Amitriptyline
substance
Amitriptyline belongs to the group of antidepressants. More precisely in the group of substances called tricyclic antidepressants. Together with the substances Imipramine, clomipramine, desipramine and Doxepin Amitriptyline is one of the best-known and most frequently prescribed drugs in this group of substances.

Mechanism of action
Every second there is a release of so-called messenger substances between the opposing nerve endings. The messenger substances include adrenaline, noradrenaline, serotonin, dopamine and a few others. The nerves communicate with each other through this release. Only in this way can stimuli be passed on and thought processes and control of mood and emotional sensations in the brain. Antidepressant drugs work on the delicate balance of the release of these neurotransmitters. The amount of neurotransmitters released can be influenced in different ways. After it is released, these are taken up again from the gap between the nerves, rendered ineffective and released again when a subsequent nerve action occurs. This neurotransmitter uptake can be blocked. This means that they stay between the nerves longer (synaptic gap) and can work there longer.
Read more on this topic: The role of serotonin / neurotransmitters in depression
In terms of the mechanism of action, acute effects must be distinguished from long-term effects. With short-term administration, tricyclic antidepressants lead to an inhibition of the mentioned reuptake mechanism for noradrenaline, serotonin and dopamine. Long-term administration of amitriptyline leads to a reduction in the number of receptors to which the neurotransmitters bind and act (beta receptors). At the same time, alpha receptors are regulated more highly and made more sensitive to neurotransmitters. This leads to a general increase in drive. Furthermore, with prolonged use of the drug, activities of the messenger substance gamma-amino-butyric acid are increased in the frontal lobe. It is assumed that i.a. in depression this activity is reduced and amitriptyline can therefore have a depression-relieving effect. Amitriptyline has a calming effect (sedating) from the first week, increasing drive (thymeretic) from the second week and mood-enhancing (thymoleptic) but the third week.
Side effects of amitriptyline
At Use of amitriptyline are the most common Side effects:
- Dry mouth
- Difficulty urinating
- Constipation, increased heart rate
and - Increase in intraocular pressure (glaucoma).
Furthermore, the seizure threshold is lowered. This can cause it to trigger a Seizure (epilepsy) come under amitriptyline.
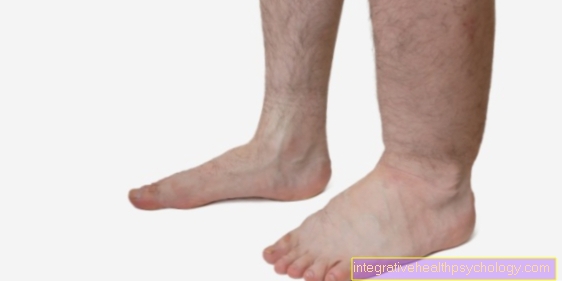
At the Heart it can Arrhythmia (Cardiac arrhythmias) and a Heart failure trigger.
Furthermore, it can be too Skin rashes, increased liver function tests, blood formation disorders, increased appetite and weight, increased hair growth and to sleep disorders and daily fatigue (Burnout syndrome)and Difficulty concentrating come.
You can find more about the side effects of amitriptyline at: Side effects of amitriptyline
Like many other psychotropic drugs, amitriptyline has several side effects, which, however, do not necessarily occur to the same extent in every patient.
While some patients experience almost no side effects even after long-term use of amitriptyline, other patients suffer from several simultaneous side effects of amitriptyline.
Weight gain
One occurs particularly frequently when taking amitriptyline Weight gain, which is caused by repeated hunger attacks and the resulting increased food consumption.
Overall, weight gain is a common side effect of amitriptyline, affecting one in ten patients. Some patients develop one due to weight gain and increased food intake Diabetes mellitus, so the so-called diabetes.
fatigue
Another common one Side effect of amitriptyline is fatigue.
This occurs primarily at the beginning of treatment and can also be used therapeutically if patients have problems falling asleep. In this case, amitriptyline can be taken before going to bed and thus help the patient to get better rest. Nevertheless, fatigue is an unwanted side effect of amitriptyline as it can quickly turn into a lack of drive, which is by no means desirable in depressed patients.
