Inflammation after apicectomy
introduction
If the area of the tooth root tip is inflamed, the root tip often has to be amputated. This carried out surgical intervention is called apicectomy, in which the remaining part of the tooth can be preserved. After a certain healing phase, in most cases the inflammation has been overcome and the pain has disappeared. But what if afterwards pain and swelling reappear in the area and the inflammation comes back?
Read on under: Swelling after apicectomy

Since the root tip resection is a surgical procedure, like any operation it also harbors various risks. These risks include not only a re-developing inflammation, for example due to inflammation sources not completely removed, also the typical side effects of inflammation. These include redness, swelling, pain, and wound infections.
Sometimes pus forms, which is encapsulated in the tissue to protect the rest of the organism from the spreading inflammation. This process is usually very painful and is known as an abscess. In this case, an antibiotic must usually be taken.
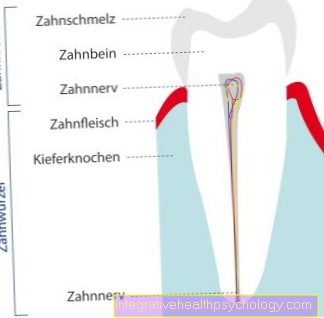
The procedure: root tip resection
After local anesthesia will that Gums cut open. The one above root lying bones is removed so that one has a clear view of the Root tip (apex) Has. Possible lateral ramifications of the root tip must also be recognizable.
The tip is severed and inflamed tissue is removed. A filling is attached to the previous entry point in the following step and, if this has not already been done in advance, a root filling is carried out. After everything has been rinsed and cleaned, the open area is closed and sewn again.
Read detailed information on: Procedure for a root tip resection
Symptoms
A renewed inflammation makes itself through one over the healing phase persistent pain noticeable. This can be limited to the location or radiate. A feeling of pressure is also possible. If bacteria cause the inflammation again, it can also lead to a Accumulation of pus come. Problems eating, as it puts pressure on the tooth and makes it contact with food, are also a sign of inflammation.
Pain after apicectomy

