Pain between the shoulder blades
definition
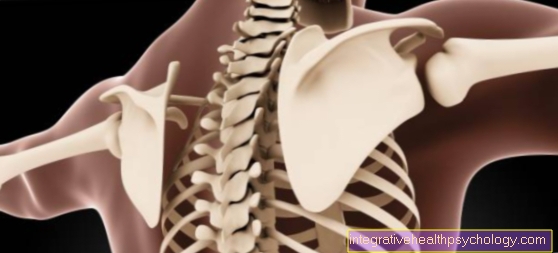
The pain between the shoulder blades can come in many forms. The area between the shoulder blades is in the upper back and surrounds parts of the thoracic spine. Nerves, muscles and ribs run under the shoulder blades and end at the vertebral bodies. Pain in this area can be attributed to the numerous anatomical structures in this area, whereby on the one hand superficial triggers are possible, but also the thoracic and upper abdominal organs must not be overlooked, which are protected by the rigid rib structure.

causes
The many causes of pain between the shoulder blades can be narrowed down by specifying the location and type of pain. Organic causes can also be behind the pain, but they are far less common than the more likely musculoskeletal complaints.
Very often the cause of the pain between the shoulder blades is to be found in the back muscles. The strong muscles of the upper back and neck can be strained by certain movements and strength exercises and lead to pain, similar to sore muscles. This pain can appear quickly after doing strength exercises with the upper back or after doing sports like road cycling. The neck muscles are also very susceptible to tension and pain. The neck is often not covered by clothing and can therefore become hypothermic and tense. In addition, the neck muscles bear a relatively heavy weight with great flexibility. Even during sleep due to a wrong position, the muscles can quickly become tense. This pain can pull along the muscles in the upper back, causing pain between the shoulder blades.
More rarely, the spine can be responsible for the pain. Spinal problems are often due to the intervertebral discs between the individual vertebral bodies. In the upper back, too, incorrect loading and heavy lifting can cause a herniated disc. The pain occurs in the middle between the vertebral bodies and can be provoked by movement. In some cases the pain can radiate to the arms or chest.
Read more about this under Symptoms of a herniated disc
In rare cases, the chest and upper abdominal organs can be behind the pain. An organic cause must be ruled out, especially in the case of very sudden and very severe pain, but also in the case of persistent pain that has no muscular cause. The lungs, heart and stomach can be particularly affected.
If the pain is very acute, there may be an indication of a heart attack. The pain can radiate into the left arm and it can also lead to shortness of breath.
Read more about this under Symptoms of a heart attack
Sharp pain that occurs more or less suddenly after eating or drinking may be related to the stomach. In the case of severe heartburn or a stomach ulcer, for example, eating can lead to severe pain, which in most cases occurs behind the breastbone but also between the shoulder blades. The lungs may also be causing the pain between the shoulder blades. Inflammation, injuries to the pleura or tumors can be responsible for this.
lung infection
Pneumonia often occurs in the context of carried forward flu-like infections. Typical symptoms are a feeling of illness, shortness of breath, cough, fever and pain. Pain can occur in the chest and spread to the lower abdomen and between the shoulder blades. In principle, all joints and muscles can cause pain when infected. Typically, pain between the shoulder blades and chest area increases when you inhale. If pain between the shoulder blades and other possible symptoms of pneumonia occur, pneumonia should be ruled out by the attending physician.
Read more on this topic at: Pneumonia pain
cold
In addition to the typical cold symptoms, runny nose, cough and sore throat, a cold can cause a pronounced feeling of illness and pain in all joints and muscles. A (common) cold is a possible cause of pain between the shoulder blades.
Can that be an indication of lung cancer?
In very rare cases, pain between the shoulder blades can originate in the lungs. Often only pneumonia is responsible for this. If the pleura is affected, these can develop painfully because the lungs themselves are not sensitive to pain. External injuries to the pleura, for example from needle sticks or a broken rib, can also lead to this pain.
