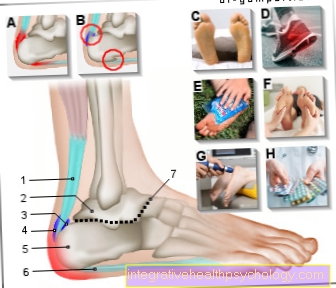
Pain in the interphalangeal joints
introduction
The end joints of the fingers are the most distant joints in the area of the fingers, close to the nail bed. The end joints of the fingers are stressed by numerous hand movements, for example gripping movements.
Various causes can provoke pain in the finger joint joints. Pain can occur with certain movements and / or at rest.

The causes of pain in the interphalangeal joints
There are various possible causes for pain in the end joints of the fingers. Arthrotic changes are very common from the age of 50. Other possible causes for the development of pain in the end joints of the fingers are an acute attack of gout, psoriatic arthritis and rheumatism.
An acute attack of gout can affect every wrist and finger joint and cause a very painful joint inflammation. Psoriatic arthritis can also lead to painful joint swelling in the end joints of the fingers and often affects the whole finger, "sausage finger" symmetrically.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the articular joints of the fingers are also often affected, typically symmetrical and with symptoms characteristic of rheumatism. In addition, cysts, such as a mucoid cyst or ganglion, and Raynaud's syndrome can be responsible for pain in the interphalangeal joints. Injuries to the anatomical structures, such as a rupture of a finger extensor tendon, can equally trigger severe pain in the joint area of the fingers.
Find out all about the topic here: Rheumatism.
Heberden osteoarthritis
Heberden osteoarthritis refers to arthritic changes in the distal interphalangeal joints, also known as the end joints of the fingers. Heberden osteoarthritis is particularly common in the index fingers and little fingers. It is a generative disease that develops without a known cause. Nonetheless, genetic and hormonal connections are often found in the development of osteoarthritis.
Early symptoms of joint disease are pain on exertion, when the joint is tired and the pain is radiating. As the disease progresses, the pain can worsen and cause permanent pain. Other late symptoms are night pain in the joints, a pronounced restriction of movement and sensitivity to the weather.
Read more about the topic here: Finger osteoarthritis.
The gout
An acute gout attack is a common disease in our society. This creates a painful joint inflammation of one joint with effusion and signs of inflammation. The end joints of the fingers are affected in about five percent of cases, which is called a chiragra.
The cause is an increased uric acid level with precipitation of uric acid crystals, which are deposited in joints and trigger the gout attack. The acute gout attack of a wrist joint typically occurs at night and subsides after a few days. Without treatment, relapses occur with symptom-free intervals.
You can find more information on this topic here: The attack of gout.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammation of the joints that occurs with psoriasis. The so-called peripheral type of disease, the most common type of psoriatic arthritis, typically affects the metacarpal and metacarpal joints symmetrically on both hands.
Those affected suffer from severe soft tissue swelling in the area of the diseased fingers. Usually the entire finger is affected, which is called the "sausage finger" or a "sausage toe". Without adequate treatment, the affected joints are destroyed in the course of the disease and osteoporosis develops.
For more information, read on: Psoriatic arthritis.
Torn finger extensor tendon
Finger extensor tendons can tear, especially if they are previously damaged by wear and tear and are heavily stressed, for example during sports. The tendons can tear completely or partially.
Symptoms come on suddenly. Typically, the affected finger can no longer be stretched properly and causes severe pain. There will also be swelling and bruising.
You can find more information on this topic here: Torn off the extensor tendon of the finger.
Raynaud's Syndrome
Raynaud's syndrome is a vascular disease that is characterized by vascular spasms. Blood flow disorders occur like attacks, especially in the fingers. As a result, the fingers are briefly less well supplied with blood. They become pale and cold, and they can feel numb and cause pain.
A distinction is made between primary Raynaud's syndrome with an unknown cause and secondary Raynaud's syndrome, which occurs in the context of other diseases such as scleroderma.
Read more on the following topic: Raynaud's Syndrome.
The accompanying symptoms of the pain in the ankle joint
Depending on the cause of the wrist pain, various accompanying complaints can occur.
In the early stages, osteoarthritis of the osteoarthritis shows itself with fatigue and stress pain that can radiate. In the course of the disease, permanent pain, night pain, severe limitation of the mobility of the joint and sensitivity to the weather can occur.
If an acute gout attack is the cause of the pain in the wrist joint, there is usually a pronounced effusion with severe swelling, reddening and tenderness. There may even be systemic signs of inflammation, such as fever and malaise.An accompanying symptom of psoriatic arthritis is psoriasis, although both symptoms do not have to occur at the same time. The pain in the affected joint is accompanied by swelling and is often accompanied by tendinitis in the surrounding tissue.
