Bone Bruise - How Dangerous Is It?
definition
Bone bruise is the English name for a bone contusion.
This is an injury to the bone that was caused by direct, blunt force and can be accompanied by severe stress-dependent pain.

causes
The cause of a bone contusion (Bone bruise) is generally a direct blunt force of force, such as can occur through falls, hitting hard objects and edges or sports injuries. This bruise is called a contusion, both in the case of bones and internal organs or superficial bruises.
As a result, in the case of bones, small to medium-sized blood and lymph vessels in the bone marrow, under the skin and especially between the bone tissue and periosteum, tear (Periosteum). This causes edema (Water accumulation in the spaces between cells) and bruises (Hematomas) covering the periosteum (Periosteum) painful stretching and irritation. This is one of the most sensitive tissues in the body and is responsible for pain in all direct injuries in the area of the bones.
Athletes in particular are often affected by bone bruise. Bone contusions also occur more frequently with increasing age, due to poorly developed muscles, which protect the skeleton in healthy people from injuries and ensure sufficient coordination to prevent falls.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Is a bone bruise a bone marrow edema?
A bone bruise can be accompanied by bone marrow edema. The bone marrow is found within most bones and is primarily used to produce blood. It is very well supplied with blood and therefore prone to bleeding. As a rule, it is well protected by the bone surrounding it on all sides.
If the bruise is more severe, however, small microcracks in the vessels can lead to an effusion. This build-up can damage the bones, poor blood flow and nourishment, and long-term complications such as bone loss and fatigue fractures.
The effusion can only be determined in an MRI scan. The therapy options for bone marrow edema are also limited. As a rule, all that helps is waiting. Unfortunately, complete resorption of the bone marrow edema can sometimes take several months. Until then, the affected part of the body must be relieved.
Symptoms
The first symptom of a bone bruise is one that occurs immediately after the injury severe painbut only for a short time usually a few minutes, continues. Later on, persistent, stabbing pains appear, which are mainly caused by burden and when exercising pressure on the affected area become stronger.
The very sensitive periosteum is primarily responsible for this pain (Periosteum) responsible, under the one Bruised bone frequently Bruising (Hematomas) arise, which stretch and irritate the periosteum.
Often also show up on the affected area as a result of the injury superficial bruising. The area can also be severely swollen.
Due to bleeding and edema in the Bone marrow Damage to bone tissue and thus development of a temporary one can occur over the next few weeks osteoporosis come. This favors fractures in the area Spine.
Read more about the topic here: Bone Bruise - what to do?
How dangerous is a bone bruise?
As a rule, a bone bruise heals by itself by protecting and cooling the affected area, does not cause any consequential damage and is not very dangerous. Complications such as bone marrow edema with long-term damage to the bone usually only occur in the case of very severe bruises.
Figure Bone Bruise

Bone bruise
Body parts particularly at risk:
- Skull - Cranium
- Shoulder joint - Articulatio humeri
- Elbow joint - Articulatio cubiti
- Wrist (upper, lower) -
Articulatio (radiocarpalis,
mediocarpalis) - hip joint - Articulatio coxae
- Kneecap - patella
- Shin - Tibia
- Ankle joint (ankle + USG)
= Cylinder joint -
Articulatio cylindrica - Metatarsal bones - Os metatarsi
- Periosteum - Periosteum
- Dense (compact) bone -
Substantia compacta - Marrow cavity with yellow bone marrow -
Cavitas medullaris + medulla ossium flava
a - Bruising (hematoma) - b - osteoporosis (bone loss)
Therapy / treatment:
P - pause
(Immobilization of the affected
Bone, possibly support bandage)
E - ice cream
(Cooling the injury)
C - compression
(Pressure and support bandages around
Prevent swelling)
H - Elevate
(for bleeding and swelling
to minimize)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Localizations
Body parts that are made without a protective soft tissue covering are particularly at risk Muscles or Adipose tissue directly under the skin lie. As a result, the pressure exerted by an injury is only distributed over a small area and the bones are directly affected. Above all, these regions are mostly that Shin (Tibia) and the knee, but also hip, Ankle joint, shoulder and the skull.
Bone bruise on the foot
A bone bruise in the area of the foot, especially the metatarsal bones, is mostly found in athletes in the field of martial arts, especially Taekwondo.
The symptoms are similar to bone bruises in other parts of the body; First and foremost, these are pain when exerted and swelling. As a result, after a fracture has been excluded, the injury should be cooled and immobilized.
Bone Bruise on the metatarsal bone
The metatarsal bones are a rare location for a bone bruise. Injuries to the metatarsus usually occur when heavy objects fall on the foot or after being kicked.
