spoke
Synonyms
Radial head, styloid process, radius fracture, wrist, elbow
Medical: radius
English: radius
anatomy
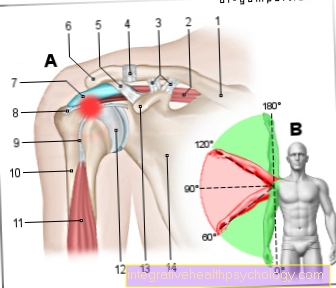
The spoke is also referred to medically as the radius. The spoke forms with the ulna, the bones of the forearm.
Together with the carpal bones of the moonbone (os lunatum) and scaphoid bone (os naviculare / scaphoideum), the spoke forms the essential part of the wrist. Towards the elbow the spoke becomes smaller and ends with the radius head. There the radius forms the smaller part of the elbow joint (cubital joint). With the radius head (caput radii), forearm turning movements are possible. The biceps tendon (Musculus biceps brachii) attaches directly above the radial head.
Illustration of the spoke

- Spoke shaft -
Corpus radii - Ellschaft -
Corpus ulnae - Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri - Upper spoke ellipse
Joint -
Radioulnar articulation
proximalis - Lower spoke-ellbow
Joint -
Articulatio radioulnaris distalis - Roughness of the spoke -
Radial tuberosity - Spoke neck - Collum radii
- Ring band of the spoke -
Annular radii ligament - Spoke head - Caput radii
- Interbone membrane -
Membrana interossea antebrachii - Stylus process of the spoke -
Radial styloid process
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
function
The radius (spoke) has two main functions:
- makes up most of the wrist
- forms the smaller part of the elbow joint

X-ray wrist
- Ulna
- Moon bone (os lunatum)
- Spoke (radius)
- Scaphoid bone (os naviculare / scaphoideum)

X-ray of the elbow joint
- Radius head (Capitulum radii)
- Olecranon from the elbow (Ulna)
Also read our topic X-ray
Diseases of the spoke
Broken spoke = med. distal radius fracture
Of the Broken spoke is the most common fracture in the human body. Typically there is a broken spoke when falling on the outstretched hand (extension fracture). The spoke breaks 2-3 cm above the wrist (distal radius fracture). More on this in our topic: distal radius fracture.
In addition to the distal radius fracture, there are also fractures of the spoke shaft. The radial shaft fracture in childhood is also a more common type of fracture. As a specialty in childhood, the often breaks bone, The still elastic periosteum (periosteum) remains intact. This is called a so-called Greenwood fracture.
Greenwood fracture
The arrows point to the barely visible break. Only the kink (axis deviation) of the spoke is noticeable.