diabetes
Synonyms in a broader sense
Diabetes mellitus, diabetes
English: diabetes
introduction
The term Diabetes mellitus comes from Latin or Greek and means something like "honey flow". This name comes from the fact that those affected excrete a lot of sugar in their urine, which used to help doctors diagnose with a simple taste test.

Diabetes mellitus is just an umbrella term for various metabolic diseases. There are many different types of diabetes, all of which have in common that there is a lack of insulin in the body for some reason. Since this is the most important hormone in the regulation of blood sugar, the result is an increased blood sugar level, which in the long term can lead to a large number of secondary diseases.
The most common types are type 1 diabetes, which is also called youth diabetes and is based on an absolute insulin deficiency, type 2 diabetes, which is also known as adult diabetes and is based on a relative insulin deficiency or insulin resistance, and gestational diabetes.
Epidemiology of diabetes

According to estimates from the Year 2007 At that time, around 246 million people worldwide were suffering from the disease Diabetes mellitus, of which around 7 million lived in Germany. This means that around 8.9% of the German population are affected. In addition, however, there is probably a very high number of unreported cases, as it is assumed that almost half of diabetics among adults remain undetected.
It is estimated that 20% of those over 65 do with Diabetes mellitus are diagnosed.
According to projections, it is not unlikely that the number of people with diabetes will double again within the next 10 years. This is mainly due to the fact that only about every 20th person is affected Type 1 diabetes has and the remaining cases with very few exceptions from Type 2 diabetes be asked. Because this type is mainly due to risk factors of modern lifestyles, such as Obesity and physical inactivity, the number of diseases will increase rapidly.
causes
There are many causes of diabetes. Depending on the origin of the diabetes, the disease is divided into different types. Types 1 and 2 and gestational diabetes are the most common.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease and is based on an absolute insulin deficiency. This means that the hormone insulin, which is responsible for regulating the blood sugar level, is not produced at all or not produced in sufficient quantities by the body.
Type 2 diabetes is based on a relative lack of insulin. This means that the body still produces insulin, but can no longer meet its needs. This can either be because the need is increased for some reason or the target structures, in this case the membranes of the cells to which the insulin is supposed to “dock”, no longer show sufficient sensitivity to the hormone. This is known as insulin resistance. This type is most commonly found in overweight people and those with a genetic predisposition.
Read more on the topic: Abandonment of insulin
Pregnancy can also cause diabetes mellitus and affects up to 3% of all pregnant women. In contrast to the other types, however, this usually disappears completely after the pregnancy has ended.
Read more on the topic: Gestational diabetes
There are also many other reasons for diabetes: diseases of the pancreas, other hormonal disorders, medication, infections, genetic defects in B cells or insulin secretion or other syndromes that cause this disease.
Symptoms of diabetes
The characteristic symptoms of a Diabetes mellitus are frequent urination with a compensatory increased feeling of thirst, a headache, Inefficiency, fatigue, visual disturbances, increased susceptibility to infections and itching. However, all of these complaints usually only appear at a relatively late stage of the disease, especially during Type 2 diabeteswhich is why the time between the time and diagnosis of diabetes or treatment of the disease is often far too long.
In addition, there are type-specific symptoms such as severe weight loss in type 1 diabetes or large stature of the fetus Gestational diabetes.
Consequential and concomitant diseases:
The bad thing about diabetes mellitus is usually the diseases that develop secondarily on its basis. These include, among others high blood pressure, Heart attack, Vascular diseases (especially in the area of the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy and in the worst case it can lead to vision loss), neuropathy and renal insufficiency. However, these only occur if diabetes has remained undetected for a long time or is poorly controlled.
Read more about the here Consequences of diabetes.
diagnosis
There are several ways to diagnose diabetes mellitus that can be used with all types.
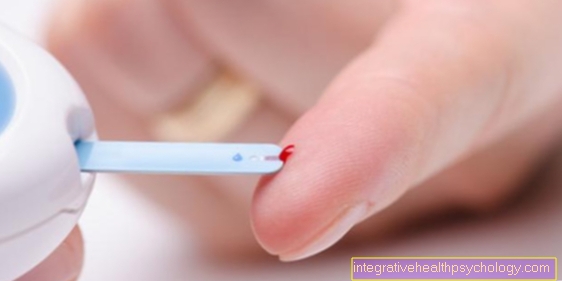
First of all, the blood sugar level should be measured, which should normally be below 110 mg / dl when fasting. If it is higher than 126 mg / dl, diabetes is present.
Various laboratory tests are also available. Above all, the measurement of the HbA1c. This is a value that affects hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood cells. Usually only a very small fraction of hemoglobin is associated with glucose. When there is an excess of sugar in the blood, as is the case with diabetes, this proportion is significantly increased above the normal 4-6% of hemoglobin. Since this value reflects the blood sugar level of the last few weeks, it is not only a good way to diagnose, but also to check whether a therapy for diabetes is successful. If it is in the normal range, consequential damage is unlikely.
In addition, there is the measurement of sugar or ketone bodies in the urine, which should be below a certain value in healthy people. In order to determine the body's own production of insulin, the so-called C-peptide can be measured in the blood. This is always released by the pancreas in the same amount as the insulin, which means that it is released.
Another way to detect diabetes early is to do the sugar stress test. Find out more at: Glucose Tolerance Test - What You Should Know!
therapy

