Vaginal fungus
introduction
The colloquial term vaginal fungus (synonyms: Vaginal fungus, vaginal mycosis, vaginal thrush, thrush vaginitis or Thrush colpitis) is an infectious disease of the female vagina caused by a fungus from the genus Candida (mostly Candida albicans). It is estimated that around three quarters of all women get such a yeast infection at least once in their lives. This makes vaginal thrush one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases, but fortunately it is usually easy to treat and heals again without permanent damage.
For more information on this topic, read: Yeast in the vagina

causes
In most cases, vaginal thrush is caused by yeast Candida albicans triggered, more rarely by other fungi of the same genus. Candida albicans is found on the mucous membrane of the vagina in many women and is therefore part of the natural vaginal flora in some healthy people.
Please also read our article on this Mushrooms
However, under normal conditions these fungi cannot spread. This is because there is a very specific milieu in the vagina.The main characteristic of the natural vaginal flora is that it has an acidic pH value (normally between 4.0 and 4.5). This is mainly caused by the lactobacilli (lactic acid bacteria) and ensures that fungi and other pathogens find it difficult to settle in the vagina and multiply there.
Read about this: vaginal pH
If this flora is right and the woman's immune system is functioning properly, it is very unlikely that she will develop vaginal yeast infections. However, there are some factors that can weaken the immune system. This includes different underlying diseases, for example
- congenital immune defects,
- Cancer
- Diabetes mellitus
- AIDS
or taking broad-spectrum antibiotics and other drugs like cortisone. In addition to disorders of the immune system, changes in the healthy vaginal environment can also promote the development of a vaginal fungal infection. Such fluctuations in the pH value can result from hormonal changes such as
- Pregnancy,
- during menstruation,
- in menopause,
- in the puberty
- when taking birth control pills
- stress
- incorrect intimate hygiene (especially the excessive use of vaginal douches or intimate sprays unbalance the vaginal environment)
- certain contraceptive products (for example, sperm-killing creams, foam suppositories) or lubricants.
In addition, external influences such as
- Sexual intercourse (if the partner is infected),
- Incorrect behavior after defecation (you should always wipe backwards from the vagina to prevent germs from entering the vagina from the intestines)
- shared use of laundry or towels,
- Visiting public facilities such as swimming pools or saunas
- Clothing made from synthetic fabrics that are too tight-fitting, impermeable to air (particularly dangerous) can cause vaginal thrush.
Also read: Vaginal infections.
Vaginal thrush from an antibiotic
A fungal infection in the body often occurs when the immune system is weakened. It usually affects the mouth, esophagus and genital area as well as the vagina. A weakening of the immune system can be triggered by diseases such as diabetes, cancer or HIV. However, pregnancy or previous antibiotic therapy can also cause vaginal thrush.
The antibiotic destroys the lactic acid bacteria in the vaginal flora. These build up a protective layer in the mucous membrane and are responsible for maintaining the environment in the vagina. The antibiotic thus also destroys the protective layer and makes it easier for the fungi to multiply quickly in the warm and moist vaginal environment. The longer an antibiotic is taken, the more likely it is that vaginal thrush will develop. Usually the fungus can be treated well with a vaginal thrush and does not reappear after the antibiotic is stopped.
Vaginal thrush by the pill
One reason for the first or general onset of vaginal thrush may be the use of birth control pills. By taking pills, hormones are added to the body. The increase in hormones, especially with pills containing estrogen, causes a change in the vaginal environment similar to that of pregnancy. The fungi, which are typically found in the vaginal flora, multiply under a high level of estrogen.
The infection can easily be treated with an antifungal medicine. If, despite treatment, the fungus does not go away or if it recurs, the doctor should consider changing the pill or choosing a lower dose
What are signs of a yeast infection?
There are a number of signs and symptoms that could indicate and make a vaginal infection likely.
The most common and annoying symptom is severe itching. It itches especially in the area of the labia and or at the vaginal entrance. The fungus can affect both the external and internal female genitalia.
Read more on this topic at: Itching in the vagina
Other common signs include a burning sensation when urinating and pain during or after intercourse. The discharge is usually also changed. Typical is an increased, white-yellowish and crumbly discharge. Usually odorless though. In addition, the mucous membrane on the vagina can have white coatings. Not all signs and symptoms need to appear equally or simultaneously.
If there is no relief from the symptoms despite therapy, a doctor should be consulted for clarification.
Symptoms
The main symptom of vaginal thrush is often massive itching, which is sometimes restricted to the inside of the vagina, but mostly affects the entire primary external sexual organ (the pubic or vulva).
A burning sensation can also occur in this area. The infected skin is often red and / or swollen, which is an expression of an existing inflammation.