Martial arts such as Taekwando are a common cause of bone bruises in this area. The kicks can quickly lead to small bruises of the superficial bones on the back of the foot. Depending on the severity of the bone bruise, subsequent movements and occurrence can be painful. Cooling and rest should be maintained until the bruise heals by itself.
Bone Bruise on the heel
The heel and the ankle are bone regions that often suffer from bruises, especially during sports. A typical formation of a bone bruise at this point is a collision or a straddle in football.
The heel will then swell up and be very painful under pressure. With a high heel bone contusion, walking and walking are not very restricted. However, if the bruise is deep on the heel, every step will cause pain.
Unfortunately, in order to enable quick healing, only protecting the heel helps.
Bone bruise on the talus and ankle

The talus, i.e. the talus, is a bone of the tarsus and is located directly above the calcaneus. As such, it is an important part of the ankle. A bone bruise of the talus or other bones of the ankle occurs mainly during exercise.
Often he is the result of a foul e.g. described in soccer or basketball. This is usually accompanied by severe pain and a clearly visible bruise under the ankles.
Since the ankle joint is a heavily loaded and heavily used part of our body, an injury in this area is associated with considerable restrictions in everyday life. To treat the bruised bones, a splint can be put on for a few weeks. Later on, crutches should at least be used to relieve the ankle joint or talus.
Pain as a result of the bone bruise can last for a very long time, complaints of up to a year or more are not uncommon. After a few weeks to months, when the worst pain has subsided, you can definitely go back to sports as long as the pain does not worsen significantly.
Sports such as cycling or swimming are preferable to sports such as jogging or playing football. A wandering of the pain is also often observed and is related to a pain-related altered gait pattern and the associated unusual stress on the joints.
Bone bruise on the tibia head
Since the tibia (Shin) is only slightly covered by cushioning muscles and fat along its entire length, it is often affected by bone contusions. This is particularly the case in football as a result of fouls. If this happens in the area of the tibial head / tibial plateau, joint effusions can occur at the same time, which results in pain in the area of the kneecap (patella) express.
If it is severe, the clinical examinations show a "dancing patella“, A kneecap that floats on the effusion. At first, this can be seen mainly through the ultrasound examination.
The treatment of a bone bruise of the tibial head is the same as for other bone bruises. Since an injury in the area of the tibial head can also result in ligament ruptures, pain in the knee should always be clarified.
Read more on the subject below Bruised tibia.
Bone Bruise on the kneecap
A bone bruise on the kneecap is not uncommon. The kneecap has a prominent position in the body and is therefore affected by abrasions, fractures or bruises in many falls and impact injuries.
Here, too, it is important to first rule out whether structures have been injured before the entire knee should be cooled and spared. Small microtraumas on the kneecap and the soft tissues under the kneecap can lead to the typical bruises. This can lead to significant pain in the kneecap.
Because this is a bone marrow injury, blood enters between the bones and the periosteum of the kneecap. Since the kneecap can easily be seen as a superficial bone under the skin, the bruises can often be seen externally. It is also important to distinguish whether the kneecap itself or the head of the tibia is affected. This can also lead to slight microfractures, with similar bruising.
In addition, hematomas (bruises) can develop in the knee joint, which restrict movement and are very painful. If the effusion spreads into the joint cavities, the body may not be able to reabsorb the blood itself. In these cases, punctures may have to be initiated by a doctor in order to withdraw the blood from the joint with a needle. If the bruise spreads over the surface under the kneecap, the phenomenon of the "dancing patella" occurs. The kneecap swims and "dances" on the effusion. In these cases, the diagnosis can easily be made through an ultrasound scan.
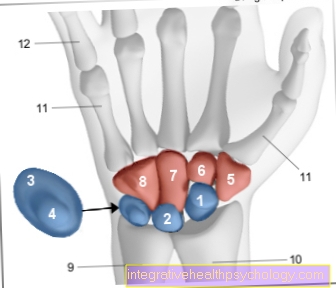
Bone bruise on the wrist

Bone contusions (bone bruises) of Wrist are mostly the result of falls in which the fall is caught by hand. Pain and significant swelling are usually the result. After a break has been ruled out, there is a Immobilization of the wrist, connected to its cooling, the most important measure. A support bandage is ideal for this.
Since the wrist is very often and heavily used, a bone contusion in this area is often associated severe restrictions in everyday life and a lengthy healing process. Pain often occurs many months after the injury itself.
Bone Bruise on the elbow
Due to its superficial location, the elbow also has an increased risk of bruises.
In particular, if the arm falls, rotates quickly or moves jerkily, the elbow can quickly suffer from bone contusion when the arm is bent. The bone marrow edema causes swelling to a greater or lesser extent. On the one hand, these can be very painful, but on the other hand they can also significantly restrict movement.
