What are the consequences of a herniated disc?
synonym
med: Disc prolapse
introduction
The herniated disc is now one of the most common diseases in orthopedics. Above all, increasing age and years of incorrect or overstressing of the spine lead to pronounced signs of wear and tear, which promote the development of a herniated disc.
Contrary to what most patients expect, a herniated disc does not necessarily lead to back pain. In general, it can even be assumed that persistent back pain is comparatively rarely caused by a herniated disc. Much more often the complaints can be based on muscular tension.
People with a herniated disc often notice sensory disturbances in the form of numbness or tingling due to nerve root irritation. In addition, an advanced herniated disc, which leads to significant compression of the nerve root, can lead to limitations in muscle strength.
An untreated herniated disc can therefore have significant consequences for the affected patient. For this reason, people who observe such complaints should consult a specialist as soon as possible. Long-term consequences, which are primarily due to nerve damage, can only be avoided through targeted diagnostics and the introduction of suitable treatment measures.

Consequential damage of a herniated disc
A herniated disc does not always have to be painful. Nevertheless, some of the affected patients describe sudden, sharp pain. The exact localization of this pain depends on the height of the affected spine segment.
As one of the direct consequences of a herniated disc, pain can radiate from the back to the arms, buttocks and / or legs.
Read more on this topic at: Symptoms of a herniated disc in the leg
If a herniated disc occurs in the area of the cervical spine (Cervical spine), particularly severe, stabbing pain in the neck area can be one of the consequences.
A deep herniated disc in the lower part of the lumbar spine, on the other hand, typically provokes pain in the back, buttocks and legs. In addition, impaired sensation can be one of the consequences of a herniated disc.
Affected patients often notice abnormal sensations such as numbness and / or tingling in an advanced herniated disc. The exact localization of these sensory disorders depends on the affected spinal column segment. Already during the diagnosis, such complaints can be assigned to a specific spinal segment on the basis of defined dermatomes (skin areas in which the abnormal sensations are perceived).
In the case of a herniated disc in the cervical spine, sensory disturbances in the dermatomes of the arms are one of the direct consequences. If the leaked intervertebral disc tissue presses on the nerves running in the spinal cord over a longer period of time, one of the consequences can also be limitations in muscle strength. Even with this typical symptom of a herniated disc, identification of the muscles in which this muscle weakness occurs can only be used to draw a conclusion about the affected spinal column segment.
While herniated discs in the cervical or lumbar spine are comparatively common, herniated discs in the thoracic spine (thoracic spine) are more of a rarity.
The main reason for this is the fact that the vertebral segments in the thoracic spine area can only move slightly with respect to one another. However, if a herniated disc of the thoracic spine does occur, blockages in the individual vertebral joints can often be observed. Because of this, belt-shaped pain that runs along the back and ribs is one of the direct consequences.
In addition, affected patients are usually very sensitive to passive pressure on the thoracic spine segments.
Patients who notice such symptoms should consult a specialist immediately. The reason for this is the fact that the direct consequences of a herniated disc may not be permanent if appropriate treatment is initiated immediately. Sustained compression of the nerve root, on the other hand, can cause severe damage and lead to permanent discomfort.
Furthermore, long-term compression of the nerve roots, especially in the lumbar spine, can cause further serious consequences. In this section of the spine, in addition to the sensory and motor nerve fibers, also those nerves that are involved in the regulation of the bowel and bladder function run.
If the protruding intervertebral disc tissue presses on these nerve fibers over a longer period of time, the affected person can develop intestinal and bladder emptying disorders (Stool and urinary incontinence) come.
In addition, the decreasing muscle strength can lead to significant gait uncertainty. This can have a strong influence on normal everyday life and have further consequences due to an increased tendency to fall.
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Consequences of a herniated disc of the lumbar spine (lumbar spine)
The herniated disc in the lumbar spine (lumbar spine) is the most common form of this disease, along with high disc prolapse of the cervical spine (cervical spine).
Due to the fact that back pain does not necessarily have to occur in the case of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine, the prolapse is often only discovered very late.
The consequences of a herniated disc in the area of the lumbar spine are shown primarily by impaired sensory perception. Affected patients usually report pronounced numbness and / or tingling of the buttocks and legs.