You can also read our article on the development and treatment of vaginal inflammation below: Vaginal inflammation
Another characteristic is a discharge from the vagina (fluorine vaginalis), which is usually crumbly, whitish and odorless. White deposits on the mucous membrane are also possible, which cannot be stripped off. Sometimes more serious skin defects (such as pustules or eczema) occur that can even spread to the thighs.
Because the affected areas are sore, some patients may experience additional pain when urinating or during sexual intercourse.
Read more about this at: Symptoms of vaginal thrush
Discharge as a symptom of vaginal thrush
A symptom of vaginal thrush (vaginal candidosis) can be changes in the discharge (fluorine vaginalis).
This can be more and differ in color and consistency from the normal. As a rule, however, the discharge from vaginal thrush is odorless. Most of the discharge is yellowish-white in color and has a crumbly consistency. Many patients then describe the discharge as "cottage cheese-like".
Smell of discharge
The smell of the discharge usually does not change with vaginal thrush (vaginal candidiasis). If a foul-smelling discharge is noticed, this should be examined by a gynecologist. Because this can be an indication of a bacterial infection that must definitely be treated with medication by a doctor.
Here you can find detailed information on the topic: Discharge from the vagina
Pain as a symptom of vaginal thrush
Another symptom of vaginal thrush (vaginal candidiasis) can be pain. Many patients describe a strong burning sensation in particular, and pain when urinating, similar to a urinary tract infection.
Painful intercourse is also common when infected with a fungus. In order not to infect the partner as well, sexual intercourse should be waited until the vaginal fungus has healed.
Vaginal fungus without itching
With vaginal thrush, there is almost always severe itching. Usually it itches before the vagina becomes reddened and swollen. However, vaginal thrush can also be detectable without causing bothersome symptoms. Then the fungus only colonizes the vaginal flora in small quantities.
What can you do against infection with vaginal thrush?
The yeast does not always cause symptoms such as itching, burning or pain. Because fungi and bacteria are part of the normal vaginal flora and are not dangerous. These can also occur naturally in the mouth and digestive tract.
Excessive intimate hygiene or a weakened immune system due to chronic illnesses or medication can lead to an imbalance in the vaginal flora. The fungi multiply due to the warm and humid environment and can cause discomfort.
People who suffer from a disease that weakens the immune system are more likely to get infected with a fungus. The use of certain medications can also lead to this. If the partner has a genital fungus, a condom should be used to prevent transmission.
In addition, towels and underwear should be changed regularly and washed with hot water, as the fungus can colonize there and causes repeated infection. It is also possible to get a fungal infection after staying in a swimming pool for too long. Because the chlorine attacks the vaginal flora and promotes fungal growth.
Can a man get infected with vaginal thrush?
Since vaginal thrush is not a sexually transmitted disease and originates from the body itself, it is rarely contagious and is rarely transmitted through sexual intercourse.
The fungus can multiply best in a moist and warm environment, such as in the vagina. Since the man's limb is rather dry and more in contact with air, the fungus has little opportunity to multiply and settle there. That is why there is very seldom an infection with a fungus, which is colloquially known as penis fungus. However, the fungal infection often goes unnoticed in men and has no symptoms.
Read more on this topic at:
- Penile fungus - candidiasis in men
- How contagious are yeasts?
How is vaginal thrush transmitted?
The fungal infection of the vagina is not a sexually transmitted disease and therefore strictly speaking cannot be transmitted. The fungus is caused by a disruption of the vaginal flora. By changing the environment, the fungus has the opportunity to multiply.
The cause of the changed vaginal environment can have various reasons. A weakened immune system due to diseases such as diabetes, infections or stress, but also some medications, in particular antibiotics, can be responsible. Another common reason is excessive intimate hygiene. Too frequent cleaning in addition with soap, shower gel or spray can irritate the vaginal environment and mess it up. Daily cleaning with normal, lukewarm water is better.
Furthermore, an incorrect wiping technique on the toilet can cause a smear infection and thus favor a fungus. To prevent re-infection, the underwear should be washed regularly at a high temperature in order to reliably kill the fungal spores.
Diagnostics of the vaginal fungus
In order to make a diagnosis of vaginal thrush, a detailed medical history (anamnesis) is first of all of great importance. The doctor asks the patient exactly
- their current complaints
- since when these exist
- how they express themselves
- what possibly caused
It also records any underlying ailments and other possible risk factors for vaginal thrush, including whether the woman is currently in a hormonal transition phase. This is followed by a physical exam.