As an important joint in everyday life, mobility in the elbow should be restored as quickly as possible. In the healing process, however, it primarily helps to protect the joint so that the blood can be resorbed. The joint may need to be punctured if the effusion is too large to absorb by itself.
Bone Bruise on the shoulder
In the shoulder area, a so-called bone bruise usually only occurs when severe injuries have occurred in this area. In high-speed traumas such as In a car accident, the very strong forces exerted on the shoulder can cause bones to be crushed.
If the bones are crushed in the shoulder area, this is called a bone bruise phenomenon. A bone bruise is very uncomfortable and rarely occurs in isolation. Mostly there are still hematomas, other bruises, etc. somewhere in the shoulder area.
A bone bruise usually leads to severe pain that can last for weeks to months.
In the case of a bone bruise of the shoulder, by definition, no fracture of the bone must be detected in the imaging. A bone bruise is a bruise or contusion of the bone in the shoulder area.
Read more on the subject below Bruised shoulder.
diagnosis
To more serious injuries to the bone, that is especially fractionsTo rule out one should first of all X-ray image of the affected body part. A bone bruise selsbt is in this one, however not visible. The characteristic microfractures and tissue swelling of the bone are only possible by means of one MRI to recognize. Usually the clinical symptoms In addition to an X-ray image, however, sufficient for diagnosis.
In addition to the bruised bones themselves, very similar symptoms can also be caused by other diseases. Next Fractures of the bone are here mainly Tendinitis to call. Especially in the area of the shin, this can be noticeable in the form of sharp, stabbing pain. However, unlike a bone bruise, they are not associated with trauma.
Bone Bruise Signs on MRI
In the MRI, a bone bruise is characterized by signal amplification. You can see a lightening in the affected bone. The lightening is not created by a fracture, but rather by a increased water and blood retention in the area of the bone.
It is believed that the smallest micro-traumas that trigger a bone bruise lead to an influx of fluid. These are primarily water, but also around flammable liquidwhich flows in more strongly the stronger the trauma was in the shoulder area.
In diagnostics, there is often a risk that a hairline fringe in the shoulder area cannot be seenbecause it has been obscured by the lightening created by the water. The fluid breaks down bit by bit within a few weeks.
In some cases, however, it can also become a months of evidence of water come in the shoulder bone area. It is not known whether there are other causes than the microtraumas that lead to water retention in a bone bruise.
therapy
For the treatment of a bone bruise, the so-called "PECH rule“.
- Break - immobilization of the affected person Bone or. Joint, possibly with a support bandage and in the lower extremities with a splint and / or crutches if necessary; Sport should be avoided for the next few weeks or months
- ice - Cooling the injury
- Compression - in the form of a pressure and support bandage to prevent swelling and stop small bleeding
- Elevate - also to minimize bleeding and swelling
In addition, the ingestion of pain reliever and anti-inflammatory drugs to recommend. They are for example ibuprofen- and diclofenac Painkiller.
Paracetamol is less suitable here because it lacks the anti-inflammatory effect. Ointments and gels are mainly used for cooling the bruised bone.
Big ones form Bruisingthat are obviously poorly reabsorbed, i.e. persist for a long time, surgical opening of the hematoma can be considered to prevent infections.
Read a lot more information on this topic at: Treatment of a bone bruise.
How long does one have to take relief for the bone bruise to heal quickly?
The therapy of a bone bruise takes place for the most part in the first minutes after the injury. In addition to other immediate measures, the affected part of the body should be relieved in order to reduce a hematoma.
The immediate protection and cooling attempts to stop the flow of blood quickly so that no large amounts of blood can penetrate the soft tissue and the bony membranes. Externally, reddening can also be seen in the first few minutes after the injury. However, as soon as the blood coagulates and no more blood escapes, there is no longer any need for relief. This is usually the case after about half an hour. However, the duration also depends on the severity and the exact location of the injury. Bleeding in the abdomen or chest area may last longer. If the bleeding cannot be stopped, a doctor must be consulted urgently.
Does physiotherapy make sense with a bone bruise?
A bone bruise is usually not a major injury that involves restricted movement.
Physiotherapy is mainly used to maintain or restore normal body movements. The pain of a bone bruise is also only high in the first few minutes of the injury and then felt as tenderness at the site of the hemotome.
For this reason, physiotherapy is rarely necessary and can hardly accelerate the healing process.
Duration
Overall, a bone contusion is with one lengthy healing process connected. Stress pain often occurs around 6 weeks long on. Still, pain is also after a year or beyond that not uncommon.
Adequate and immediate treatment (see above) the healing process can be accelerated considerably. Above all, immobilization of the bone is very important. The exact duration of the healing process is however hardly predictable and individually very different.