Metatarsal fracture
General
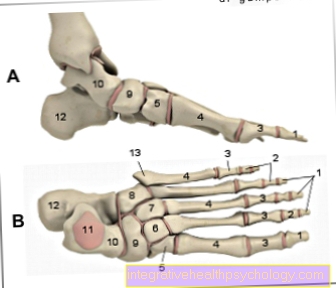
The metatarsals (medically: Metatarsal bone) connect the toes of the foot with the so-called tarsus. There are thus five metatarsal bones on each foot. The fracture of one of these bones is usually caused by a significant direct or indirect force on the foot. In addition to objects that fall on the foot, accidents and sports injuries are common causes that can lead to a metatarsal fracture.

If a metatarsal fracture is suspected, a doctor should be consulted who can confirm the diagnosis and initiate therapy if necessary.
Depending on the severity of the fracture and the accompanying injuries which often occur with a metatarsal fracture, the prognosis of such an injury is to be assessed differently. A simple metatarsal fracture without major soft tissue injuries should return to normal after about six months. In individual cases, however, the healing time can be delayed.
root cause
Much of the Broken bones in the foot concern the Metatarsal bones. Falling objects or indirect forces in an accident break these bones more quickly than other structures on the foot and are therefore often affected by fractures.
It is noteworthy, however, that one high force is necessary to break the metatarsal bones because they have a strong stabilization have numerous ligaments and muscles. If the metatarsal bones break with only low intensity, it is therefore recommended to use the Tape apparatus as well as bone density to check in order to exclude any diseases that may be responsible for a break.
In addition, athletes who add severe stress to the structures of the metatarsus are statistically often affected by fractures of the metatarsal bones. In particular, they are dancers or athletes who run a lot.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
Athletes (joggers, soccer players, etc.) are particularly often affected by diseases of the foot. In some cases, the cause of the foot discomfort cannot be identified at first.
Therefore, the treatment of the foot (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, heel spurs, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of foot diseases.
The aim of every treatment is treatment without surgery with a complete recovery of performance.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Fatigue fracture
A fatigue fracture or generally a fracture of the metatarsal bone is understood to be an interruption in the continuity of the corresponding bone. If the bone is "tired" it is no longer strong enough to withstand a load, so that it breaks. A stress fracture on the metatarsal bone can also be referred to as a stress or marching fracture.
The metatarsal is a typical place of fatigue fractures. The 2nd metatarsal is most frequently affected. Due to a strong, long-lasting mechanical load or overloading, the metatarsal bone can no longer keep up with its physiological adaptation processes as a reaction to the load. This has the consequence that it gives way and it comes to a break. In comparison to traumatic metatarsal fractures, a fatigue fracture does not occur suddenly and unexpectedly. Rather, it is a gradual process. The respective metatarsal bones initially reacts to the load with signs of fatigue such as small cracks in the bone. Resilience continues to decrease over time, as the metatarsal bones are unable to repair the small cracks in the bone structure due to sustained heavy loads. At some point, the metatarsal is no longer strong enough and breaks.
In general, competitive athletes from the running area or people who put excessive strain on their metatarsus for a long time without being used to such strain are particularly at risk. Soldiers and hikers are also prone to a so-called march fracture, i.e. a fracture due to fatigue.
Read more on the subject at: Fatigue fracture in the metatarsus
Symptoms
The symptoms that occur with a metatarsal fracture are typical of most fractures in the body. One of the main symptoms is severe pain, which is particularly noticeable when stepping on or when pressure is applied to the foot. In addition, there is usually a swelling of the affected foot and a bruise. This can encompass large parts of the foot.
In addition, specific symptoms may occur depending on whether and how many soft tissues are affected by the injury. For example, if nerves are damaged, sensory disorders in the foot can occur.
If there is a so-called open fracture, parts of the bone have pierced the surface of the skin. If the wound becomes infected in this case, other symptoms such as fever, reddening of the skin and overheated skin come to the fore.
