Artificial knee joint
Introduction / definition
The knee joint is one of the most complex joints of the human body. It is made up of many different joint surfaces that are connected to one another. Additionally there are a number of Ribbons in and around the knee joint, which are intended to stabilize its movements. In addition, the two still exist Meniscithat as a kind Buffer discs lie in the knee joint.
An artificial knee joint, as the name suggests, is a replacement for the natural joint. An artificial knee joint is therefore not used immediately if the natural knee joint is slightly defective, but requires a precise one Consideration.

Generally a Wait and trying one conservative therapy in the context of a knee joint disease always the first choice. First, one tries the injured or damaged knee by means of drugs such as Anti-inflammatories and Painkillers or by means of physiotherapy therapy to stabilize. At the same time you want to go through training build up the thigh muscles and thus create a certain relief.
The most common indication for the use of an artificial knee joint is degenerative wear and tear of the knee joint, called the so-called Knee osteoarthritis is known. Osteoarthritis in the knee also has the name Gonarthrosis.
In osteoarthritis, the cartilaginous joint surface slowly wears out. The increased abrasion of the cartilage surface causes strong pain and at some point it can only be treated by replacing it with an artificial knee joint.
In general, there are different models of the artificial knee joint. Depending on how much is worn and defective in the knee joint, there is one Partial knee replacement as well as the Full knee replacement. It should be noted that it is also possible to replace only the worn parts. If, for example, the articular cartilage is only defective on the inner part of the joint surface, then only this part is replaced. The outer joint portion is retained.
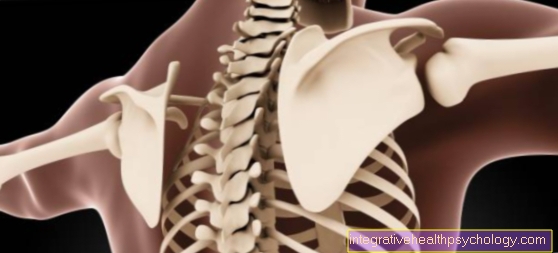
Illustration of a knee joint
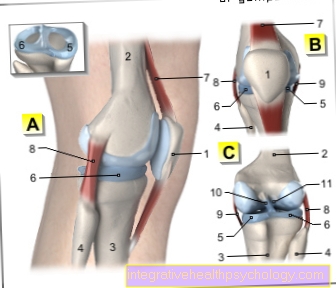
A - Right knee joint from the left
B - Right knee joint from the front
C - Right knee joint from behind
- Kneecap - patella
- Femur - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
- Fibula - Fibula
- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Kneecap ligament -
Ligamentum patellae - Outer band -
Ligament collaterale fibulare - Inner band -
Ligament collateral tibial - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Ligament cruciatum posterius - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Ligament cruciatum anterius
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work.On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Indication for an artificial knee joint
To make the decision to install an artificial knee joint easier, there are defined indicationswhen it makes sense to install an artificial knee joint. Basically, if you have a diseased knee joint, a conservative therapy by means of Pain medication and physiotherapy exercises to be started. However, if these therapy options have been exhausted and have not achieved any effect, then the doctor can indicate the installation of an artificial knee joint.
Read more about this under When should knee osteoarthritis be treated conservatively?
The most common symptoms of osteoarthritis are Pain when moving, but also Resting pain are possible at an advanced stage. This pain at rest is particularly common during the night.
Patients may also notice some Stiffness in the joint. Overall, the quality of life of the affected patients is significantly reduced.
The most common indication for an artificial knee joint is the so-called degenerative wear and tear of the joint. The bone surfaces of a joint are covered with a protective layer. This protective layer consists of Cartilage tissue. This layer is used to ensure that the joint can move smoothly and without pain. If there is increased abrasion of this cartilage layer in old age and ultimately the complete absence of it, bone comes into permanent contact with bone, so that this happens severe pain leads in the knee.
Osteoarthritis is no longer just a problem of age. More and more young people are also affected. Be it through one accident or one Sports injury. Also through Misalignment of the feet or legs, by overload, Previous operations or through chronic obesity knee arthrosis can develop.
Types (sled prosthesis / full prosthesis)
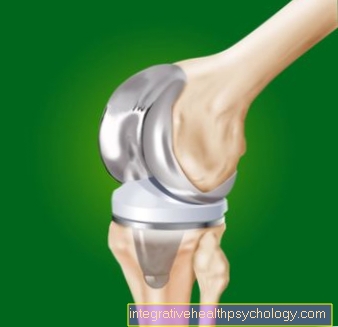
There are different types of artificial knee joints. Depending on the extent of the damage to the knee joint, different types of artificial knee joint are used. If only a certain side is worn out or destroyed, then only this has to be replaced by artificial material. So-called Partial dentures for use. These are also called so-called Sled prostheses because they look like the runner of a sled.