Slowly progressive, dull pain, however, can also be one of the first symptoms of lung cancer. Since the lungs themselves are not sensitive to pain, the tumor has time to grow large and spread locally. Only when the tumor spreads to the edge of the lungs, the chest or other organs does the pain occur. Often the focus is on discomfort, pressure and pain in the chest. If the tumor is located in the back of the lungs, pressure pain between the shoulder blades can occur. These increase over time and are only slightly controllable through movement or breathing. If symptoms such as cough, tiredness or malaise are added, a doctor should be consulted.
Read more about this under How do you recognize lung cancer?
Can that come from the heart?
The heart can also provide an organic cause of pain between the shoulder blades. A typical constellation of symptoms in acute cardiac events is severe pain in the back and chest with a feeling of tightness and shortness of breath. It can be an acute heart attack. In this case, an emergency doctor should be called and the person concerned should take a seated position and support breathing by supporting their arms.
In the case of known heart diseases, the pain between the shoulder blades can appear as an occasional attack after a brief exercise. Depending on the degree of severity, just a few meters or steps of movement are enough to trigger pain. There is a narrowing of the coronary arteries, which restricts the oxygen supply to the heart.
Can this come from the stomach?
The stomach lies in the upper abdomen and reaches under the ribs. If pain occurs in the stomach, it can be projected onto the sternum, ribs or between the shoulder blades. The most common cause of this is heartburn. Oily food, caffeine, alcohol or nicotine can lead to excessive acid production in the stomach, which irritates the mucous membrane there. A burning sensation can occur in the chest and between the shoulder blades. If the irritation is severe, an ulcer may appear in the stomach, which also leads to severe pain associated with eating.
This painful irritation of the mucous membrane will heal itself within several weeks if no other acid acts on it. Therapy consists of reducing the acidity in the stomach.
Read more about this under
- Heartburn symptoms
- Causes of heartburn
Can this come from the pancreas?
Pancreatic cancer is a very feared and rare disease. This is not noticeable for a very long time and the first symptoms often only appear after a growth and spread. Pain between the shoulder blades is a very non-specific, potential symptom of the pancreas. Often there is constant, slight, diffuse pressure pain that does not get much worse or better. In this case, too, a cause in the pancreas is still very unlikely, as many changes in the spine also cause similar pain.
Read more about this under This is how you can recognize pancreatic cancer
Concomitant symptoms
The accompanying symptoms are very dependent on the cause of the pain between the shoulder blades. The accompanying symptoms can also provide further clues to a cause, for example an organ region, and facilitate the diagnosis. Muscular problems are often accompanied by aching or burning pain that is aggravated by movement. Symptoms of the thoracic spine can be acute or slowly insidious. Surrounding nerves may be affected, radiating the pain and causing tingling, numbness, or even paralysis.
Organic causes are rarely only noticeable with back pain. In the case of acute diseases of a particular organ, further specific symptoms occur. Heart problems can lead to chest pain, pain in the left arm, shortness of breath and fainting. Even with diseases in the lungs, worsening shortness of breath can occur.
Where does sharp pain come from?
Sharp pain suggests acute pain that has a direct trigger. Muscular complaints or spinal diseases are rarely acute, but incorrect movements can also trigger sharp pain. If there is a sharp stabbing pain between the shoulder blades for no apparent cause or movement, there may be an organic disease. A heart attack or stomach ulcer are typical causes of acute, sudden, sharp pain.
Pain between the shoulder blades when breathing
Breath-dependent pain can in turn represent several clinical pictures. Breathing causes the chest to rise and fall, causing movement in the rib, neck and upper back muscles. If the muscles are in severe pain, breathing can trigger sharp pain. The ribs or the bony spine can also be damaged if pain is caused by breathing.
Breath-dependent pain can also be localized in the lungs. There only the pleura is sensitive to pain, which rubs against the inner layer of the pleura with every breath. If there are inflammations or large tumors in the lungs, they can rub painfully against the pleura while breathing.