Neurological side effects
In general, so-called central nervous disorders (side effects affecting the brain) are common and occur in every tenth patient. In addition to fatigue as a side effect of Amitriptyline it can too a headache (Cephalgia), dizziness (Vertigo), Aggression and increased tremors (tremor) come.
Amitriptyline can also cause side effects on the eye. Above all, this can lead to a change in the pupils. By taking amitriptyline, they can no longer react adequately to stimuli from far or near, and so-called adjustment disorders of the eyes occur (Accommodation disorders).
In general, however, central side effects are to be feared, i.e. side effects that are controlled by the brain. These include movement disorders (Ataxia), the already mentioned tiredness and sleepiness, confusion, concentration disorders, increased anxiety, very euphoric moods (mania), Insomnia, nightmares, and rarely hallucinations.
A side effect of amitriptyline dreaded by many male patients is the loss of sexual desire and potency (Loss of libido up to loss of potency).
Side effects on the heart
Over 10% of all patients also experience side effects from amitriptyline that affect the heart.
Which includes Palpitations (Palpitations), one to fast heartbeat (Tachycardia) as well as problems with the circulation (orthostatic hypotension).
Furthermore, Amitriptilyn can cause a Heart failure increase or even worsen. Very rarely there is a so-called AV block, i.e. a conduction disorder in the heart, which the patient then perceives as a disturbance in the heart rhythm.
Because of the side effects of amitriptyline on the heart, a regular heart check-up using a EKGs obligatory.
Side effects on the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (Gastrointestinal tract) is influenced by amitriptyline and it occurs more frequently Constipation (Constipation), nausea (Nausea) and Dry mouth (Xerostomia).
This can become so uncomfortable for the patient that he can only consume food with liquid as there is no longer sufficient saliva in the mouth.
Side effects on the skin
Side effects on the skin due to amitriptyline are rather rare, but patients do increased sweatingwhich is found to be very uncomfortable for many patients.
Also Sensory disturbances (Paresthesia) are among the side effects of amitriptyline that can affect the skin. In general, when you start treatment with amitriptyline (about the first 2 weeks) the side effects predominate and the antidepressant effect only sets in after about 2 weeks. After these first two weeks, when the body has got used to the new drug, the side effects should decrease and the actual antidepressant effect of amitriptyline should be increased.
You can find more about the side effects of amitriptyline here.
Weight gain from amitriptyline
A weight gain under Amitriptyline therapy is one of the most common side effects of the psychotropic drug.
Over 10% of all patients gain weight while taking amitriptyline. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that amitriptyline can impair digestion and thus more frequent constipation (Constipations), on the other hand, many patients suffer from food cravings while taking the psychotropic drug.
As a result, amitriptyline can lead to weight gain. In some patients, on the other hand, they lose weight by taking amitriptyline, as they are increasingly under nausea and Vomit Suffer. Other patients, on the other hand, complain neither weight gain nor weight loss taking amitriptyline.
However, if a patient notices that he has gained significant weight due to amitriptyline, the attending physician (psychiatrist) an urgent decision must be made as to whether another psychotropic drug can be used as weight gain also leads to the development of a Diabetes mellitus (Diabetes) or to Heart problems (coronary heart disease) can come.
application areas
Main field of application of amitriptyline are depressive illnesses. However, it has to be said that this substance is rather than second choice used to treat depression. First choice drug are the so-called Serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Amitriptyline is the drug of choice for depression that is associated with arousal.
Amitriptyline for migraines
Amitriptyline can be used to treat migraines. However, this does not mean the acute migraine attack, but the preventive (prophylactic) use. This means that the drug has to be taken daily in order to achieve an effect and not only in an acute attack. In the best case, after a few weeks of use, this leads to the frequency of migraine attacks being significantly reduced.