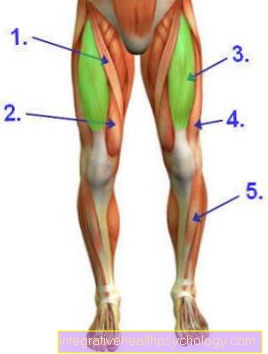
In the area of the lumbar spine, a herniated disc occurs particularly frequently between the 5th lumbar vertebra and the first sacral spine segment. In this form of lumbar disc prolapse, numbness in the dermatome of the L5 nerve root can be a direct result. The corresponding dermatome of the L5 nerve root extends over both sections of the thigh and areas of the lower leg. For this reason, a pronounced numbness and / or pain on the back of the thigh are typical consequences of a herniated disc between L5 and S1.
In addition, the outside of the knee, as well as the front and side lower legs, belong to the dermatome of this nerve root.
In addition to the limitations of sensitive perception, impaired muscle strength is one of the most common consequences of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine. Affected patients are often no longer able to stand on their toes or heels without any problems. The reason for this is the fact that individual muscles (so-called identification muscles) are no longer adequately supplied with nerve impulses due to the sustained pressure on the nerve roots.
A particularly pronounced herniated disc in the lumbar spine can also damage those nerve fibers that are involved in the regulation of bowel and bladder function. For this reason, bowel and bladder emptying disorders can be the consequences of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine.
Read more on the topic: Herniated disc of the lumbar spine
Consequences of a herniated disc of the cervical spine (cervical spine)
A herniated disc of the cervical spine (cervical spine) is comparatively common. The consequences of this form of intervertebral disc prolapse range from sensory disturbances to impaired muscle function. The sustained pressure on the nerve root of the affected spinal segment causes numbness and / or tingling in the upper and lower arms. In addition, the consequences of a herniated disc of the cervical spine can manifest in the form of neck pain that radiates into the arms.
Both the intensity and the nature (quality) of this pain depend primarily on the location and severity of the herniated disc in the cervical spine.
Although the development of back pain in a herniated disc of the thoracic or lumbar spine is not mandatory, pain in a herniated disc of the cervical spine is usually the first sign of irritation of the nerve roots.
Read more on the topic: Herniated disc of the cervical spine
Consequences of a slipped disc of the thoracic spine (thoracic spine)
Since the individual spinal segments of the thoracic spine (thoracic spine) can only be shifted slightly against each other, a herniated disc in the thoracic spine is a rarity. In most cases, the development of a herniated disc of the thoracic spine can be related to a previous traumatic event.
Affected patients usually feel significant pain in the thoracic spine area. This pain typically radiates in a belt shape down the ribs into the anterior chest. In addition to these pain phenomena, increased sensitivity to pressure is one of the most common consequences of a herniated disc of the thoracic spine.
Read more on the topic: Herniated disc of the thoracic spine
Consequences of an operation
The most common surgical technique used to remove a herniated disc is open surgery (microsurgical discectomy).
With this procedure, you have full insight into the area to be operated on, even in complicated and difficult cases.
This operation requires general anesthesia, which in turn involves risks. Especially in elderly patients, the anesthesia can lead to a "passage syndrome". Patients are briefly confused after the operation. However, this confusion usually disappears in the following days.
The risks of such an operation are sudden bleeding, injury to nerves in the spine, and infection from the open wound. Since a lot of business is destroyed in an open operation, the body needs a relatively long recovery time. Such an operation is associated with a hospital stay of several days.
Further consequences of such an operation are of course the elongated scar and, in this context, also greater wound pain.
In rare cases, bleeding may not occur until after the operation if one suture was insufficient. If nerves were damaged in the course of the operation, nerve failure may occur after the operation (depending on the location, for example, tingling and sensory disturbances in the arm or leg). In extremely rare cases, a nerve injury can lead to complete paralysis. Has the surgical wound been contaminated with germs or has the edges of the wound become infected after the operation (for example, if the wound is not covered with sterile plasters for long enough after the operation)? fever or, in severe cases, life-threatening blood poisoning (sepsis) can occur. This is why nowadays more and more attempts are made to remove the ban disc prolapse in a minimally invasive way. This can take place on an outpatient basis and even only under local anesthesia. The scars are smaller and the patient recovers much faster.
Sepsis is one of the possible consequences of an operation. You can find detailed information on this at: Blood poisoning
Psychological consequences of a herniated disc
Depending on how long the herniated disc and its symptoms persist, it can cause psychological stress. Especially if the herniated disc causes severe, long-lasting pain, it can mean a lot of suffering. In addition to the pain, muscle tension can significantly limit the ability to cope with everyday life. Personal hobbies, especially those relating to sport, can often no longer be exercised. The pain can also cause difficulty sleeping. Those who cannot sleep because of the pain feel weak all day, are in a bad mood and easily irritable. This also has an effect on the immediate environment, for example friends and family. Depending on how strong the social support and personal handling of the disease are, a herniated disc can have different effects on each patient.