Diencephalon
Synonyms in the broadest sense
Diencephalon
introduction
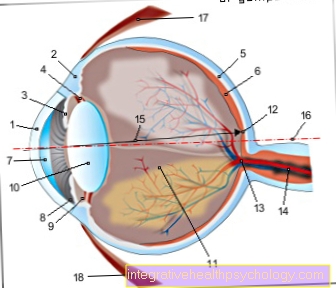
The diencephalon as part of the brain is located between the endbrain (cerebrum) and the brain stem.
Its components are:
- Thalamus
- Epithalamus (epi = on it)
- Subthalamus (sub = under) with Globus pallidus (Pallidum)
- Hypothalamus (hypo = below, less)
Thalamus
The egg-shaped paired thalamus is the largest and, together with the hypothalamus, the most important of these structures in the diencephalon and is located in the center of the brain. It limits the III. Ventricle; The caudate nucleus runs above it, below which one finds the hypo- and subthalamus as well as the midbrain. Above the III. The epithalamus is located in the ventricle, while the thalamus is composed of several nuclei and medullary lamellae. The pineal gland (epiphysis, glandula pinealis) as part of the epithalamus is located at its posterior pole.
Illustration brain

Cerebrum (1st - 6th) = endbrain -
Telencephalon (Cerembrum)
- Frontal lobe - Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe - Parietal lobe
- Occipital lobe -
Occipital lobe - Temporal lobe -
Temporal lobe - Bar - Corpus callosum
- Lateral ventricle -
Lateral ventricle - Midbrain - Mesencephalon
Diencephalon (8th and 9th) -
Diencephalon - Pituitary gland - Hypophysis
- Third ventricle -
Ventriculus tertius - Bridge - Pons
- Cerebellum - Cerebellum
- Midbrain aquifer -
Aqueductus mesencephali - Fourth ventricle - Ventriculus quartus
- Cerebellar hemisphere - Hemispherium cerebelli
- Elongated Mark -
Myelencephalon (Medulla oblongata) - Big cistern -
Cisterna cerebellomedullaris posterior - Central canal (of the spinal cord) -
Central canal - Spinal cord - Medulla spinalis
- External cerebral water space -
Subarachnoid space
(leptomeningeum) - Optic nerve - Optic nerve
Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
= Cerebrum + diencephalon
(1.-6. + 8.-9.)
Hindbrain (Metencephalon)
= Bridge + cerebellum (10th + 11th)
Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)
= Bridge + cerebellum + elongated medulla
(10. + 11. + 15)
Brain stem (Truncus encephali)
= Midbrain + bridge + elongated medulla
(7. + 10. + 15.)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Subthalamus
The Subthalamus contains among other things the Globus palliduswhich, from a developmental point of view, belongs to the diencephalon.
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus forms the base of the diencephalon under the floor of the III. Ventricle. Before that one finds the junction of the optic nerves (Optic chiasm), behind it the pituitary stalk with transition to the pituitary gland (pituitary gland). The hypothalamus is divided into different areas, which contain typical nuclei with vegetative functions. The bean-shaped Pituitary gland is divided into neuro- and adenohypophysis, with the neurohypophysis making up the posterior part and the adenohypophysis making up the anterior part of the pituitary gland. Only the neurohypophysis belongs to the diencephalon, the adenohypophysis is not part of the brain, as it is made up of the so-called Rathke bag which is part of the ectoderm, one of three cotyledons in embryonic development.
The structures mentioned - with the exception of the pituitary gland once created - can also be found twice (left and right) in the brain (diencephalon).
function
The Thalamus As the largest part of the diencephalon, it fulfills a variety of functions in the brain. All information for the terminal cortex is switched over in it. For one thing, he's on limbic systeminvolved in processes of well-being and mood, in seeing, hearing and smelling processes, and on the other hand in motor processes. The thalamus is also referred to as "Gateway to Consciousness", because it forwards sensory information to the cerebral cortex and this is how it is made conscious.
The Epithalamus (Diencephalon) is with the limbic system, the olfactory system, nuclei of the secretion processes of the mouth and vegetative centers of the Brain stem interconnected. The Epiphysis as part of the epithalamus represents a gland that contains the hormone Melatonin forms and releases. In addition, it affects the sympathetic nervous system and the Control of the day-night rhythm.
The Subthalamus (Diencephalon) as part of the brain includes in its function that motor systemas well as the one belonging to him Globus pallidus, which as a motor center is part of the Basal ganglia loop represents.
The Hypothalamus has an impact on a variety of body processes. These include regeneration, power, the Daily rhythm, the female cycle, Food and water intake included Feeling of satiety. In addition, the hypothalamus regulates sweating, organ activity and tremors, and various hormones are formed: Endogenous opiates, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Oxytocin and Control hormones that act on the adenohypophysis (Liberins, statins). It is possible to influence these different processes via connections between the hypothalamus and the limbic system, Brain stem and pituitary gland.