Biceps tendon
introduction

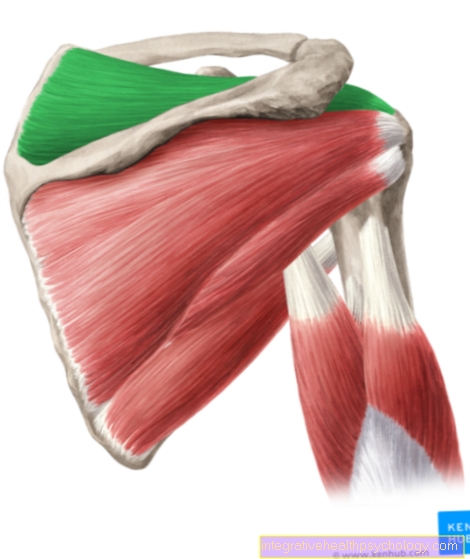
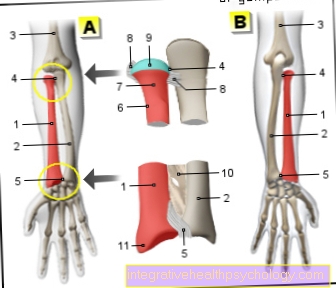
In its entirety, the biceps muscle, as the name suggests, has two sinewy origins. A distinction must be made here between the short and long biceps tendons or the caput breve and caput longum. The origin of the long tendon begins at the upper edge of the socket of the shoulder joint and the "cartilage lip" located there (Supraglenoid tubercle). The short tendon of the biceps brachii muscle arises from the coracoid process, a bony extension of the shoulder blade, which is also called the raven beak extension.
The long biceps tendon runs along the Humerus (Humerus) through a kind of bony canal, the so-called sulcus intertubercularis, and has its starting point at the bony roughening of the spoke (radius). This tendon runs not only over the entire head of the humerus, but also intracapsularly, i.e. it has a tendon sheath-like covering that promotes the sliding mechanism.
Torn / injury to the biceps tendon
Ruptures of the biceps tendon, i.e. a tear in the tendon, one differentiates based on their location.
In the proximal rupture, a tear in the tendon further towards the middle of the body, is usually the long biceps tendon affected. The reason for this is often one sudden and intense exertion of force at a Previous damage to the tendon.
This injury is the most common.
Another proximal injury is the so-called SLAP lesion. The SLAP lesion is a tear in the long biceps tendon directly at its anchorage on the acetabular roof.
A SLAP lesion is often very difficult to diagnose (even with an MRI of the shoulder) and often severe to treat.
In the distal rupture, i.e. a tear in the tendon further from the center of the body, is usually the cause severe trauma.
Acute ruptures of the biceps tendon, triggered by maximum stress or a fall, are often accompanied by symptoms such as Painfulness, Restriction of movement and Loss of strength (especially with bending and turning movements).
To a severe swelling above the crook of the elbow it usually occurs when the long biceps tendon ruptures. Distal ruptures have their muscle bulges on the proximal one upper armwhere it is clearly visible. Means Ultrasonic (Sonography) this is easy to represent.
A clear diagnosissPositioning is often difficult. It is important for the examining doctor to do a thorough one clinical examination perform. The implementation of the Supination tests with close observation of the biceps muscle serves as an important criterion for making a diagnosis.
The diagnosis is supported by the preparation of a MRI.
A subsequent imaging procedure using roentgen serves to exclude bony avulsions.
Inflammation of the biceps tendon (tendonitis)
The Inflammation of the long biceps tendon (Caput longum) represents an acute and painful inflammation. It mostly affects athletes e.g. in swimming, tennis or handball, where there is long-lasting strong or excessive strain on the tendon.
A trauma from e.g. an accident is rarely a possible cause.
Pain are often in the range of front shoulder localized, which continues until Elbow can radiate.
At Stretch and pressure the pain is usually particularly severe in the tendon area. Swelling in the shoulder area is less common.
Mineral deposits lead in this inflammatory process not only to pain, but also to further damage the tendon.
The physiotherapy treatment is the means of choice in terms of therapy. This should be combined with taking breaks from physical activity or exertion to worsen the inflammation or even injury.
Surgical intervention should serve as the last resort in therapy.
Please also read our topic on this Biceps tendonitis
Taping
The use of Kinesio taping for muscular problems.
The use of Kinesio Tape is also beneficial for the inflammation of the long biceps tendon. It can also be used prophylactically. It works tension-relieving and anti-inflammatory at the same time. It is also said to have a positive impact on the reflux Lymph fluid (Lymph drainage) in the upper arm.
It is recommended that the tape 7 days remains applied. The main effect occurs after about 3-5 days.
The tape as such is available in various degrees of strength and elasticity. If the tape is stretched actively, i.e. through one's own movement, or passively, i.e. through the course of the tape on the corresponding area of the body, a local one is created Stretching stimulus. This effect is of great importance as there is to increased blood flow in this area comes what definitely healing is.
To use it should be noted that one Y shape should stick. First becomes the victim poor stretched backwards as far as possible. Now the tape is stuck on a few centimeters below the elbow towards the roof of the shoulders (Acromion) or shoulder height.
However, the tape must not generate any tension. This could cause skin damage in the form of tension blisters, which are not only painful but also lead to inflammatory processes. Simple stretching can also lead to a reduction in pain. However, it does not have the scientifically proven success such as taping.