Swollen eyelids
introduction
Most people have had to deal with swollen eyelids at some point. Often the eyelid swelling is accompanied by dark circles under the eyes, which gives those affected an exhausted and overtired impression. Such a situation occurs particularly often after a night that is far too short.
But too much alcohol the night before, particularly salty or protein-rich foods or simply an unfavorable sleeping position can lead to swollen eyelids. In the vast majority of cases, the unpleasant but harmless swelling of the eyelids disappears within a short time.
Of course, swelling of the eyelids can also have serious reasons or be an expression of a disease. In such cases, the swelling does not usually go away on its own and should definitely be assessed by a doctor.

causes
At the beginning, those affected often ask why eyelids tend to swell at all? The reason is due to their structure and the anatomy of the skin around the eyelids. Because of its nature, the skin on the lid is particularly sensitive. On the lid, it is only about a third of the thickness of the rest of the facial skin.
It also lacks both the firming connective tissue and the subcutaneous layer, which are normally responsible for heat storage, nutrition and padding. But also in the skin of the eyelids, as in the rest of the body, are the small lymph vessels that transport the lymph through our body and thus ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and at the same time ensure a continuous removal of waste materials.
If it comes to a congestion of the lymph in the vessels, be it due to increased alcohol consumption the night before or simply an unfavorable position during sleep, the fluid quickly collects here and the vessels have to expand in order to accommodate this additional volume. This explains why even the smallest amount of fluid that collects under the eyes can lead to a highly visible swelling of the eyelids. The causes that can lead to this lymphatic congestion and subsequent swelling of the eyelids are diverse.
In addition to the already mentioned alcohol consumption or the position during sleep, allergies or other diseases of the eyes can make the eyelids temporarily thick.
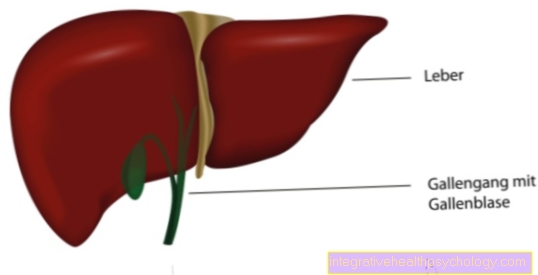
Other possible causes include stye or hailstones, tumors around the eyes, conjunctivitis, dry eyes, orbital phlegmon, and local or generalized allergic reactions. In addition, the eyelids can swell due to kidney failure, Quincke's edema, cardiac insufficiency or thyroid problems.
Simple crying, heredity and age, a blow or bump in the eye or the area around the eyes, and the woman's cycle can also cause temporary eyelid swelling.
Find out more about the topic here: Quincke's edema.
Crying as the cause of puffy eyelids
Also cry can cause the eyelids to swell and become thick. That can easily be explained by the crying and the doing vincreased tear fluid produced a increased pressure in the eyes and the area around the eyes.
The delicate and thin areas in the area of the lower eyelid and below are particularly sensitive to it and tend to swell. But all of this is completely normal and as soon as you stop crying, the swelling will subside within a few hours.
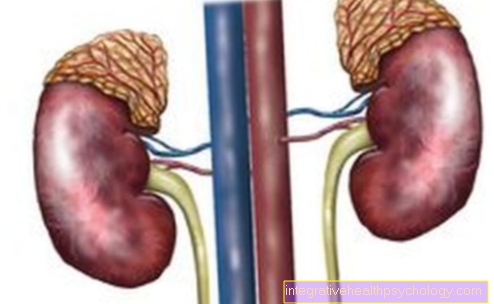
Kidney disease as a cause of swollen eyelids
Since the kidneys are the central organs that regulate the body's own fluid balance, diseases of the kidneys often affect the eyelids immediately, causing them to swell and become thick due to excessive fluid volume.
The kidneys are extremely complex organs with many different structures, so the diseases affecting the kidneys are diverse.
In the so-called nephrotic syndrome, in the course of an inflammatory process in the kidneys, glomerulonephritis, there is a pronounced loss of endogenous protein via the urine, as the damaged kidneys are no longer able to sufficiently filter the proteins and retain them in the body .
