Pericardium
Definition and function
The pericardium, also called pericardium in medicine, is a sac made of connective tissue that encloses the heart, with the exception of the outgoing vessels.
The pericardium acts as a protective cover and prevents the heart from expanding excessively.

Anatomy and location
The pericardium consists of two layers: the layer that rests directly on the heart and an outer layer. In medicine, they will Pericardium fibrosum (outer layer), which consists of collagen, and Pericardium serosum (inner layer) called. The Pericardium serosum again consists of two layers. Once the Lamina parietalis pericardii and those lying directly on the heart Lamina visceralis pericardii.
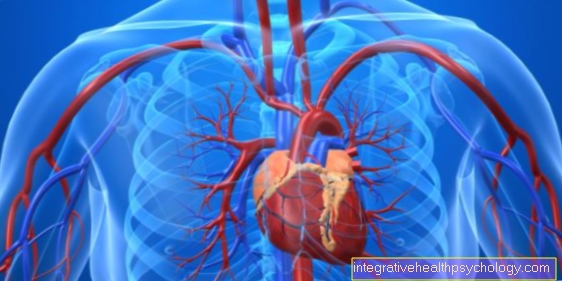
Figure pericardium

- Pericardium -
Pericardium fibrosum - Heart point - Apex cordis
- Coronary artery right -
Coronary artery dextra - Left coronary artery -
Left coronary artery - Right atrial - Atrium dextrum
- Right ventricle -
Ventriculus dexter - Left atrium - Atrium sinistrum
- Left ventricle -
Ventriculus sinister - Aortic arch - Arcus aortae
- Superior vena cava -
Superior vena cava - Lower vena cava - Inferior vena cava
- Pulmonary artery trunk -
Pulmonary trunk - Left pulmonary veins -
Venae pulmonales sinastrae - Right pulmonary veins -
Venae pulmonales dextrae
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
There is one between the two inner leaves liquid, Pericardial fluidwho the Reduce friction between the leaves should. The amount of liquid is about 10 ml. The leaves beat in the area of the large vessels, ie on the aorta and the Vena cava, around.
The pericardium is innervated, that is, he of annoy is supplied. One of these nerves is the Vagus nerve and the Phrenic nerve, both of which give off small branches that lead to Heart pull. The blood supply takes over Internal thoracic artery over the branch Pericardiacophrenia artery.
Diagnosis
The easiest way to get the pericardium is in the Ultrasonic represent. Especially with effusions ultrasound is the examination method of choice. You can also use a Puncture of the sacrum make and examine the obtained liquid. There is also the option of using the pericardium Computed Tomography to investigate. For example, calcifications can be made visible.
pathology
The Inflammation of the pericardium is called Pericarditis. You can at Listening to the heart perceived as rubbing. The accumulation of fluid in the pericardium is called Pericardial effusion. If an increasingly large accumulation of fluid is not treated, it can lead to Pericardial tamponade come. Depending on the size of the pericardium tamponade, the heart can no longer expand and it comes to cardiogenic shock. The therapy with the pericardial tamponade is one Puncture with drainage.










.jpg)





.jpg)