpy speech and bad breath.
Earache
In acute tonsillitis, earache is often caused by radiating sore throat.
The severe sore throat radiate into the corners of the jaw, ears and adjacent soft tissues.
A unilateral earache can indicate a complication of tonsillitis, namely the peritonsillar abscess.
pus
The tonsils are red and swollen when inflamed.
If bacteria are responsible for the disease, the tonsils are often covered with pus.
The bacterially colonized almonds secrete a whitish to yellowish, viscous mass, which is also called detrius (cell waste) or pus specks.
In the case of severe inflammation, the pus specks can merge or even extend beyond the tonsils.
This is how tonsillitis differs from tonsillitis
A tonsillitis is an infection of the paired tonsils that lie laterally in the back of the mouth.
In contrast to the palatine tonsils, the pharynx cannot be seen when the mouth is open.
It is located in the middle of the posterior wall of the pharynx above the uvula.
There is only one pharynx compared to the paired tonsils.
The symptoms of tonsillitis differ from those of tonsillitis.
The pharyngeal tonsil is anatomically located on the roof of the nasopharynx.
This means that this almond mainly attacks pathogens that get into the throat via the nose.
Typical complaints are a stuffy nose and difficult nasal breathing, painful swelling of the tonsil tissue in the upper throat and ear pain.
The tonsils lie deeper in the throat and are colonized by bacteria and viruses that enter the throat via the mouth.
Therefore, other symptoms occur, such as difficulty swallowing and a radiating sore throat.
Inflamed tonsils can usually be seen with the naked eye if you open your mouth and look inside with a light. You can see reddened, swollen and mostly purulent-coated tonsils.
Treatment and therapy
Treatment of tonsillitis depends on the cause of the tonsillitis, the symptoms, and how it has progressed.
In the case of acute tonsillitis, pain relievers and fever lowering agents are usually used.
Ibuprofen and paracetamol are possible drugs that can relieve pain and reduce fever.
In addition, complaints such as swallowing difficulties and sore throats can be relieved with various home remedies.
If bacteria are causing the inflammation, the doctor will usually prescribe an antibiotic.
Penicillin is often used.
Surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is an option if the tonsils are chronically inflamed.
Surgery is only indicated if at least 7 tonsillitis occurs in one year, at least 5 infections in a year over two years, or at least three infections in the tonsils in a year over three years.
Read more on the subject at:
- Treatment of tonsillitis
- Ibuprofen
- Paracetamol
Home remedies
Gargle solutions with sage tea or chamomile tea are popular home remedies that have anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effects.
Gargling can relieve symptoms such as a sore throat and difficulty swallowing, and can promote healing.
A neck wrap can help relieve the sore throat and a wagon wrap can be used to naturally lower the fever.
There are numerous different lozenges that have an analgesic effect and relieve short-term swallowing difficulties.
It is also helpful to eat only soft and spicy foods and to drink a lot. You should avoid fruit juices and acidic drinks, as the acids additionally irritate the inflamed tonsils.
Cold drinks and ice have a positive effect on swallowing difficulties and sore throats.
Read more on the subject under: Home remedies for tonsillitis
homeopathy
A tonsillitis must be examined by a doctor and the pathogen treated accordingly.
Homeopathic remedies can be used for tonsillitis to aid healing. Different globules can be taken.
The remedies belladonna and aconite help with a red throat caused by acute tonsillitis.
If the throat is dark red, rough and sore, Pyrogenium can help.
Hepar Sulfuris is used for pus sticks, while Mercurius Solubilis can be taken for pus pads.
In the case of pronounced tonsillitis with severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, swollen neck lymph nodes and fever, the remedies Lachesis, Lac caninum or Lycopodium can be tried.
In addition to the globules, Schüssler salts are often taken, which are supposed to fight tonsillitis from the inside. In the case of tonsillitis, the Schüssler salts Ferrum Phosphoricum, Kalium chloratum, Sodium Phosphoricum, Calcium Sulfuricum and Kalium bromatum are possible.
Homeopathic globules and Schüssler's salts can be used to aid the healing process in cases of tonsillitis. Homeopathic therapy is not sufficient for long-term symptoms and fever. A doctor should be consulted if symptoms persist or if a fever occurs.
Duration
Acute tonsillitis lasts for one to two weeks with the right therapy.
If the tonsillitis is present for more than two weeks, there is a risk of chronic tonsillitis.
Chronic tonsillitis is dangerous as the streptococci can cause serious illness over time. Examples are rheumatic fever, kidney and heart infections, joint inflammations and skin diseases.
In order to avoid complications of tonsillitis, early diagnosis and targeted therapy are very important