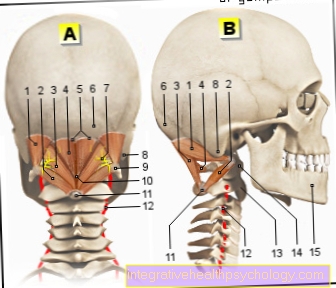
Swelling on the neck under the jaw
Definition - What is a swelling on the neck under the jaw?
A swelling on the neck under the jaw can basically occur both in the middle of the neck and a little to the side under the jaw arch. Depending on the location of the swelling, different structures run below the swelling. Lymph nodes, for example, lie below the jaw. However, if there is swelling under the jaw, the jaw itself may also be involved.
Swelling due to superficial skin problems is also typical. These occur particularly often with beard growth (especially during puberty) on. However, swelling on the neck under the jaw can also originate from deeper structures.

Causes of swelling on the neck
-
Swelling of the lymph nodes
-
Submandibular (under the jaw)
-
Submental (under the chin)
-
One / both sides
-
-
Inflammation
-
Oral pancreas
-
abscess
-
Jaw / tooth root
-
-
Cervical cyst
-
tumor
-
Malignant / benign
-
Mouth floor, tongue base, etc.
-
Lymph node swelling under the jaw
Both the submandibular ("located under the jaw") As well as the submental ("located under the chin“) Lymph nodes. Due to various diseases, these can lead to swelling of the neck under the jaw.
The most common cause are infectious diseases such as a cold or the flu. In the context of such a systemic infection (an infection of the whole body) the lymph nodes are particularly in demand as “immune stations”, which is why they can swell in response to the disease.
Local infections, for example in the area of the teeth, can also cause lymph node swelling under the jaw. Tumors are less often the cause of such lymph node swelling. Usually only a few lymph nodes are swollen, often only one side is affected.
Are you more interested in this topic? Read more information on this under: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the lower jaw
Abscess on the neck
When an abscess forms, a new body cavity develops due to inflammation. Most of the time, the pus produced by the inflammation melts into the surrounding tissue. This creates a pus-filled cavity: the abscess.
The origin of the abscess lies precisely in the area of the neck under the jaw, often on the surface of the skin. Due to impurities, especially with beard growth and in adolescence, superficial pimples can quickly become infected and cause severe local inflammation.
Conversely, inflammations in the mouth area such as the jaw or teeth can eat through the tissue and thus form an abscess under the jaw from the inside. Due to the accumulation of pus, the abscess usually appears as a swelling, and the area can also be reddened and overheated.
For more detailed information on this topic, see: Abscess on the neck - what to do about the boil?
Root inflammation
Root inflammation refers to inflammation of the tooth root. This inflammatory process usually begins with a disease of the affected tooth with caries. If this focus of infection is not treated in time, the inflammation can spread to the root of the tooth. From there, inflammatory cells can easily get into the surrounding tissue.
This can lead to inflammation of the jaw. Once the inflammation has spread that far, it is usually no longer just a toothache and possibly a thick cheek. Often there is also a painful swelling on the neck under the jaw.
For more detailed information on this topic, see: Tooth Root Inflammation - What to Consider
Pine necrosis
Necrosis is the technical term for the death of tissue. In the case of jaw necrosis, various processes can damage the jawbone, causing the individual bone cells to die. The causes of pine necrosis are diverse, for example a lack of nutrients can damage the cells and thus lead to necrosis.
Inflammation of the jaw, for example due to chronic inflammation in the oral cavity, is also a conceivable cause of jaw necrosis. Necrosis of the jawbone can also occur due to tumors or as a complication after radiation therapy or treatment with strong drugs.
As the body tries to break down the necrotic cells, many immune cells are washed into the area of the jaw necrosis. This can lead to swelling under the jaw.
Cervical cyst
The cervical cyst is a structure that arises due to the defective development of the pharyngeal arches during the embryonic period. This is an encapsulated space that is typically filled with liquid. This cervical cyst can appear both on the side and in the center of the neck, under the jaw. Because the cyst takes up more space than the surrounding tissue, swelling occurs in the affected area.
The neck cyst usually occurs between adolescence and the age of 30 to 40. In principle, treatment of the neck cyst is not absolutely necessary. However, one fears the formation of a neck fistula, in which the cyst opens to an internal organ or to the outside of the skin. This complication harbors a high risk of infection, which is why the neck cyst is usually surgically removed as a precaution.