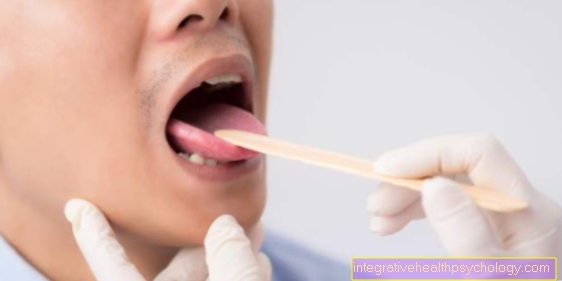
This examination reveals a fungal infection through the reddened, swollen vaginal mucous membrane and the crumbly, white coating. However, in order to find out which exact pathogen is responsible for the vaginal thrush in a particular case, it is necessary to take a smear from the mucous membrane. This means that the gynecologist (gynecologist) takes a little vaginal secretion with a cotton swab.
This smear is prepared and then placed under the microscope and examined there for the presence of fungal spores (recognizable by fungal threads or sprout cells). In addition, part of the sample is sent to the laboratory, where a fungal culture can be grown on certain nutrient media.
This is sometimes particularly important because bacterial infections of the vagina or the labia are often associated with symptoms very similar to those of a fungal infection, and it is not uncommon for mixed infections to occur. In bartholinitis, for example, glands in the labia minora become inflamed from a bacterial infection, which can lead to similar symptoms. However, since bacterial infections have to be treated differently, it is essential to differentiate between these pathogens!
Read more on the topic: The first visit to the gynecologist
How can I test whether I have vaginal thrush?
Vaginal fungus is particularly noticeable through severe itching. In addition, there may be pain when urinating or burning. In addition, severe reddening in the genital area can often be observed. In addition to a fungal infection with the species Candida albicans, bacteria or other pathogens can also be responsible for these symptoms.
To find out whether it is actually a vaginal thrush, there are self-tests (pH test strips) that can be used at home. The test is available from various manufacturers in pharmacies to buy without a prescription.
The self-tests measure the pH of the vagina. The vaginal environment is normally in the acidic pH range. This is necessary to maintain the bacterial balance in the vaginal flora. The test changes color in the event of a change in pH. Depending on the manufacturer, this means an infection with a fungus or bacteria. However, the diagnosis by a gynecologist is more reliable. This should be sought out if the treatment with a cream has not been successful.
Therapy for vaginal thrush
Antifungal drugs
The treatment of vaginal thrush is relatively simple in most cases and can often be done by the patient at home. Special anti-fungal agents, so-called antimycotics, are almost always used. Frequently used active ingredients are, for example, nystatin or imidazoles (among others Miconazole or Clotrimazole).
Such drugs are available in the form of creams or ointments or vaginal suppositories. They are available from pharmacies without a doctor's prescription. Nevertheless, it is important to always follow the instructions on the package insert exactly during therapy and to consult a doctor if anything is unclear. It is essential that the treatment always takes place locally.
The creams and ointments should be inserted into the vagina with the help of a special applicator and also applied to the labia and, as a precaution, on the anus in order to really reach all the fungal spores that are present. This process should be repeated about once or twice a day.
The vaginal tablets (suppositories) can be inserted into the vagina either with an applicator or with a finger. This variant is not advisable during your period (menstruation), as at this point the active ingredient can be flushed out of the body by the escaping blood without having its effect beforehand.
With proper treatment, the symptoms will improve after a few days. Depending on the active ingredient, the therapy must be carried out consistently for one to six days (depending on the dosage and type of preparation, see package insert!) And not be discontinued at the first signs of improvement, as otherwise individual fungal spores may survive and lead to renewed infection. Systemic treatment with oral medication is only indicated if there is no therapeutic success or if the infections keep recurring.
Further information on this topic can be found at: Treatment of vaginal thrush
Canesten®
For the treatment of vaginal thrush, there are preparations from Canesten® that can be bought over the counter at the pharmacy.
Canesten is a combination therapy. This contains a tablet and a cream. The tablet is inserted into the vagina and is supposed to work there for 72 hours to fight the fungus. It is recommended to use the tablet in the evening before going to bed. The cream is used on the external genital area. The cream should be applied 1-3 times a day for at least 1, preferably 2 weeks in order to treat the fungus successfully.
Both the tablet and the cream contain the active ingredient clotrimazole. This is usually well tolerated. The advantage of Canesten is only a single use of the tablet to treat vaginal thrush.
Vagisan®
There is a preparation from the Vagisan® brand for treating vaginal thrush. This can be purchased at the pharmacy without a prescription.
Vagisan® Myko Kombi is a 1-day therapy for vaginal thrush. It contains a suppository and a cream. The suppository is inserted into the vagina and fights the fungus there. It is recommended to use the suppository in the evening. The cream is used to treat the external genital area.To treat the itching and pain, the cream should be applied thinly 2 times a day for at least a week. Both the cream and the suppository contain the antifungal agent clotrimazole.
Antiseptics
So-called antiseptics are an alternative to antimycotics in the treatment of vaginal fungus. These contain the active ingredient povidone-iodine and are also available in various forms (creams, tablets, solutions and suppositories). They are particularly used when the infection is only mildly severe and / or is only just beginning. It should be noted that this course of treatment must not be chosen if a patient has a thyroid disorder, as the iodine administered can lead to serious complications in such a case.