The direct occurrence of pain and postoperative swelling after a root tip resection are part of the normal healing process. The pain becomes worse the night after the procedure, it remains constant for the next 2-3 days, after which it becomes weaker. Ibuprofen can be used as a pain reliever. You should avoid using products that contain acetylsalecylic acid (aspirin), as these inhibit blood clotting and thus prevent bleeding.
Read more about the topic: apicectomy pain
Cooling the wound from the outside also helps relieve the pain. Ice should always be wrapped in a cloth and not held directly to the cheek. The mouth opening can be restricted and smoking should be avoided.
Read more on the topic: Apicectomy and smoking
After a week the sutures are pulled and the healing of the bone should be complete after a few months, which will be checked radiologically at a later time.
How long does inflammation last after a root tip resection?
After every operation, which naturally involves a wound, a healing process begins. This is accompanied by the typical signs of inflammation such as pain, redness, swelling and warming in the affected area. This process begins immediately after the operation. The wound has been sutured and now the tissue has to regenerate.
The inflammatory process usually intensifies immediately after the operation and increases over the first night. It is therefore typical that the Pain the first night after surgery felt to be very strong. The inflammation remains over Constant for two to three days. During this time, it is not uncommon for a bruise to form, which can then be seen through the skin. Then the inflammation forms over two to three days back away and with it the symptoms of pain, swelling, redness and warming.
The duration of the inflammation as Healing process after a root tip resection is about 1 week. During this time, the symptoms lead to functional restrictions, which should then decrease.
After approx. 7-10 days can finally the Pulled strings become.
When is it allowed to smoke again after an inflammation after the root tip resection?
24 hours after the operation of a root tip resection, under no circumstances should you smoke or consume coffee. In the following days the wound must begin to close and heal. This creates an inflammatory process with typical symptoms such as pain, redness, swelling and warming of the affected area in the mouth. This inflammation usually lasts about 1 week.
You should not smoke during this week either, as this would worsen the inflammation and delay the healing process. However, it is not strictly prohibited. After 7-10 days, the sutures are removed from the sutured wound. Then at the latest you can smoke again. However, it should not be forgotten that this naturally increases the risk of infection or inflammation.
You might also be interested in: Apicectomy and smoking
Recurrent inflammation after the apical resection
In a root tip resection, inflamed tissue is removed from around the root tip. It can often happen that not all of the inflamed tissue is removed and Foci of inflammation remain behind. In such cases, this may prevent the inflammation from submitting properly on its own.
Although the symptoms may go away and only come back later, the inflammation will persist. Most of the time, however, the pain or inflammation persists beyond the healing phase.
This can also be a sign of renewed or not completely removed inflammation. In addition, in the general case of a root resection refrained from smoking or coffee because this worsens the chances of recovery and that Increased risk of infection.
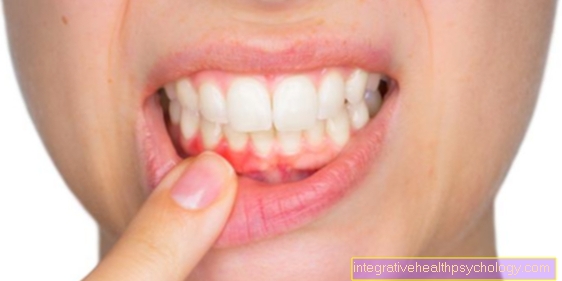
Inflammation of the gums after apicectomy
If the healed gums begin to bleed after an apicectomy when brushing your teeth or if they are very tender and painful, this can be a sign of gum inflammation. Depending on the duration and intensity of the inflammation, bad breath and pus may develop. As soon as the symptoms of gingivitis become noticeable, a dentist should be seen. This administers anti-inflammatory agents to contain the painful inflammation as quickly as possible. Read more about this at: Inflammation of the gums
Risks of apicectomy / possible causes of inflammation
Since this treatment is a surgical intervention a variety of risk factors can occur during or after treatment.
in the upper jaw, especially in the posterior region, there is a risk that the Maxillary sinus is opened and bacteria get into it. This is the case when the patient's tooth roots are particularly long, sometimes even reaching into the maxillary sinus.
In the event of inflammation and removal, the close proximity to the maxillary sinus is a problem.
If there is an opening, it should be covered with plastic to prevent the migration of bacteria from the oral cavity.
Should bacteria nevertheless have got into the maxillary sinus and triggered an inflammation there, the therapy is with Antibiotics after a Antibiogram the most effective method.
The appropriate antibiotic is either applied directly to the maxillary sinus or taken in the form of tablets.
in the Lower jaw there is a greater risk that important supply components, such as nerves or blood vessels, will be injured, because these are located in the vicinity of the tooth roots. Loss of sensitivity and taste can be the consequences.
Of course it can too Wound healing disorderscaused by external factors or illnesses. In people who e.g. under a weakened immune system Suffer, Diabetes mellitus or have poorer circulation in general, this is more common. But even if you are not spared after the operation (avoid sneezing, as this creates high pressure), the Oral hygiene is neglected or nicotine got to the place.
If the neighboring teeth have a tight connection to the treated tooth, they too can be damaged during the procedure.
A root tip resection unfortunately does not always lead to the desired success, so that renewed inflammation can occur afterwards. Because it can happen that root tips stay behind and become inflamed. This is noticeable by the pain after removal of the root tips beyond the normal healing phase do not subside and persist.
Furthermore, re-inflammation can last for a long time (sometimes many years) go unnoticed and only emit inflammation symptoms at a later point in time.
Since only the root tips were removed and the remaining part of the root still with one filling (the previous filling is retained or a new one is carried out during the procedure), it can happen that bacteria that are still present from the filled ducts get into the surrounding bone tissue and there a Jaw osteitis trigger.
What are the alternatives to apicectomy?

What alternatives are there to avoid apicectomy and the associated risks and foci of inflammation?
In many cases this depends on the individual situation of the patient. In general, to avoid an apicectomy, there is the option of extracting the diseased tooth.
A root resection is done primarily to preserve the tooth for as long as possible, even if it is less stable due to the shortened root. It can be crowned or maybe still available as a bridge pillar. Extraction of the tooth would rule out many of the possibilities of inflammation, since the bacterial component causing the problem is completely removed and the healing process usually only results in wound healing disorders and no longer caused by inflammation caused by remaining or migrated bacteria. But even with such an operation there is a risk of complications after the operation.
If the inflammation recurs, additional interventions may be necessary, depending on what caused it. The apicectomy can be performed again, inflamed tissue removed or abscesses that have formed cut open. If problems still occur or if a new intervention does not seem sensible, the tooth can also be pulled.
Summary
The Apical resection has the great advantage that you can preserve the tooth for many years through this procedure, but also the disadvantage that it is a very delicate and fine procedure, in which bacterial residues can remain, which can trigger renewed inflammation.
Healing complications can also arise, as with any surgical procedure. However, if the root tip was removed properly and the healing process proceeds without complications, the tooth has been saved despite the previous severe impairment.