Amitriptyline is only one of the second choice drugs in migraine prophylaxis. A dose of 50-150 mg is recommended, with the dose starting gradually and only increasing slowly. First choice migraine prophylaxis include drugs from the group of beta blockers (metoprolol, propranolol, bisoprolol - see also: Beta blockers against migraines) and the anti-epileptic drugs (topiramate and valproic acid) - see also: Drugs for epilepsy.
Metabolism
Amitriptyline is extensively absorbed. Due to its high metabolism in the first run, the liver a large part of the substance has already been inactivated, so that only a small part can get into the rest of the body and work. The drug is also completely metabolized in the liver. In the event of poisoning with amitriptyline, for this reason, dehydrating antidotes cannot help.
Interactions with other drugs
All drugs that are also a antidepressant, sedative or respiratory depression effect should only be combined with amitriptyline with caution. This includes the combination with Alcohol, antihistamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, hypnotics, narcotics, neuroleptics, opioids and muscle relaxants. So-called pharmacodynamic agonism occurs with these substances, i.e. these drugs act similarly to amitriptyline and increase the effect accordingly. The combination of these preparations should be avoided or the dose should be adjusted accordingly.
Anticholinergics, how Atropine and Antiparkinson Drugs such as Sympathomimetics (Sympathetic) add their anticholinergic and sympathomimetic effects of amitriptyline. So-called MAOIs, which are also used in the treatment of depression in individual cases, can have effects of the central nervous system increase (so-called excitation). This can reduce the seizure threshold and thus lead to seizures. Also can Impaired consciousness (Vigilance reduction) occur.
The combination of amitriptyline with drugs that are actually against you increased blood pressure (high blood pressure) are used can reduce the antihypertensive effect. These drugs include Clonidine, guanethidine and Methyldopa.
Medicines that are used against cardiac arrhythmias and combined with amitriptyline can increase the antiarrhythmic effect exhibit. The side effects described with the following drugs can also be increased: Amiodarone, Quinidine, and possibly others Class I antiarrhythmic drugs (Medicines for irregular heartbeat).
Amitriptyline and alcohol
The drug amitriptyline is a so-called one Psychotropic drugs.
This means that amitriptyline can influence the psyche of people, for example their emotional state. Most psychotropic drugs should not, or only to a very limited extent, be consumed with alcohol.
Before the combination of Amitriptyline and alcohol every pharmacist and doctor must warn the patient as this can lead to interactions. In general, alcohol often increases the side effects of amitriptyline even further.
For the patient, this means that the alcohol when taking amitriptyline increases the central sedation, so the patient becomes very tired and exhausted very quickly.
In addition, the actual antidepressant and mood-enhancing effects of amitriptyline may be weakened by alcohol.
Overall, alcohol promotes the side effects of amitriptyline and at the same time ensures that the actual effect is weakened. Nevertheless, many patients who have been taking amitriptyline for years have learned to cope with the drug and its side effects so well that they can consume a glass of champagne or wine every now and then without any severe side effects.
Dangerous interactions from the joint intake of amitriptyline and alcohol are usually not to be expected. Nevertheless, you should try to take the drug in the morning, for example, if you know that you want to drink a glass of alcohol in the evening.
Above all, it is important that large amounts of alcohol and amitriptyline are not compatible, as psychotropic drugs, like alcohol, are broken down by the liver and liver damage can occur if excessive alcohol consumption and simultaneous use of psychotropic drugs are taken.
However, infrequent, moderate consumption of alcohol is not a problem, especially since most patients take amitriptyline over a long period of time (usually about 0.5-1 year) take and thus be able to assess how you will react to the drug and its side effects. Still, it is important to be aware of the possible side effects of taking amitriptyline with alcohol consumption.
In addition to stronger sedation (increased tiredness, fatigue) the ability to drive may also be impaired. This means that even a glass of sparkling wine can lead to the patient no longer being able to drive a car because the amitriptyline makes the patient feel less safe ("drunker“) Feels like it would be without the antidepressant.
Accordingly, driving should be avoided at all costs in patients who take amitriptyline and have had something to drink. Furthermore, the combination of amitriptyline and alcohol means that the patient's gait security and the ability to speak are restricted more quickly.
