Peroneal tendons
Synonyms
Fibular tendons
definition
Tendons are the end sections of muscles that ensure that the respective muscle is attached to a specific point in the bone. The peroneal tendons belong to the muscles of the peroneal group and attach them to the foot.
anatomy
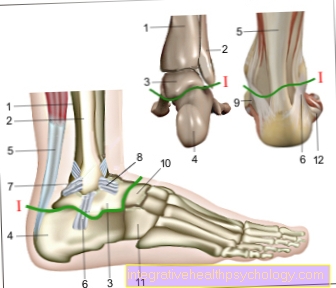
The muscles known as the peroneal group or the fibularis group are made up of the Peroneus muscle (or fibularis) longus and the Peroneus muscle (or fibularis) brevis, so a long (longus) and a short (brevis) Fibula muscle.
They are located on the outer lower leg, where they are in the area of the Fibula (Fibula), whereby the M. peroneus longus arises further proximally (i.e. further up on the fibula) than the M. peroneus brevis.
The long muscle pulls along the side of the lower leg and then tapers into its tendon, which forms a Tendon sheath behind the Outer ankle (Lateral malleolus) runs along to the foot.
Part of the tendon attaches to the sole of the foot, more precisely on the Os cuneiform (Sphenoid bone), while the other part is on the back of the foot, on the Base of the 1st metatarsal, starts. This means that the second part mentioned runs diagonally over the entire back of the foot to its starting point.
The tendon of the short peroneus muscle also runs in a tendon sheath behind the outer malleolus and has its attachment to the Base of the 5th metatarsal.
function
The tendons serve as Attachment points of the muscles.
The function of the two muscles consists primarily in one Plantar flexion (i.e. lowering) and the Pronation (i.e. the outward rotation) of the foot.
Innervation
The two muscles are derived from the nerve of the same name, namely the Peroneal nerve (or fibularius) superficialis , i.e. the superficial calf nerve, is innervated.
The deep calf nerve (Peroneal or deep fibular nerve), on the other hand, supplies the muscles of the front lower leg with motor.
In addition to innervating the two fibula muscles, the superficial fibular nerve is also responsible for the sensitive supply of the dorsum of the foot, albeit with a recess in a small area between the first and second toes, which is supplied by the deep peroneal nerve.
Clinical Aspects
A tear in one or both peroneal tendons is rare; it can occur as part of a twisting event.