Ligaments of the ankle
introduction
The ankle joint impresses with its high degree of mobility and immense stability and resilience at the same time. This only works because of the complex ligamentous apparatus, which supports the bone and muscle-tendon apparatus at the ankle with numerous ligaments. These ligaments are necessary because the body weight puts enormous pressure on the ankle.
They connect the tibia and fibula with each other, as well as these with the tarsal bones and the foot bones with each other.
anatomy

The ankle is actually made up of two joints: an upper and a lower ankle.
Some of the ligaments are limited to only one of the joints, while the other part works across the joints.
The upper ankle is secured by the outer ligaments, the delta ligament and the syndesmosis. The lower ankle joint has numerous, generally less common, small ligaments (ligamentum talocalcaneum interosseum and ligamentum talocalcaneum laterale). Better known, however, is the acetabular ligament, which is partly covered with cartilage (ligamentum talocalcaneonaviculare plantare).
Tasks of the ligaments
The Ligaments of the ankle ensure the Movement of the foot in all directions, with varying degrees of stability. Above all, they are responsible for limiting mobility, which is a too frequent "Twist“Prevented.
Besides that they also hold against the tendency of the Malleole fork (formed from the tibia and fibula) to move apart through the weight of the body. There are also ligaments that do not primarily provide stability, but rather the joint apparatus through a Enlargement of the joint surface or supplement encapsulation.

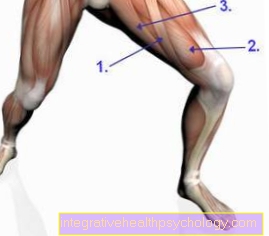
I - Lower ankle
(Joint line green) -
Articulatio talocalcaneonavicularis
- Shin - Tibia
- Fibula - Fibula
- Ankle bone - Talus
- Heel bone - Calcaneus
- Achilles tendon -
Tendo calcaneus - Fibula-calcaneus tape -
Calcaneofibular ligament - Hint. Shin-fibula
Tape-
Posterior tibiofibular ligament - Front Fibula ankle
Tape-
Lig fibulotalare anterius - Delta band - Deltoid ligament
- Scaphoid bone - Navicular bone
- Cuboid bone -Os cuboideum
- Fibula short muscle -
Musculus fibularis brevis
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
The outer bands
definition
At the Ankle joint is there three outer bands: Posterior talofibular ligament, Talofibular anterior ligament and Calcaneofibular ligament. All in all, they make up that Ligamentum collaterale laterale.
Of all the ligaments on the ankle, they are also the most susceptible to injury in the human body.
anatomy
All three outer bands arise from the outer anklewhich for Fibula heard. The posterior talofibular ligament and the anteral talofibular ligament each attach to the Ankle bone on, the one at the back, the other at the front.
The calcaneofibular ligament ends at Heel bone. Compared to the delta band on the inside, the outer bands do not run as a plate, but in individual strands and are therefore not that stable. Nevertheless, they are an important part of the entire ligament system at the ankle.
tasks
The Outer bands should avoid it for typical twisting motion of the foot (supination) comes inwards.
Due to their shape and their low strength, they only fulfill this task to a limited extent, especially when the foot is on tiptoe (Plantar flexion) and the bony stability is not ensured. In addition, the outer bands should have a Varus position (Joint misalignment in which the joint axis bends outwards). Still, they guarantee one safe flexion and Elongation of the foot.
Injuries
Does it come to Twist (Supination), depending on the strength of the movement and the nature of the ligament, it can either lead to Overextension an outer band or all outer bands or even to the Crack to lead. In any case, the ankle joint is no longer adequately secured when moving.
Therefore, after injury, the Ankle joint spared be and in Fixed pronation position so that the ligaments can grow together again. The load can be increased again later.
The delta band
definition

The Delta band ("Ligamentum deltoideum" or Ligamentum collaterale mediale) is, as the name suggests, a triangular band, which is on the Inside of the ankle is located. It consists of four shares: Pars tibiotalaris anterior, Pars tibiotalaris posterior, Pars tibionavicularis, Pars tibiocalcanea.
anatomy
All four tape parts arise together from that Inner anklewhich for Shin heard. From there, they harness themselves like one another subjects to their starting points, the tarsal bones. Two of the ligaments, pars tibiotalaris anterior and pars tibiotalaris posterior, pull towards the Ankle bone (Talus) and end once at its front part and once at the back part.
The pars tibionavicularis ends at Scaphoid (Os naviculare), whereas the pars tibiocalcanea am Heel bone (Calcaneus) attaches. Due to the closely connected course of the individual parts of the tape, a tight plate is formed from extremely stable collagen fibers.
tasks
That is on Inner ankle located Delta band primarily has the task to prevent the foot from bending outwards (Pronation).
also prevented it the Valgus position of the joint (joint malposition in which the joint axis bends inwards).
Due to its nature, the delta ligament makes a huge contribution to the stability of the entire ankle. This stability comes into play, among other things, when the foot is in the tiptoe position (plantar flexion), as the bone guidance of the ankle is then less stable.
Injuries
A injury of stable delta band comes very Rare in front. Most of the time it comes through Bending the foot outwards initially to one Overextension of the delta tape, as this is very tear-resistant. Nevertheless, the stability can be affected.
A Crack of the ligament or a portion of the ligament in such a movement is compared to the other ankle ligaments very rare and associated with great force applied to the injury.
If such an injury does occur, it should joint and thus the delta band first relieved become, splinted and then slowly increasing the load. If you don't succeed, you can surgical intervention, at which the tape is sewn, can be helped.
The syndesmosis tape
definition

Syndesmosis is one connective tissue band structurethat holds two bones together and creates a fake joint, i.e. without a joint space. Thereby the bones - in the case Shin and Fibula - not freely movable against each other, which contributes to a certain stability.
anatomy
In the human body, among other things, there is such a syndesmosis between the lower parts of the tibia and fibula, which "Syndesmosis tibiofibularis". Thanks to her, the inner and outer ankles form the so-called Ankle fork, also called the malleole fork, which the Ankle bone and thus form the upper ankle joint.
The syndesmosis consists of two strong bands, the front and the rear Syndesmosis tape. These bands become those of the upper ankle counted. However, both bands have their own particularities. The front band the syndesmosis has a somewhat oblique course and runs from the outer part of the shin to the front edge of the fibula. The posterior syndesmotic ligament runs more horizontally from the back of the fibula to the back and side of the shin.
tasks
Purpose of this Syndesmosis there is a certain amount in connection with the remaining ligaments of the ankle stability to guarantee. With every step, this ligament structure is heavily stressed both by the body weight and by the forces that occur during movement. Still, it is not as prone to injury compared to the other ligaments. The reason for this is one Connective tissue plate, which is stretched between the tibia and fibula and thus, in addition to the syndesmosis, is a high part of stability. Additionally limit the ligaments of the syndesmosis due to their tension, which arises when one pulls the foot towards the tip of the nose, these Degree of movement.
Injuries
Will it get through anyway? strong violence to the violation of the syndesmosis or the bony structure in the immediate vicinity, targeted treatment is necessary in order to restore the degree of movement and stability, which are of great importance.
Also, a violation of syndesmosis can cause one minimal divergence of the ankle joint that lead to one without immediate treatment increased joint wear brings with it.