Inflammation in the groin
introduction
An inflammation of the groin or the groin area can have various reasons and causes. There are a number of different tissues and structures in the groin that could become inflamed. Among other things, there are lymph nodes or hair follicles and hair follicles, just like inflammation of the skin in the groin can also occur.

Causes of an inguinal infection
The causes are completely different depending on the affected structure and the associated clinical picture.
- Fungal infection of the skin
- psoriasis
- Carbuncle or follicular inflammation
- Inguinal hernia
- Inflammation of the female genital organs
- Disease of the testicle
- Inflammation of the pubic bone
- Sports injuries from overuse
Inflammation or swelling of the lymph nodes in the area of the groin can be caused by injuries, infections and inflammations in the area of the drainage area of the corresponding lymph node. Most of the lymphatic fluid from the legs drains through the lymph nodes in the groin. If there is an infection, for example in the area of the foot, it is very likely that there will also be a subsequent swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin.
You might also be interested in these topics: Pain in the groin - these are the most common causes and swelling of the lymph nodes after surgery
Fungal infection
If you find inflammation of the skin in the groin in particular, it could be an infection with fungi or bacteria in this region. Inflammation of the groin can be caused by an infection with a inguinal fungus. The clinical picture is then called tinea inguinalis. The fungal infection often extends from the groin to the buttocks. In most cases it is the skin fungus Trichophyton rubrum. It is the same pathogen as in athlete's foot. Tinea inguinalis often also develops on the floor of a foot fungus, namely when the fungal pathogens are spread.
The so-called erythrasma is very similar to the inguinal fungus, but it is caused by infection with a bacterium. This is usually part of the natural skin flora. If there is an imbalance in the skin barrier, the bacteria can better penetrate the upper layers of the skin and lead to an infection.
Read more on this topic at: Inguinal fungus
psoriasis
The so-called psoriasis inversa can also lead to inflammation of the groin. Psoriasis is generally known as psoriasis, but the inverse form occurs in rather unusual places in contrast to "normal" psoriasis, which tends to affect the extensor sides of the extremities.
You will find more information on this topic here: psoriasis
Carbuncle, or inflammation of a hair follicle
In the case of folliculitis or carbuncle as the reason for the inflammation of the groin, bacteria are the main possible causes. If the body does not manage to destroy the invading bacteria quickly, an abscess can develop in the groin.
Inguinal hernia
In men, inflammation in the groin area is often triggered by an inguinal hernia. An inguinal hernia is also possible in women, but it is about 8 times more common in men. The structures involved in the inguinal hernia (groin-forming structures or the contents of the hernial sac) can become inflamed and cause severe pain and redness in the groin.
Also read: Symptoms of an inguinal hernia
Inflammation of the female genital organs
As with men, inflammation in the groin in general can be triggered by any possible cause such as infection, muscle strain, or tendinitis in the groin. However, there are also specific causes of inflammation in the groin for women that originate from the female reproductive organs. These include uterine, fallopian tube or ovarian inflammation.
There may also be painful swelling and drawing in the groin due to ovulation or during menstruation. These symptoms are mainly caused by hormones. Since women are more prone to urinary tract infections, such an infection can also be the cause of swelling, inflammation or pain in the groin area more often than in men.
In addition, there is usually pain when urinating with little urine (oliguria). Sometimes there is blood in the urine. During pregnancy, loosening of the pubic symphysis can lead to pain in the groin.
Diseases of the testicle
Various inflammations of the testicle can cause swelling or inflammation in the groin. Care should always be taken here, as testicular diseases are usually emergencies that should be treated as soon as possible.
In addition to general infections from bacteria, fungi and viruses or inflammation of the muscles and tendons in the groin area due to, for example, overloading, specific causes of inguinal inflammation in men are also to be found in diseases of the male genital organs. This causes inflammation of the testicles (Orchitis), Vas deferens (Deferentitis), Prostate (Prostatitis) or epididymis (Epididymitis), which can spread to the groin area, are in question. In the case of groin inflammation in men, a doctor should therefore always be consulted, as testicular torsion can also be the cause of the inflammation.
In the case of testicular torsion (testicular stem rotation), the testicles, epididymis and spermatic cord twist into one another. The supplying vessels can be constricted and the tissue can die. This can cause inflammation and swelling in the testicle area, but also in the groin. Since one possible consequence of tissue destruction can be infertility, action must be taken quickly.
