These are the symptoms you can tell if you have vasculitis
introduction
Vasculitis is an inflammation of the blood vessels. A distinction is made between countless different types that are assigned to this group of diseases. Vasculitis can cause many different symptoms as it can affect almost any organ.
If certain symptoms occur without any other identifiable cause, these can indicate the presence of vasculitis.Ultimately, however, the diagnosis can only be made through special laboratory tests in the blood and, if necessary, a tissue sample.

Overview of the symptoms
Because blood vessels are in every organ and area of the body, vasculitis can cause symptoms in any organ system.
- Changes to the skin such as discoloration or bleeding are common, for example.
- The eyes can also be affected and redness or visual disturbances occur.
- If the brain is involved, headaches but also a stroke with paralysis and speech disorders can occur.
- One possible symptom on the hands is painful fading of the fingers.
- Difficulty breathing and coughing up blood are possible symptoms of vasculitis with lung involvement.
However, none of the above symptoms are conclusive for the presence of vasculitis. Another cause can always be responsible and a diagnosis can ultimately only be made through a medical examination.
Learn more about: Vasculitis - When blood vessels become inflamed
Symptoms on the skin
Various symptoms of vasculitis may appear on the skin and may indicate the presence of the disease.
Are the smallest blood vessels (Capillaries) Affected by the inflammation, so-called petechiae can develop demonstrate. These are punctiform hemorrhages that cannot be pushed away with a finger. They most commonly arise on the lower legs.
Another symptom on the skin that indicates a specific form of vasculitis is that Livedo reticularis. This is net-like redness. For another form of vasculitis, lightning-figure, bluish-red skin changes are typical, which are called Livedo racemosa are designated. In addition to the skin, the mucous membrane is also often affected by vasculitis and, for example, painful canker sores and petechiae can form.
Nervous system symptoms
When the nervous system is affected by vasculitis, the symptoms can vary widely.
If smaller vessels in the nervous system are damaged, this usually leads to tingling or abnormal sensations, usually the Hands or feet affected are. Damage to special nerve fibers can also impair the function of the sweat glands, so that dry skin can also be a possible symptom.
In rare cases, even the robust nerves that transmit the signals for movement are impaired, so that a possible symptom of vasculitis in the nervous system can be paralysis of an arm or leg, for example.
Symptoms in the brain
Some forms of vasculitis affect, among other things, or even exclusively the brain. This can be recognized by symptoms such as persistent dull headache, poor memory, difficulty concentrating or dizziness. Psychological symptoms are also possible like a change of being.
If large vessels are affected by vasculitis, it can also result in a stroke. If this occurs in young people with the typical symptoms such as hemiplegia or speech disorders, this can indicate vasculitis. Epileptic seizures or psychoses are also possible symptoms that can be attributed to vasculitis in the brain.
You may also be interested in this topic: What are the symptoms of a psychosis?
Symptoms of allergic vasculitis
An allergic vasculitis is a special form with a previously unexplained cause. The underlying reason for the vascular damage is presumably an excessive activity of the body's own defense system, which among other things also leads to an inflammatory reaction of the small blood vessels. As a rule, allergic vasculitis cannot be distinguished from other forms by its symptoms.
Usually, general symptoms such as fever or fatigue appear first. Other possible symptoms of allergic vasculitis are joint pain and punctiform skin hemorrhages. Symptoms such as reddening or pain can also occur in the eyes. Abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea are possible symptoms when the gastrointestinal tract is also affected.
If several of the symptoms mentioned come together, the presence of vasculitis should be considered. Ultimately, the only way to determine whether the symptoms are due to allergic vasculitis is a tissue sample.
Also read: Allergic reaction
Symptoms of leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Leucocytoclastic vasculitis is a large subgroup of vasculitides that are defined on the basis of certain changes that can be detected in the tissue.
Diagnosis is therefore only possible through a microscopic examination of a skin tissue sample by a pathologist. Symptoms cannot distinguish leukocytoclastic vasculitis from other forms of vasculitis.
Possible symptoms are therefore generally all those that can basically occur due to vasculitis. In addition to general symptoms such as fever and reduced performance, red eyes and joint pain are among the most common. Punctiform hemorrhages or rough lumps can form on the skin. If internal organs are involved, numerous other unspecific symptoms are possible, depending on the infestation.
Symptoms around the eyes
When vasculitis affects the eyes, symptoms may include reddening of the conjunctiva or eyelids, and blurred vision.