The filter function itself is taken over by the so-called kidney corpuscles, which can be impaired by poorly controlled diabetes, infections, other metabolic disorders or due to medication. If the body loses protein via the kidneys, the reaction to this is fluid deposits, which are first noticeable in the area of the eyelids due to the anatomical conditions described.
Thyroid disease as a cause of swollen eyelids
Also the thyroid is one of the organ systems that, if they do not function properly and fulfill their task, become one swelling of the eyelids being able to lead.
So, among other things, the case with one Hypothyroidism, the so-called Hypothyroidism. If the thyroid cannot produce enough hormones anymore, this manifests itself in a general Swelling of the connective tissue all over the body. As already described above, the connective tissue in the area of the eyelids and around the eyes is particularly thin and therefore vulnerable. Persistent swelling of the eyelids should be interpreted as a warning sign and should result in a thyroid function test.
In the case of an underactive thyroid, there are often more other symptoms. A swelling of the eyelids alone does not necessarily indicate an underactive thyroid gland.
Symptoms
The symptoms of swollen eyelids, like the causes, can be diverse.
The main symptom is, of course, swelling of the entire eyelids or parts of the eyelid. This can be seen with the naked eye or, in less pronounced cases, only palpable with the finger.
Of course, the duration of the swelling is not always the same. A distinction is made between acute and chronic events on the eyelid. The entire eyelids, including the area around the eyes, or just the upper or lower eyelid can be affected.
It can also happen, as in the case of a stye or hailstone, that the swelling can only be clearly defined on the nasal side of the eyelids or on the outer edge of the eyelid.
The swollen area can also be slightly reddened or those affected complain of unpleasant itching, a burning sensation or a feeling of tension.
The swelling can either feel soft or hard and like a small, rough lump in the skin of the eyelid. Depending on what caused the swelling of the eyelids, adjacent areas of the eye may also be affected.
It is also important to note whether the eye itself, next to the lid, is affected. The eyes may then be red or dry, for example.
Of course, there is also congenital swelling of the eyelids, such as can be found in blood sponges, the so-called capillary hemangiomas.
Badly developing moles can also rise above the skin level and cause unevenness and swelling on the eyelid. Incidentally, liver spots do not necessarily have to be brown, so that they are sometimes recognized as such relatively late.
You might also be interested in: Puffy eyes and red eyelids - what's behind them?
diagnosis
Since the causes of puffy eyelids are so diverse, deciding whether to see a doctor may not always be easy at first.
As a rough rule of thumb: as long as it is only a harmless swelling of the eyelids and you already know for yourself that it was a short night again, you drank a glass or two over your thirst or maybe cried, the eyelids are thick very likely to disappear completely after a short time, at the latest an hour after getting up.
If this is not the case, however, or you are too no explanations apparenthow it could cause the swelling of the eyelids is a Doctor visit advisable.
In any case, it is important that you leave the eyelid alone in the case of eyelid swelling with an unclear cause, so that no manipulation is carried out. Should it be an infection of the eyelids or other bacterial processes, they can Pathogen of the Eyelid in the eye get there yourself and cause inflammation.
If those affected wear contact lenses and the problem of swollen eyelids occurs frequently, it would be advisable to consult an ophthalmologist.
therapy
For the Treatment of swollen eyelids Unfortunately, due to the wide range of possible causes, no general procedure can be given.
The attending physician must first find out how and why the swelling of the eyelid occurred in order to be able to think about the further steps of the treatment. As everywhere in medicine, it is primarily the anamnesis discussion that is groundbreaking. This alone is often enough to identify the cause of the swelling.
In general they are Doctor different treatment options available, which are used depending on the cause. In certain cases, relief can be created by cooling, while others require anti-inflammatory eye drops or antibiotics. In other cases, surgical intervention may help. However, this can only be decided after a professional diagnosis.
Fortunately, in the vast majority of cases these are only the usual, puffy eyes early in the morning acts are definitely sufficient measures to alleviate or circumvent them. Sufficient fluid intake ensures that the flow of lymph fluid is stimulated and set in motion and the congestion in the eyelids disappears more quickly. Cool light, for example with a damp rag or a spoon left in the refrigerator overnight will also help relieve the swelling.