Hydatid torsion can also cause swelling and pain in the testicles - similar to testicular torsion - and in the groin. Hydate torsion is the twisting of an appendage on the upper pole of the testicle. The inflammation of the epididymis (Epididymitis) - triggered e.g. Urinary tract infection - can also cause swelling of the testicles and groin.
In rare cases, inflammation in the groin can also be caused by testicular cancer. Often there is no pain in the testicular area. However, the testicles and groin can be swollen - usually only on one side. In addition, swollen lymph nodes can become noticeable in the groin.
Also read: Itching on the testicles- what's behind it
Inflammation of the pubic bone
Due to the anatomical proximity of the groin and pubic bone, inguinal inflammation can spread to the pubic bone.
If both structures are affected by inflammation at the same time, however, a previous inflammation of the pubic bone is often more the trigger for an inflammation in the groin.
The left and right pubic bones form the anterior pelvis. They are through the pubic symphysis (Symphysis), which consists of fiber cartilage, are connected to each other. The pubic bones and symphysis are often affected by inflammation, which then migrate up into the groin and there can also cause inflammation or at least pain.
In most cases, the pubic bone becomes inflamed as a result of excessive stress during sporting activity, especially in sports such as football, tennis or general running sports. The treatment should relieve the pelvis and take a break from exercising. In addition, anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac) can be taken for a short time.
In women, pregnancy and childbirth can be the cause of pubic bone inflammation that spreads to the groin. Surgery in the pelvis (for example on the prostate) can rarely lead to inflammation of the pubic bone and groin.
Read more on the topic: Pubic bone pain - these are the causes
Sports injuries
As already described above, an inguinal inflammation can result from an inflammation of the pubic bone that was caused by excessive exercise. However, inguinal inflammation can also be triggered directly by exercise. Therefore, competitive athletes are often affected by pain and inflammation in the groin.
Muscles, tendons and tissues in or near the groin can become inflamed and cause swelling, redness and pain in the region. On the other hand, untrained people can get inguinal inflammation due to overuse of the muscles due to training that is increased too quickly. Wrong or jerky movements during sport can cause strains in the muscles or the inguinal ligament to cause swelling and inflammation in the groin region.
Therefore, as a preventive measure, it should be ensured that movements are carried out correctly and in a controlled manner and that the training is always adapted to the personal fitness level in order to avoid overloading the muscles and tendons
Symptoms of inflammation of the groin
The classic symptoms of inflammation are actually always the same in every part of the body, since the mechanism of inflammation is always the same. The inflammation always leads to redness, swelling, overheating and of course pain. If the skin is primarily affected by the inflammation, there can be several causes.
Weeping inflammation of the skin indicates intertrigo. This occurs mainly on body folds, such as in the groin area or the gluteal fold or on the armpits. The layers of skin rub and lie on top of one another, so that a moist chamber can arise, which makes it easier for pathogens to overcome the skin barrier. Intertrigo manifests itself through reddening of the skin, oozing, small skin injuries, itching and burning. The shape of the changes is relatively the same on both sides of the fold.
At the beginning of the disease, a inguinal fungus is mainly associated with reddening of the inside of the thigh in the area of the groin and genitals. The reddening, which may be relatively small and small at the beginning, can increase significantly over time. At the edge the skin is reddened and inflamed. In addition, there may be flaking of the skin at the edge of the reddening. The center of the spots is noticeably paler and sometimes also has a more brownish color. The inguinal fungus is often accompanied by a burning sensation, itching is rather rare.
The so-called erythrasma is very similar in appearance to the inguinal fungus. However, this leads to an infection with the bacterium Corynebacterium minutissimus. Symptoms here are sharply defined brownish spots, the color of which is reminiscent of coffee with milk. The affected areas of the skin are not raised and have tiny wrinkles. The affected skin is provided with small scales. Itching may or may not be present. Erythrasma occurs mainly in areas where there is increased sweat production and where there is an increased temperature, i.e. especially in the area of wrinkles (armpit, under the breast, in the area of the groin).
Another possible diagnosis of inflammation of the groin is what is known as psoriasis inversa (psoriasis). It does not appear in the usual places of common psoriasis, but mainly reappears in the area of the body folds, for example in the armpits, on the anal folds, in the area of the groin or the belly button. This does not, as is typical for common psoriasis, the large, silvery scales, but rather a blotchy, sharply defined reddening without flaking.
