Tendinitis in the hollow of the knee
definition
Tendonitis in the hollow of the knee is a disease of the muscles and tendons that are located in the hollow of the knee. Tendonitis (tendinitis) is usually the result of excessive strain on the muscles. Inflammatory systemic bases or bacteria and viruses are less common causes of tendinitis. It is noticeable through pain, possibly also redness and swelling in the hollow of the knee. Movement restrictions can also occur in the affected leg.

causes
In most cases, tendinitis in the hollow of the knee is caused by excessive strain on the muscles around it. Overloading causes small damage to the tendons, these are repaired by the body, whereby small inflammatory processes occur temporarily. In the case of permanent overload, the foci of inflammation can no longer heal, instead a chronic inflammation develops, which manifests itself in a tendinitis.
The permanent inflammation in the body also plays a role in inflammatory systemic diseases such as rheumatism. In such diseases, the immune system attacks the body's own cells, which also causes inflammatory reactions. If this happens in the hollow of the knee, tendinitis can quickly develop. Infectious causes of tendinitis in the hollow of the knee also rarely occur.
Inflammation of the biceps tendon
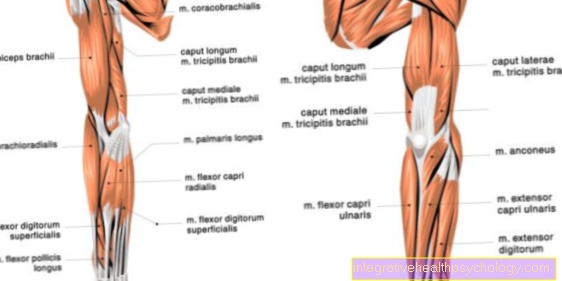
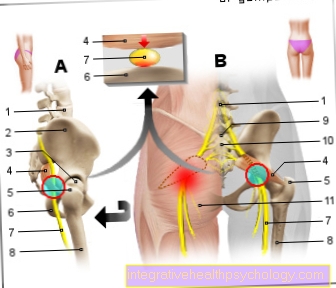
The thigh biceps (Musculus biceps femoris) belongs to the group of so-called ischiocrural muscles. It pulls along the back of the thigh and participates in both hip and knee movement. In the hip it causes a stretch and in the knee joint a flexion of the leg. The biceps tendon can become inflamed in the event of excessive stress and chronic inflammatory diseases. Mostly the tendon in the hollow of the knee is affected, causing pain, redness and swelling in the knee area.
Inflammation of the popliteus tendon
The popliteus muscle is a very small muscle that is located at the back of the knee. It pulls from the outside of the thigh over the hollow of the knee to the inside and back of the lower leg bone. There he is involved in knee flexion. Inflammation of the Popliteus tendon can be both acute and chronic. Athletes, especially runners (also in ball sports) and sometimes cyclists, are most frequently affected by the disease. In the first phase, rest, cooling, elevation of the leg and medication that reduce inflammation and relieve pain help.
Concomitant symptoms
Tendonitis in the hollow of the knee has five typical symptoms of inflammation: pain, redness, overheating, swelling and restricted mobility of the hollow of the knee.
The pain is particularly noticeable when the affected muscles are stressed and are therefore more noticeable during physical exertion. The reddening and overheating of the hollow of the knee occurs mainly in the case of acute tendinitis in the hollow of the knee. The swelling and restricted mobility, on the other hand, can occur in both chronic and acute tendinitis.
In many cases, the inflammation of the tendon also leads to a reduced load-bearing capacity of the affected muscles, so that there is a loss of strength in the leg. This results in an uneven gait pattern and reduced physical performance. If such tendinitis in the hollow of the knee persists for a long period of time, movement patterns can be incorrectly memorized, which can have an impact on neighboring joints. This can damage the ankle and hip in the long term. It is not uncommon for diseases of the muscles in the legs to lead to back pain.
Appointment with a sports orthopedic specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
As a passionate athlete, I have specialized in the treatment of sports diseases for professionals and hobby athletes.
The focus is therefore on diseases of the muscles, tendons and joints.
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
diagnosis
The diagnosis of tendinitis in the hollow of the knee is initially based on the patient's survey by the doctor. The complaints can be inquired about in more detail, and initial theories for the origin of the complaints can be drawn up. This is followed by the physical examination, during which pain points and restricted mobility can be determined. The physical examination often allows initial conclusions to be drawn as to which tendon in the hollow of the knee is affected.
As a rule, an ultrasound examination is then sufficient, with which the diagnosis of tendinitis can be established. The ultrasound is particularly suitable for showing muscular structures as well as the tendons; accumulations of fluid are also noticeable in the examination. Further diagnostic tests such as laboratory examinations, imaging (usually MRI) or biopsies rarely need to be performed.
therapy
At the beginning of the symptoms, the first therapy according to the PECH scheme (break, ice, compression, lying down) should take place. The physical exertion should be stopped immediately. The painful hollow of the knee can be cooled, a bandage is applied to prevent swelling and the affected leg is raised. Since cooling the hollow of the knee can temporarily relieve the symptoms, there is a risk of overloading the tendon again afterwards. Therefore, one should strictly adhere to a break from stress. In the first few days, anti-inflammatory and pain reliever medication can also be taken.
A firm tape bandage or a supportive bandage can also be used to immobilize the knee.
Once the initial symptoms have subsided, the use of heat is recommended instead of cold therapy. This improves the blood circulation and the metabolic activity of the muscles, so that the inflammation of the tendon can be better combated by the body. Careful exercise therapy can then be started. In doing so, you should avoid putting heavy strain on the tendons in the hollow of the knee. Rather, it is first about creating full mobility in the hollow of the knee.
Under physiotherapeutic and medical supervision, the load can be carefully increased over time. The strengthening of the muscles comes increasingly to the fore. In rare cases, when the tendinitis has an infectious cause, antibiotic therapy may be necessary.
Read also: Home remedies for tendinitis
Duration
The duration of tendinitis in the hollow of the knee depends heavily on the cause and on the success of the therapy. In the case of acute tendinitis, for example due to infectious causes, the symptoms usually disappear after a few weeks.
Most tendinitis, however, is more chronic in nature, so treatment extends over several weeks to a few months. In order to prevent a recurrence of the symptoms or a severe chronification of the tendinitis, one should rather allow a longer recovery period.










.jpg)





.jpg)