Blockage of the thoracic spine
In the thoracic spine, blockages in individual vertebral bodies can trigger the pain between the shoulder blades. This is particularly common in the upper thoracic spine or in the cervical spine. A wrong movement can block the joints between two vertebral bodies, which leads to acute stabbing, rapidly shooting pain. The vertebral body is restricted in its movement. The muscles become tense, which is why it can take some time to resolve the blockage. The blockage can be reversed through slight manipulation, i.e. manual intervention. Then the muscles must be loosened through exercise therapy.
Read more about this under Vertebral blockage
Pain between shoulder blades after eating
If the pain occurs immediately after eating, the cause may be in the stomach. Ingesting food stretches the stomach. If the stomach is already irritated, for example by an ulcer, any ingestion of food can be very painful with pain that radiates into the back. Easily digestible food must be consumed and fatty foods avoided until healing. In rare cases, there may also be a hole in the diaphragm through which the stomach can get into the chest cavity. One speaks of a "thoracic stomach". If the stomach expands from eating, it presses on surrounding organs and can cause pain.
When coughing and cold
Coughing is a reflex used to clear foreign objects from the airways. The diaphragm tenses abruptly and the entire auxiliary breathing muscles also contract. If the muscles are damaged, every cough can be very painful. Even with longer infections and colds, the cough can become painful. Due to the high levels of tension in the muscles when coughing, the muscles can hurt and burn like a sore muscles.
Pain between the shoulder blades with difficulty swallowing
Difficulty swallowing is an unpleasant condition. Those affected subjectively have the feeling that they cannot swallow properly. At the same time, swallowing is often uncomfortable and sometimes painful. If there is also difficulty swallowing and pain between the shoulder blades, the person should be examined for infection. A simple cold and pneumonia are possible causes for the parallel occurrence of both complaints.
diagnosis
The diagnosis must always be started with a targeted questioning of the time, place and type of pain. Accompanying symptoms and potential triggers can also provide important clues. Further examinations can then be carried out. In the case of muscular complaints, the cause can often be determined through a physical examination. Numerous means are available for diagnosing the organs of the chest and upper abdomen. For example, in the case of recurring pain emanating from the heart, a so-called catheter examination can reveal possible constrictions in the coronary arteries.
What to do if there is pain between the shoulder blades
The therapy varies greatly with the identified cause.
Muscular complaints often do not require therapy. Only light massages and heat therapies can accelerate healing. Spinal diseases are also difficult to treat. In the case of chronic complaints, muscle building and exercises to support the spine are particularly important. Symptomatic pain therapy is also carried out in most cases for a herniated disc in the spine. Surgery may only be necessary in some cases.
The treatment of diseases of the lungs, heart, stomach or pancreas must be very specific to the clinical picture. A heart attack must be treated in a clinic according to certain criteria. This includes drug but also interventional therapies. Tumor diseases, which are only in rare cases behind the pain, may be treated surgically and with medication.
Taping against the pain
There are two basic methods to be distinguished when taping. There is a conventional tape that is stuck tightly to the skin, restricts movement and supports joint functions. Nowadays, however, one often speaks of the so-calledKinesio tape". This is an elastic tape that is also stuck tightly to the skin. It does not restrict the movement, but is supposed to cause movements to be carried out more consciously through the slight external pulling effect. This should lead to less jerky movements, so that strains and tension occur less often. In addition, the tape promotes blood circulation under the skin and has a warming effect. The tape can be used in sports for prevention or in the case of muscular injuries to support therapy.
Read more about this under
- Kinesio tape
- Tape bandage
Duration of pain between the shoulder blades
The duration of the pain between the shoulder blades depends on the cause and the success of the therapy. Muscular complaints can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on their severity. Strong strains and torn muscle fibers above all require a long healing time. In the case of problems with the thoracic spine, care must be taken that the back pain does not become chronic. If the pain is not treated adequately in a timely manner, it can persist for a long time. If the pain lasts 6 months, it is already referred to as chronic pain. The duration of organic diseases cannot be predicted. Heart disease, for example, can worsen over the years. Drug and surgical therapies can often stop the progression of the disease but cannot cure the disease.
You might also be interested in this article: Pain under the shoulder blade