Therapy for diabetes depends on the type of diabetes a patient suffers from.
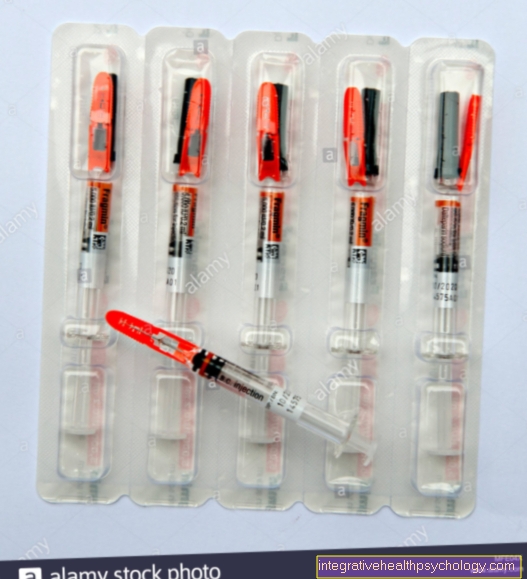
At the Type 1 diabetes The insulin deficiency must be for life with the help of an artificially supplied one insulin be balanced. There are various preparations that differ mainly in terms of their duration of effectiveness. The therapy of a Type 2 diabetes takes place according to a step-by-step plan and always begins without medication. At first you should try to get through the disease alone Lose weight and get a grip on activity. If this does not help (the HbA1cValue is used), step 2 follows. This means taking an oral antidiabetic.
These are in contrast to the injected ones Medication for diabetesthat are used in type 1, no insulin preparations, since there is no absolute insulin deficiency. Oral antidiabetic drugs ensure that the existing insulin can work better again by stimulating the body's own production or by sensitizing the cells to the absorption of insulin. Which antidiabetic drug is most likely to be indicated must be weighed individually and is based, among other things, on weight. The most common is the drug Metformin used. If this therapy is also unsuccessful, an additional antidiabetic is added in step 3. If this also fails, the administration of insulin is finally recommended in step 4.
Of the Gestational diabetes is usually treated with insulin and the therapy is particularly strictly controlled in order to avoid permanent damage to the embryo.
prophylaxis
Unfortunately there are no preventive measures that can be taken to prevent the emergence of one Type 1 diabetes mellitus could prevent. In contrast, the emergence of a Type 2 diabetes mellitus It is quite easy to prevent (assuming that there is no genetic component) by adopting a healthy lifestyle. Care should be taken to maintain a normal weight and exercise regularly.




















.jpg)