Read more on the topic: psoriasis
Inflammation of individual hair follicles or even several follicles in the groin area is accompanied by swelling, redness, warmth and pain. This often leads to an infection with bacteria. If the inflammation spreads to several hair follicles, a so-called carbuncle (pus bump) can develop.
Fever as an accompanying symptom
A swollen and painful groin combined with a fever often indicates an infection that activated the body's defense system. For example, an abscess (encapsulated collection of pus) near the groin - caused for example by intestinal or anal infections - can cause inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes and fever.
But injuries to the leg and foot can also lead to painful swelling of the inguinal lymph nodes and fever.
Bacteria enter the open wound and cause an infection. The venereal disease syphilis caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum (syphilis) can cause fever and inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin in the early stages. In addition, the so-called "hard chancre" (ulcus durum) - a painless, hard ulcer in the groin, genital or buttock region - also occurs in the early phase.
Cancer diseases - sometimes skin cancer of the leg - can also cause swelling of the lymph nodes and fever. In this case, however, the lymph nodes are usually not painful.
diagnosis
The diagnosis Inguinal fungus can be secured by swabbing the affected area and then growing the mushrooms on special plates.
The diagnosis of the Erythrasmas is placed with the help of the so-called Wood light. The affected areas with their scales appear bright red under the light.
Folliculitis or carbuncle are both a visual diagnosis and do not require any further diagnosis.
Frequency distribution
Inguinal fungus (tinea inguinalis) is typically more likely to occur Men than with women. An infection with the corynebacterium, which leads to the clinical picture of erythrasm, is particularly chronic in males. An infection of the skin occurs frequently, especially when it comes to skin infections obese Patients, as they often sweat more in the area of the skin folds.
Therapy for inflammation of the groin
The therapy of intertrigo consists mainly of drying the affected skin folds and keeping them dry. You can put so-called gauze strips in the folds, which absorb the moisture. In addition, the affected areas can be coated with a zinc paste to dry them out.
The inguinal fungus is mainly treated with so-called anti-fungal drugs (antimycotics). In most cases, topical therapy with ointments and creams is sufficient.
The erythrasma can be treated with antibiotic creams. Miconazole and fusidic acid creams are mainly used here to treat the affected areas. An important measure would be to pay attention to increased and more thorough body care of the affected areas and to dry them particularly well after washing.
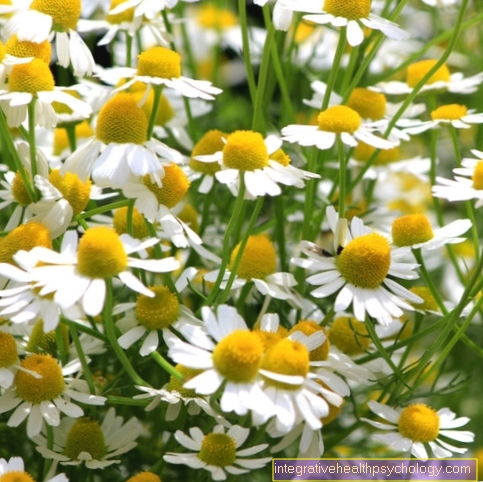
When treating psoriasis, it is important not to wear clothing that is too tight in the affected areas, so as not to irritate the skin there. You should also keep the affected areas as dry as possible and then treat them with special creams. Anti-inflammatory baths with chamomile or calendula are often helpful. Cortisone creams should only be used for a short time if possible in order to reduce the inflammation.
Vitamin D supplements could also help in the treatment of psoriasis inversa. For psoriasis in the area of the skin folds, therapy with UV light is also an option.
Folliculitis is mainly treated with disinfectant substances. Sometimes an antibiotic topical ointment treatment can also be used. However, if a carbuncle forms, it may be necessary to split the boil in order to drain the pus.
Homeopathic therapy for inguinal inflammation
At a supportive homeopathic treatment In the case of inguinal inflammation, it must first be determined where the inflammation comes from. Is it a Inflammation of the male genitals, see a doctor as this may be an emergency. Other diseases like syphilis or Urinary tract infections men should be examined and treated by a doctor. Is it a Inflammation of the muscles and Tendons, homeopathic treatment can take place. Here are homeopathic remedies such as Bryonia (Bryony) or Rhus toxicodendron (poison sumac) Taken as globules several times a day until symptoms improve.