If the cartilage and bone tissue is defective not just in one place but in several, then another variant of the artificial knee joint is used. This variant is called the Full denture or Full denture designated.
There too Band structures are involved in the stability of the knee joint, they also play a role in the choice of the artificial knee joint. If the ligamentous apparatus is intact and therefore not damaged, you can uncoupled prostheses are used. In humans, too, the thigh and lower leg do not have a fixed and leading connection with one another.
If the ligamentous apparatus is already somewhat damaged, so-called partially coupled prostheses used to compensate for the loss of stability.
In some cases, the ligamentous apparatus is damaged to such an extent that it can no longer take over its stabilizing function of the knee joint. In these cases it will be fully coupled types of the artificial knee joint used.
To understand the different types of artificial knee joints in more detail, one has to look at the Structure of the knee joint keep in mind. The knee joint is through the Thigh, the Lower leg and the Kneecap educated. The part of the thigh that is involved in the knee joint is held by two casters, too Condyles called, formed. There is an inside and an outside role. As a counterpart, the lower leg forms a plateau for these roles. The two disc-shaped menisci serve as plain bearings and buffers. The back of the kneecap is only in contact with the thigh, not the lower leg.
The so-called sled prosthesis is usually only a role of the thigh replaced, so only one condyle. The type of prosthesis is then called unicondylar hemislide. If both roles are now replaced, the type of artificial knee joint is called bicondylar sledge prosthesis.
The unilateral sled prostheses are mostly unguided. This means that these prostheses are placed exactly on the spot that is defective. So they are only replacing a structure. For unguided types of sled prosthesis, the Tapes of the knee joint intact so that they can continue to guide the joint.
If the ligaments are not intact in addition to the joint, then the prosthesis must at least partially or even fully coupled be. So it doesn't just replace that defective surface structurebut it must be the same Function of the ligaments take over. Fully coupled prostheses are axially guided and come under a Full denture For use when both the thigh and the lower leg have to be supplied, as all structures are damaged.
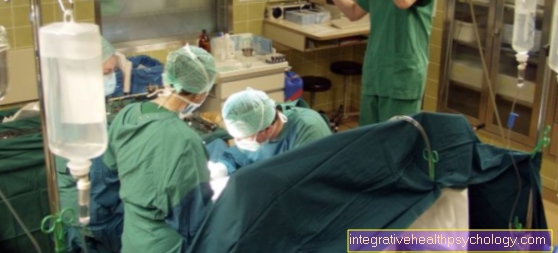
OP
The operation of an artificial knee joint can be performed in general anesthetic as well as in a so-called Spinal anesthesia respectively. With general anesthesia, the patient sleeps during the operation and is therefore not aware of the entire operation. However, under general anesthesia, the patient no longer breathes on their own, so they have a mechanical ventilation of the patient for the duration of the operation.
In contrast, the patient is awake during spinal anesthesia. So he gets to know the entire course of the operation. The anesthetic drug is used in the Spinal canal injected, which is called the spinal canal. Depending on the height at which the spine is punctured, the parts of the body that are completely anesthetized also differ.
In addition to this, you can do one more during an operation on an artificial knee joint Pain catheter which is placed in the immediate vicinity of the nerves that are responsible for the legs. This is often used for Pain therapy after the operation.
The actual operation of the artificial knee joint takes approx. 1-2 hours. The operation of the knee joint is started with a skin incision running in the middle of the knee. The OP often takes place in so-called Bloodlessness instead of. This serves to prevent the tissue from bleeding too much during the operation. For this purpose, a cuff is placed around the thigh, which is then inflated at the beginning of the operation to reduce the blood flow. After opening the knee joint, the soft tissues and the kneecap are usually held away from the outside with various tools and levers.
The damaged cartilage and the damaged structures are now worn away. The procedure differs slightly depending on the type of prosthesis to be used. Once the knee joint has been opened, the damaged structures away. This means that damaged Tapes or also the Menisci removed. Also be bony attachments, also Osteophytes called, removed from the joint surfaces, as they can later restrict the natural mobility of the knee joint.
Now so-called Saw templates attached to the bones. They are placed where the cutting surface should later be. These saw templates can be used to create optimal surfaces for the subsequent artificial knee joint. After sawing off the defective joint surfaces, holes are made for the Anchoring the prosthesis drilled.
If the rough preparation is now done, that is done To adjust the prosthesis by means of a so-called Trial prosthesis. This is used to make the optimal size and one correct fit of the final prosthesis.
in the last step the definitive knee prosthesis with the help of so-called Bone cement built into the knee. There is also the option of cementless prosthesis. For this there must be enough good the body's own bone material be in place to anchor them. In some cases it is necessary to replace the articular surface of the kneecap as well.