Read more on the subject at: Symptoms of a metatarsal fracture
Is there a metatarsal fracture without pain?
The classic symptoms of a metatarsal fracture are, besides a bruise, possible sensory disturbances and swelling, pain. However, the pain does not necessarily have to occur in every person affected. So yes, there is a metatarsal fracture with no pain.
The symptoms of a metatarsal fracture vary from person to person and depend, among other things, on whether the injury was triggered by an acutely traumatic accident or whether it is a stress fracture. The latter often shows no noticeable pain at the beginning. Those affected usually only feel moderate pain immediately after the fracture event, such as a bruise that may be gone the next day. Therefore, the metatarsal fracture is often not recognized. The severe pain usually only occurs later, when the metatarsus continues to be stressed despite the fracture. At this point at the latest, a doctor should be consulted in order to make an X-ray to confirm the diagnosis of a metatarsal fracture.
But there is also the option that those affected are completely pain-free for several months despite a metatarsal fracture. Often these are competitive athletes who can compensate for the injury with a well-developed musculoskeletal body. In the event of overload, however, even with such groups of people the point is reached at some point that the metatarsal fracture no longer remains pain-free.
Read more on the subject at: Pain in a metatarsal fracture
How can I recognize a metatarsal fracture?
A metatarsal fracture can be recognized by the typical symptoms associated with the injury. The metatarsal fracture usually occurs after an enormous force is exerted on the foot. If pain occurs in the foot after an act of force, which increases when it occurs and when pressure is applied, this can be understood as the first sign of a metatarsal fracture.
Especially if the pain is accompanied by significant swelling of the foot and a bruise, the probability that a metatarsal fracture is present is relatively high. This can only be determined with certainty by visiting a doctor.
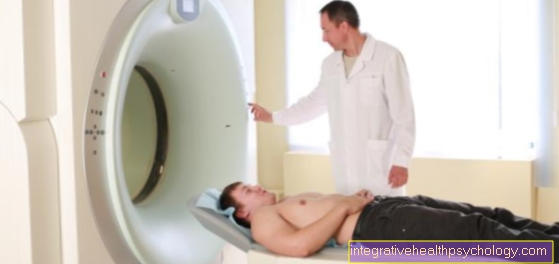
Using imaging techniques, the foot can be examined for any broken bones. Bones are best visualized with an x-ray machine or computed tomograph. The use of an MRI machine to produce an MRI of the foot can provide information on the question of whether soft tissues have also been damaged in addition to the bones.
therapy
The therapy for a metatarsal fracture basically depends on the severity and shape of the fracture. The general rule is that the pieces of bone that differ from one another due to the breakage are returned to the Original form must be brought. This is important to a adequate function of the foot after healing. To be able to bring the bones together Wires, plates and Screws be used.
Sometimes one is enough Fixation of the bones through wires without performing any surgery. Often, however, a metatarsal fracture is required open surgery in which the bone fragments are connected to one another by means of plates and screws.
Are the Bone fragments not shifted against each other can a conservative treatment with help of a Plaster cast sufficient. Of the plaster can usually after six weeks removed.
Even after the therapy, the recommendations of the attending physician should be strictly followed so that complications do not occur and complete healing can occur. After removing the plaster should recommended exercises carried out and Avoid strenuous movements if possible so that the foot gains the stability and strength it had before the injury.
The attending physician and physiotherapist can, if necessary, provide further information on how the healing process can be positively influenced by performing special exercises and closed periods.
cure
Bones are generally part of the slow healing structures in the human body. In addition to slow healing, a broken bone also needs strong fixation in order to be able to return to its initial state.
After repositioning and fixing the bone fragments, the foot is usually immobilized with a plaster of paris so that the healing of the bones is not delayed and disturbed by movement. After about six weeks, the plaster of paris can be removed and the foot is usually already lightly loaded.