A rupture of a finger extensor tendon causes sudden pain, with a bruise and swelling in the affected finger. The finger can no longer be stretched properly. Raynaud's syndrome is attack-like. The fingers are briefly poorly supplied with blood, so that they initially become pale, cold and numb and cause pain. They turn blue as they progress and red before subsiding. This is why Raynaud's syndrome is called the tricolor phenomenon.
The Knubbel
Various diseases that are associated with pain in the end joints of the fingers can trigger knobs in this area. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, so-called rheumatic nodules can lie under the skin and can be felt.
Joints that are used heavily are predestined for the formation of a ganglion. This is a bulging out of a joint or tendon cover that is filled with fluid.
More information on the topic ganglion can be read here.
The redness
Reddening in the area of the wrist is a typical sign of inflammation and is usually accompanied by swelling, overheating and functional impairment of the joint.
Redness occurs in an acute attack of gout, in an injury such as a torn finger tendon or acute arthritis in the context of osteoarthritis.
Diagnosis of pain in the interphalangeal joints
Pain in the interphalangeal joints is a symptom that can arise due to various causes. In order to find the correct diagnosis, the doctor first conducts a thorough discussion with the person concerned about the nature of the pain, accompanying symptoms and the temporal course of the symptoms. This is followed by a physical exam of both hands.
Depending on the suspected diagnosis and possible exclusion diagnoses, a blood test, imaging such as x-rays or a referral to a specialist may be indicated.
Treatment of pain in the interphalangeal joints
For pain in the end joints of the fingers, various therapies can be considered, depending on the cause of the discomfort.
Heberden osteoarthritis is initially treated conservatively with anti-inflammatory pain medication, immobilization and, if necessary, an injection of cortisone. Physiotherapy and heat applications in inflammation-free intervals are also possible. Surgery can be considered if the fingers are severely deformed.
An acute attack of gout is also treated with anti-inflammatory drugs or cortisone. In some cases the use of colchicine may be indicated. In the event of pain, the joint may be cooled, and in the event of a diagnosed gout attack, long-term drug uric acid lowering may be indicated. Psoriatic arthritis can be treated with local immunosuppressive drugs, phototherapy, and pain relievers. If this treatment is not enough, stronger immunosuppressive drugs such as retinoids or methotrexate can be considered.
The rupture of a finger extensor tendon must be sutured within a short time and then immobilized for six weeks. For Raynaud's syndrome, avoid triggers such as stress and cold. Heated gloves and not smoking can help alleviate symptoms. In the case of frequent, subjectively intolerable complaints, drugs such as calcium channel blockers can be applied to the affected areas. In secondary Raynaud's syndrome, the underlying disease should be treated as well as possible.
For more information, also read: Cortisone therapy for joint diseases.
Homeopathy
The therapeutic effectiveness of homeopathic globules has not yet been proven. Nevertheless, homeopathic remedies are becoming increasingly popular and can be taken without hesitation (in the recommended dose), as there are almost no known side effects.
The homeopathic remedies Acidum Sulfuricum, Aconitum Napellus, Bryonia, Calcium fluoratum and Sulfur are often recommended for pain in joints. The well-known agents Belladona and Arnica are also very popular.
Which doctor treats this?
Long-term treatment for pain in the articulation of the fingers depends on the cause of the discomfort. Therefore, you should first contact your family doctor and talk in detail about the symptoms and any other illnesses.
An acute attack of gout can usually be treated well by the family doctor. For complex clinical pictures such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis, treatment by a competent team with a family doctor, dermatologist and orthopedic surgeon can make sense. If the finger tendons are injured, a surgeon should be consulted.
Also read the articles:
- Therapy of rheumatoid arthritis
- Therapy of gout
The duration of pain in the interphalangeal joints
Heberden osteoarthritis is an incurable disease that cannot be reversed. Adequate therapy can help relieve symptoms and slow down or slow the progression of osteoarthritis.
An acute attack of gout typically subsides within days. With the right treatment, gout can be treated well. The uric acid level should be well controlled in the long term. Psoriatic arthritis is a disease that keeps coming back. Various therapeutic treatment options are available to alleviate the symptoms.
A tendon rupture is an acute injury that usually heals well after an operation, so that the affected finger can be used normally again after about six weeks. In Raynaud's syndrome, the prognosis depends on the cause of the syndrome. The individual attacks last about half an hour.
Can this be hyperacidity?
The frequent and well-known attack of gout is associated with hyperacidity. The uric acid level in the blood is greatly increased, so that uric acid crystals form, which can be deposited in various joints.
Some alternative physicians assume that disorders of the acid-base balance can generally lead to joint pain. Balancing the acid-base balance should help prevent acid-related pain in joints.
Find out all about the topic here: Acid-base diet.