Depending on which part of the eyes is affected, double vision can occur or visual acuity decreases. It is also possible that one eye is affected more than the other. In most cases, however, there is another form of inflammation with such symptoms, which can often be treated well and subside again. However, if there is a suspicion of a vasculitia such as temporal arteritis due to other symptoms, immediate treatment with glucocorticoids must be carried out so that no permanent damage such as visual impairment occurs.
Even if such symptoms persist over a long period of time despite medical treatment, vasculitis, among other things, is a possible cause of the discomfort in the eyes and should be clarified.
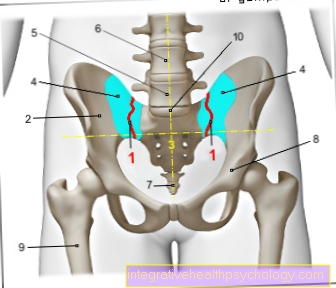
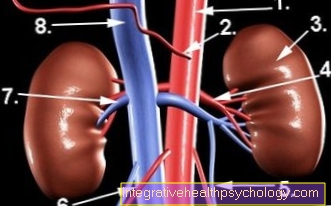
Symptoms of the kidney
In some forms of vasculitis, the kidneys are also affected.
Kidney disease can indirectly trigger various symptoms, which may indicate the presence of vasculitis. Among other things, kidney damage causes an increase in blood pressure, which among other things is caused by headaches can be noticed. Blood in the urine can also indicate a kidney disease and should be checked by a doctor.
Sometimes pain is also felt in the right or left flank. If vasculitis leads to a pronounced decrease in kidney function, water retention, itching and a clouding of consciousness can also result. In such a case, an artificial kidney replacement procedure such as dialysis usually has to be performed to detoxify the blood.
Further information on this: Symptoms of kidney failure
Symptoms on the lungs
Different forms of vasculitis cause symptoms in the lungs, among other things.
The symptoms that this causes can indicate the presence of this disease, but other causes such as an infectious disease or cancer must always be considered. A typical symptom is the coughing up of blood. Also shortness of breath at rest and intensified during exertion are possible complaints. In addition, in many forms of vasculitis there is an increased risk of blood clots forming in the vessels. Among other things, these can cause a pulmonary embolism. Such an acute illness often manifests itself as a sudden onset of shortness of breath and increased coughing.
You might also be interested in these topics:
- lung infection
- How do you recognize lung cancer?
Symptoms on the fingers
In particular, possible symptoms on the fingers that could indicate vasculitis include feeling cold and pain.
The so-called Raynaud phenomenon often appears. In this case, one or more fingers are puffed out like an attack because the blood-supplying vessel contracts. Then the affected finger (s) run blue on. After a while, more blood flows in again and it turns red.
A particularly pronounced form of this vasculitis on the fingers can be recognized by the fact that tissue on the phalanxes of the fingers dies and black skin defects remain. In such a case, part or all of the affected finger must be amputated to prevent an inflammatory reaction.
Learn more about: Raynaud's Syndrome
How do the symptoms change over time?
The disease group of vasculitis comprises a large number of clinical pictures, some of which are very different and do not develop in the same way in every person. Therefore, no general statement can be made about how the symptoms of vasculitis change over time.
As a rule, the disease cannot be cured. However, if this is recognized in good time and a consequent therapy is successful, the symptoms slowly recede. Often the person affected can even be completely free of symptoms. However, relapses and flare-ups can occur at any time.
In less favorable cases, however, the symptoms can continue to increase immediately. This can happen if the disease is not recognized in time or if treatment is not carried out or does not work. In the worst case, there is a risk of end organ damage, for example to the lungs or the heart, which can ultimately be life-limiting.
In some forms of vasculitis, a stroke is also possible at a young age and can lead to hemiplegia and speech disorders, among other things.
Churg-Strauss vasculitis
Churg-Strauss vasculitis is a special disease that particularly affects the airways. It is also known as eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis.
Attack-like shortness of breath and bloody sputum may appear as typical symptoms. In addition, in around half of all Churg-Strauss vasculitis cases, the heart is also affected. Possible symptoms are shortness of breath during exertion and pain behind the breastbone. Severe damage to the coronary arteries can even trigger a heart attack.
Recommendations from our editorial team
- Vasculitis - When blood vessels become inflamed
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- rheumatism
- Morning stiffness
- Wegener's granulomatosis