Which creams help?
There are several treatment options available to treat vaginal thrush. Antifungal agents or also called antimycotics are used for therapy. Antifungals come in the form of suppositories, creams, and tablets. A combination of cream and suppository is usually recommended.
The cream is applied to the outer area and the suppository is inserted into the vagina. In order to successfully treat vaginal thrush, the cream must contain an active ingredient against yeast. These active ingredients include clotrimazole, miconazole and nystatin.
During pregnancy, a doctor should be consulted before using any cream. The antifungal agents can be purchased without a prescription in the pharmacy. The partner should also be treated in the case of recurring infections in order to avoid re-infection through sexual intercourse.
Home remedies for vaginal thrush
Home remedies such as the example Natural yoghurt or Buttermilk (to be applied to the vaginal lining), Döderlein preparations or lactic acid bacilli used to treat a Vaginal fungus to treat. Of the Use of these forms of therapy is however highly controversial and it is assumed that the desired effect can only be achieved in the short term, if at all.
Meanwhile the Co-treatment of a partner No longer generally recommended in the context of a fungal infection of the vagina. In individual cases, if the Infections recur very oftenHowever, one still tends to be the partner also with antifungal drugs to be treated to reduce the risk of cross-infection. It is just as important, especially if you have a vaginal yeast infection change underwear and towels / washcloths regularly and to wash so as not to be infected again with your own germs.
Also, of course, it's always important to have one present underlying disease appropriate therapy in order to get a vaginal thrush permanently under control.
You should definitely consult a doctor if you have a yeast infection Uncertainty of diagnosis exists if at the same time one pregnancy exists when a Symptom improvement even after three days of consistent therapy does not occur or if the fungal infections recur frequently.
Duration of a yeast infection
The duration of a yeast infection is depending on the start of treatment and the severity and extent the infection. If the vaginal thrush is treated early and sufficiently with so-called antimycotics, the infection should not last longer than a few weeks and heal without consequences. The Treating an uncomplicated yeast infection takes about two to six days. It usually takes place "locally", i.e. directly at the site of the infection with creams, ointments or suppositories.
If a vaginal thrush is not or only insufficiently treated, chronic infection can occurwhich then lasts longer. Treatment of a chronic or very strong vaginal yeast infection usually takes several weeks and should be carried out until completely healed. In most cases it is carried out "systemically", i.e. through tablets that work throughout the body.
prophylaxis
There are a variety of steps a woman can take to make vaginal thrush less likely to develop. It is particularly important to have a adequate but not excessive intimate hygiene to pay attention.
The use of Intimate sprays or vaginal douches should be avoided, instead, the vagina should just be with clear water or a lotion containing lactic acid. Other important hygienic measures to prevent a vaginal yeast infection are the correct cleaning after a bowel movement that Use of condoms when having sex with a new partner, using own clothes or towelstaking off wet swimwear.
In addition, one should make sure that light, "breathable “underwear, if possible made of cotton or silk and not made of synthetic materials, to wear, no airtight panty liners to use and in the last days of menstrual period either none at all or only small tampons to use.
In women who are prone to vaginal yeast infections, it may be advisable to: llong term drugs to use the lactic acid (or Döderlein) bacteria to thereby reduce the to support natural vaginal flora. Despite observing all these rules, however, it cannot be ruled out that you will get a vaginal fungal infection.
forecast
The prognosis for vaginal thrush is usually very good. At a consistent treatment the course is almost always uncomplicated and the Infection heals completely again out. It only occurs in about 5% of all affected patients re-infection in the course of their lives (Relapse).
Vaginal fungus in pregnancy
Another trigger for an infection with a fungus on the vagina can be hormone fluctuations in women. In particular, increased levels of estrogen can be responsible for this. This is typically the case during pregnancy. Because the estrogen promotes the growth of the yeast fungi. There is an increased formation of a sugar that is stored in the mucous membrane of the vagina. The sugar serves as a food source for the fungus and can therefore multiply more quickly.
As a rule, the fungal infection is not dangerous for the unborn baby. Rarely, it can lead to premature labor. However, it is important to have the fungus treated as soon as possible so that it is gone by the time you are born.
If the mother has a vaginal thrush shortly before or during the birth, it can be transmitted to the baby during the birth process. The infants suffer more often from a fungal infection in the mouth and diaper area. It can be life-threatening for premature babies and sick babies. Pregnant women should consult the treating gynecologist if they suspect a vaginal yeast infection and should not do therapy on their own. The doctor then decides on the type and duration of therapy. The use of antifungal agents is also suitable and safe for the baby during pregnancy.
Read more on the topic: Vaginal thrush in pregnancy















.jpg)