The muscles can be built up through targeted mobilizing exercises of the foot without putting too much strain on the damaged structures.
The individual duration of the healing phase depends on the type of injury and a number of individual factors. In particular, the extent of the soft tissue involvement associated with the metatarsal fracture determines the course of the disease. Healing of the foot, after which the affected foot can be fully loaded, is usually only achieved after about 6 months. In individual cases, a full load on the foot can only be achieved after a year.
Read more on the subject below. Metatarsal fracture healing
Duration of healing
The duration from the injury that leads to a metatarsal fracture to the complete healing of the foot can vary greatly depending on the injury and the type of fracture. In addition, there are individual characteristics of the person affected as well as the selected therapy method, which can influence the healing time in individual cases.
The time until the affected foot can usually be fully loaded again varies between 6 and 12 months. Partial exposure is usually possible after 6 weeks after the cast has been removed. In the case of complex therapy procedures and injuries, the time until complete recovery can be significantly delayed.
Read more on the subject at: Duration of the metatarsal fracture
When can I put weight on my foot again?
When is the right time to reload the foot after a metatarsal fracture is individually different. The timing depends on factors such as the severity of the break and involvement of the surrounding tissue (the soft tissues). It also depends on how the fracture is treated therapeutically, which in turn depends on whether it is a pure and uncomplicated stress fracture or a complex traumatic fracture.
If the fracture is immobilized with a plaster of paris, the foot must not be stressed during this. Usually the plaster of paris is put on for about 6-8 weeks. You can then begin reloading the foot carefully and with the advice or guidance of your doctor or physiotherapist. It is important to be patient and gradually introduce the affected foot to a load so that the bone has enough time to react to the stress with adaptation processes in the bony structure. Therefore, from the 6th to 8th week after removal of the plaster, a partial load is recommended. Only in the further course should a full load take place.
A complete healing with full resilience as before the metatarsal fracture is in most cases only possible after about 6 months.
diagnosis
At the beginning of Diagnosis of a metatarsal fracture there is a doctor-patient conversation in which the doctor asks how the injury came about. This anamnesis helps the doctor to assess the force acting on the foot and what damage to the foot can be expected.
In addition, a look at the foot and a physical examination of the person affected help to give the doctor an idea of the injury.
You can only be certain of the extent of the injuries and whether a metatarsal fracture is present after an X-ray examination has been carried out. With the help of an X-ray machine or a computer tomograph, images can be created that can clearly show the fracture of the bone and its current position. In order to be able to assess the extent to which the surrounding tissue has been damaged, an MRI examination is also carried out in individual cases.
forecast
The forecast A metatarsal fracture is usually very good. It takes a relatively long time to heal, but most of those affected can achieve a symptom-free result after the healing process is complete. Depending on the injury, the choice of therapy and the age of the person affected, the Forecast will vary considerably.
Especially when important Soft tissue damaged became or it became a open fracture the forecast is changed unfavorably.
A Compliance with medical recommendations helps to improve the prognosis and to achieve an optimal healing process.
Metatarsal fracture in the child
Also at Children A metatarsal bone can break as a result of an accident or falling objects. The special thing about broken bones that occur in childhood is that, in contrast to adults, they are not yet fully developed childlike skeleton.
The fracture of a metatarsal bone in children is no more common than in adults. In children too, the bony structures of the foot are strong ligamentous apparatus supported and it becomes a strong force needed for the fracture of a metatarsal bone.
It is important that the bone is back in the as soon as possible Starting position is brought. Often this is without performing an operation possible. Special wires that are inserted from the outside stabilize the bone fragments.
In individual cases a open surgery can be performed using the fragments can be connected by a plate. The plaster of paris, which one Immobilization of the foot should only be created as long as necessary so that the Muscle breakdown during this phase is reduced to a minimum.
Generally, bones heal in children significantly better than is the case with adults, which is why the forecast after a child's midfoot fracture very good is.















.jpg)