If the artificial knee joint is now installed, the operation is drawing to a close. The Joint capsule comes with a seam locked. This is followed by sutures through the lower layers of tissue to bring the skin layers closer together and so relieve the tension from the skin suture. Finally, during the operation of the artificial knee joint, the closing one takes place Skin seam.
Complications
Some complications belong to the so-called general operational risks and can occur as part of any operation and of course also when using an artificial knee joint. These include, among other things Violation of the existing structuressuch as muscles, ligaments, tendons but also nerves. But this also includes Infections or emerging Thrombosis by immobilization (e.g. through bed rest after the operation). If there is an injury to nerves, it can Sensory disturbances and in the worst case, too Muscle weakness or Paralysis come.
Another complication that can occur during the operation of an artificial knee joint is a Wound healing disorder after the operation. In most cases, however, this can be avoided through careful disinfection, sterile work and good postoperative miracle care.
One of the more specific complications that can occur when the artificial knee joint is inserted is the so-called Prosthetic infection. This is a bacterial infection of the artificial knee joint, which in the worst case leads to a Blood poisoningwhat is known as sepsis.
Another risk is that postoperative loosening of the artificial knee joint. Such a relaxation can be achieved by means of a X-ray image determine early.
When installing an artificial knee joint, the Arthrofibrosis in the knee a dreaded complication. It is the medical term for an increased education of connective tissue structures within the knee joint. This happens in the further course after the operation increased adhesions and Adhesionsthat hinder the healing process and the patient Pain prepare. At the same time they lead to a significant Restriction of movement. How exactly this strong increase in connective tissue occurs is not yet fully understood.
durability
Since many younger patients now also need an artificial knee joint and it is no longer just an operation for the elderly, the durability of the prosthesis plays an important role. The general shelf life varies greatly from patient to patient. It comes through the different Initial requirements conditions. How fit and agile for example, if the patient is before the operation, how good is his or her Leg muscles trained, he may have one decreased bone density or but Obesity. All of these factors play a role in the durability of the artificial knee joint.
As a rule, an artificial knee joint holds average 15 to 20 years. This long shelf life naturally depends on which one charges the prosthesis is exposed. Certain sports like To ski or Doing more jumps damage the artificial knee joint and significantly reduce its durability.
Sports with an artificial knee joint

Many patients want to know from the doctor treating them how they feel about exercising after an artificial knee joint has been fitted. In general it can be said that you can of course also do sports with an artificial knee joint. It is important that you should be careful in the first time after the operation and the times of the Partial load should strictly adhere to so that the prosthesis does not loosens.
There is also certain sportsthat are more suitable for patients with an artificial knee joint. These include, among others To go biking, swim or hike. On sports with constant Shock movements on the artificial knee joint or sports in which it is too Rotational movements in the knee joint should be avoided. These can become a Loosening of the prosthesis lead out of their anchoring. All kinds of sports are part of this sport Ball and contact sports such as Downhill skiing and tennis.
costs
In Germany, the costs of installing an artificial knee joint are in most cases borne by the person concerned Health insurance worn by the patient. The hospital usually settles the accounts directly with the relevant fund, without the patient having to pay a subtotal.
For Privately insured It is advisable to find out in advance how exactly the health insurance company handles the assumption of costs.
The purely artificial knee joint costs depending on the type of material and the size of the prosthesis 1500-2000 euros. A full prosthesis is of course more expensive than a sled prosthesis because it contains more material. Then there are the costs for the actual operation, the doctors, the hospital stay and the diagnostic tools. Thus, when using an artificial knee joint, the total is an average around 12,000 eurosif it's a uncomplicated case acts. However, if complications arise, the costs are higher.
Duration (operating theater, hospital, rehab, incapacity for work)
The patient who needs an artificial knee joint is often interested in the duration of the operation, the duration of rehab and the possible duration of his inability to work so that he can plan the process. The actual operation of the artificial knee joint usually takes about one to two hours. If complications arise during the operation, the operation can take a little longer.
After the operation, the patient stays in the hospital for about eight to ten days. During this time, a wound check and the first physiotherapy units for mobilization take place. Physiotherapy is usually started on the first or at the latest on the second day after the installation of an artificial knee joint.
After the actual hospital stay, rehabilitation is often followed or with a shorter interval. In most cases, rehabilitation for an artificial knee joint takes around three to four weeks. This is where further mobilization, stress exercises of the knee joint and preparation for everyday stress take place.
The duration of the incapacity for work varies widely. It largely depends on the patient's occupation. In most cases it lasts at least eight weeks. In the case of physically demanding activities, however, the duration of the incapacity for work can be extended.
Read more about this under
- Rehabilitation after a knee prosthesis
- artificial knee joint - life after













.jpg)