Read more about this topic under: Cervical cyst
Inflammation of the salivary gland
The human body is equipped with several salivary glands, of which two large glands are located in the oral cavity: the lingual salivary gland and the lower jaw salivary gland. The secretion of the salivary glands contains digestive enzymes, so the saliva not only helps to moisten the food in the mouth, but the enzymes start to break down the food into its individual components.
In addition to the large salivary glands, there are also small glands on the tongue, lips and oral mucosa.
If an oral salivary gland becomes inflamed, the large salivary glands are usually affected. For example, a salivary stone can clog the duct and lead to an inflammation of the gland by backing up the saliva. This leads to a painful swelling in the area of the neck under the jaw.
Are you more interested in this topic? Read more about this at: Inflammation of the salivary glands
Oral cancer
Oral cancer is a malignant disease in which a tumor forms in the area of the floor of the mouth. In a broader sense, all types of cancer in the area of the floor of the mouth and the base of the tongue count as floor cancer. In most cases, these are cancer cells that are formed from the cells of the mucous membrane in the mouth. More rarely, the cause lies in the gland cells.
The most important risk factors for the development of oral cancer are excessive alcohol consumption and smoking. Oral cancer typically only develops in later decades of life with a peak between the ages of 60 and 70.
Depending on the extent of the tumor, treatment can be carried out surgically or using radiation therapy. The prognosis depends on the type of cancer cells and the time of diagnosis.
How is it diagnosed?
The most important step in diagnosing swelling in the neck under the jaw is taking a medical history, which the doctor can use to find most of the clues about the source of the swelling. This is followed by a physical examination of the swelling.
Then, depending on the suspected cause, various laboratory tests and imaging methods can be used. Ultrasound is particularly suitable for a quick overview.
Other accompanying symptoms
A swelling on the neck under the jaw is the most common symptom associated with pain. There may also be other signs of inflammation such as reddening and overheating of the affected area.
With lymph node swelling due to a systemic infection, flu-like symptoms such as headache and body aches, fever, fatigue, etc. can occur. Chronic diseases that trigger such a swelling are usually associated with fewer symptoms.
Pain
The painfulness of the swelling on the neck is one of the most important indications of the cause of the discomfort. It usually occurs in acute diseases such as inflammation (Tooth root, superficial inflammation, abscess, systemic infection) to a painful swelling.
Chronic diseases, on the other hand, develop slowly and are therefore usually not associated with any impressive clinical symptoms such as pain. A neck cyst, like a malignant lymph node swelling, can appear as a painless swelling on the neck under the jaw.
Therapy of swelling on the neck under the jaw
The therapy for the swelling on the neck under the jaw depends largely on the cause of the symptoms. In most cases, the symptoms can be treated symptomatically.
For example, pain medication can alleviate the symptoms and cooling the swelling can provide additional relief if the cause is an inflammation in the area of the jaw. In addition, the focus of inflammation (for example an inflamed tooth root) be treated. If a bacterial infection occurs, antibiotics can fight the pathogens and thus alleviate the symptoms.
For swellings that are not associated with inflammation, the therapy usually looks a little different. In the case of harmless causes, you can first wait, and if necessary, the cause of the swelling should be surgically removed. If the swelling in the neck under the jaw is due to a malignant process, oncological therapy (Cancer treatment) may be necessary with surgery and radiation therapy.
Duration and prognosis of the swelling on the neck under the jaw
The duration and prognosis of the swelling are mainly determined by the underlying mechanism. Acute illnesses are usually healed within a few days to weeks, while chronic processes often last for several weeks to months and can only be completely treated with causal therapy.
If the cause of the swelling is benign, the prognosis is usually good. With malignant causes such as cancers of the floor of the mouth, a shortening of the lifespan may have to be expected.
The disease progresses from swelling on the neck under the jaw
Just like the duration and prognosis of the swelling on the neck under the jaw, the course of the disease also depends heavily on the cause of the swelling. The acute illnesses usually manifest themselves within a few days, last a few days and then subside again.
Chronic or malignant processes, on the other hand, are more likely to develop over a period of weeks to months. Often times, they only go away with good treatment of the cause. The therapy often also has to be carried out over a longer period of time.
Recommendations from the editorial team
Further general information may also be of interest to you:
- Swelling of the neck
- Cervical cyst
- Lymph node swelling in the neck