There are also special eye masksthat have the same function. The cosmetics industry also offers countless care products that are either designed to have a draining, decongestant, cooling or overall rejuvenating effect. Often, however, a commercially available moisturizing cream is sufficient, since the decongestant effect is primarily based on the cooling of the eyelids caused by evaporation. The same effect can also be achieved with Cucumber slices. To accelerate the drainage of excess lymph fluid, you can use the Massage with fingers using gentle circular movements and so try to gently remove the swelling.
Duration of swollen eyelids
How long the eyelids remain so uncomfortably swollen depends entirely on what is causing the swelling.
If, as in most of the cases, it is the usual thick eyelids early in the morning and takes action shortly after getting up, it usually does not take long before the circulation gets going and the excess lymphatic fluid flows out of the eyelids again, with gravity doing the rest.
The older you get, the weaker the connective tissue around the eyes becomes and not only tends to swell faster, but most of the time the swelling lasts longer. But at the latest after one hour the swelling is usually complete and gone without consequences. If the eyelids are also lightly massaged and cooled, the swelling often disappears after a few minutes.
Swollen eyelids in the morning
Swollen eyelids in the morning They are mostly caused by a night that is too short or bad and restless sleep.
Also a excessive alcohol consumption the night before it can lead to swelling of the eyelids. But not just alcohol, also a lot salty, protein-rich meal the evening before can have an adverse effect on the eyelids. As long as there is only occasional swelling of the eyelids in the morning, this is not a problem, since it is primarily a cosmetic impairment and less a serious medical problem.
But watch them more often or even regularly in the morning With visibly swollen eyelids on, you should possibly consider her Sleep behavior, their Alcohol consumption or the choice of food rethink for dinner.
In this way, a large positive effect can often be achieved even with small and simpler measures. However, are the eyes permanently swollen and if the swelling does not go away easily after a while, it should definitely have one See a doctor.
Swollen eyelids in children and babies
Basically, the eyes and are different Children's eyelids, Toddlers and babies not from those of the adults.
However, there are some peculiarities that ensure that certain clinical pictures occur more often in children than in adults. In addition, the body of the little ones is still relatively receptive and sensitive to the influences from the environment, which is why babies in particular can develop abnormalities in the area around the eyes more quickly.
In general, as a rule of thumb, one can say that one is at Eye discomfort in young children it is better to see a doctor once too often than once too little, as the situation can sometimes be difficult for parents to assess.
For example, a very common problem with infants is a blocked tear duct. The fact that the small tear ducts, which are responsible for the drainage of the tear fluid into the nose, are not always fully open in infants, is quite normal and disappears by itself within the first few months of life. Sometimes they are small corridors but so tight that it causes discomfort. The fluid can then not drain properly and collects in the eyes, where it then ensures that the eye is permanently wet and the eyelids stick together. Mostly this only occurs in one eye, rarely in both at the same time.
Also Environmental substances such as dust, little one foreign body, smoke and the like can irritate the little children's eyes. In addition, bacteria can cause the edge of the eyelid to become inflamed.
A child suffers Neurodermatitis, the already dry, flaky skin around the eyes is special prone to such inflammation. The eyes then begin to produce more fluid, which collects on the edges of the eyelids and forms crusts there, which further irritates the eyes and causes reddening. Show the crusts a slightly yellowish color, can be a Indication of bacterial infection be.
Also relatively common in infants and young children Conjunctivitis in front. The triggers can be viruses, bacteria or small foreign bodies or just strong wind. When the eye becomes infected, the small blood vessels widen and fill up with blood, which the Conjunctiva red makes appear. The Eye swells and itches and burns unpleasant. Here, too, the eye produces more secretions and the color can be an indication of the cause of the inflammation.
From Allergies Children are not spared, and from kindergarten age onwards, for example, the little ones have more eye problems caused by external allergens. The typical clinical picture is then expressed in redden, itchy eyesthat often too tear heavily and run the nose and itches too. It is important here that the parents try to ensure that the child does not rub too hard in the eyes, because this irritates the mucous membranes even more and increases the redness and itching.