Contraindications
Amitriptyline should not be given if the patient has symptoms of any acute heart attack show if any coronary heart disease exists when a Heart failure (Heart failure) can be diagnosed when patients are simultaneously receiving a Conduction disorder of the heart or if there is a bundle branch block.
Furthermore should Amitriptyline not be given if neurological diseases, such as. epilepsy because this drug lowers the seizure threshold, making a seizure more likely. Assign patients Delirium on, should Antidepressants also not be given, as the delirious state could be aggravated by it. At manic patient Amitriptyline is also not indicated. Particular caution is required in patients with a glaucoma because the active substance could further increase the pressure in the eye. At a benign enlargement of the prostate (Prostate hyperplasia) and one Narrowing of the gastric outlet (Pyloric stenosis) the drug should also not be given. A combination with the MAO inhibitor group of drugs should only be done under strict indications. In patients with Liver dysfunction the drug should also not be given. This also applies to patients one Renal failure to have.
During one pregnancy one should avoid amitriptyline if possible. The long-suspected teratogenic effects that can lead to malformations in the child have not yet been confirmed, but amitriptyline causes Adjustment disorders in the newborn. Therefore, pregnant women who take this drug should give birth in special clinics with affiliated neonatology.
dosage
To Treatment of depression should be amitriptyline 3 times a day in the dosage of 20-25 mg are given. A maximum outpatient dose from 150 mg / day should not be exceeded. in the stationary monitored area can reach the maximum daily dose 300 mg a day be raised. In addition to the administration in tablet form, the therapy can also be carried out by an infusion through the vein. Other dosages must be observed here. By infusion should 50 mg 1-3 times a day (dissolved in sodium chloride solution) respectively. It should be noted that the Given over 2-3 hours should take place. There is also the possibility of injecting amitriptyline with a syringe muscle to inject. Individual doses of 25 mg should not be exceeded. At Children and adolescents under 16 years of age, amitriptyline should only be given if strictly indicated. A dosage of 4-5 mg / kg a day not be exceeded. In patients with a Liver dysfunction or one Renal failure dose adjustment must be made.
Amitriptyline as a drop
There is exactly one pharmaceutical supplier who offers amitriptyline in drop form. The product is called Amitriptyline neuraxpharm or Amitriptyline neurax. As with the tablets, the indication for taking the drops is a depressive illness or pain therapy for neuropathic pain. Amitriptyline is also sometimes used for migraine therapy.
1 ml of the solution corresponds to about 20 drops and contains 40 mg of the active ingredient amitriptyline. The recommended dose should be determined by the attending psychiatrist. The manufacturer recommends 150 mg of amitriptyline as the maximum daily outpatient dose, while the maximum daily dose can be up to 300 mg for inpatient treatment.
The common to very common side effects of the drops include weight gain, aggressive and restless behavior, loss of libido or impotence, dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, speech disorders, tremor (trembling of the hands), difficulty focusing the eyes on an object that is close to the eye (Accomodation disorders), palpitations and arrhythmias, drop in blood pressure, a stuffy nose, dry mouth, constipation, nausea, vomiting, headache, increase in liver values in the blood, sweating, rash and problems with urination (micturition disorders).
Amitriptyline drops neuraxpharm require a prescription and are available in pharmacies. 30 ml of the drops (20 drops = 40 mg) cost just under 15 euros. If you submit a prescription, the costs are reduced to 5 euros per prescription.
Micro Labs
The addition Amitriptyline Micro Labs does not designate a special dosage form of the drug but is the name of the pharmaceutical company that produces numerous drugs, including amitriptyline. 50 film-coated tablets of Amitriptyline Micro Labs 10 mg cost a good 12 euros, if you have a private prescription only 5 euros per prescription.
particularities
With amitriptyline it should be noted that the mood-lifting effect only after drive-increasing effect occurs and so suicidal patients are more at risk after this medication. It should therefore be asked whether or not before administering the medication Suicidal ideation available.