How to recognize skin cancer
Synonyms in a broader sense
Tumor, skin tumor, malignant melanoma, basalioma, spinalioma, spinal cell carcinoma
introduction
Initially, skin cancer usually does not cause any symptoms.
Occasional itching and bleeding can occur, but it only becomes noticeable through the visible and possibly palpable changes in the skin.
You may also be interested in this article: White Skin Cancer

Symptoms
Depending on the type of skin cancer, different skin symptoms occur. These are discussed below according to the individual skin cancer types.
Also read our article:
- Symptoms of skin cancer
- Skin changes
Black skin cancer (malignant melanoma)
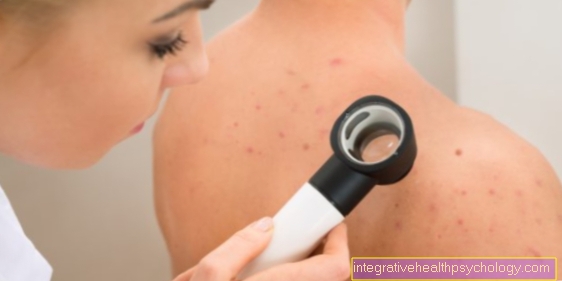
It is often not easy to distinguish a harmless birthmark from a malignant melanoma, in many cases this can only be done with the help of a microscopic examination.
However, the ABCDE rule helps you to make an initial assessment, here the skin change is assessed according to the following points:
- A - has an asymmetrical shape
- B - Boundaries of skin changes are irregular (fuzzy, jagged)
- C - Colorit = the color is not uniform
- D - diameter greater than 5 millimeters
- E - Raised - the skin bulges out
If any of the points are true, it is not a reliable diagnosis for skin cancer, but a specialist doctor should be a dermatologist (Dermatologist) or go to your family doctor for further clarification.
White skin cancer
Depending on which form of light skin cancer it is, different changes in the skin occur.
You may also be interested in this topic: Skin cancer screening
Spinalioma
Symptoms often appear on the lips, hands, or face in the form of:
- Nodules
- Cornifications
- Crusty, scaly and reddened spots
Over time, it will develop into a rough lump that causes little to no pain, but can bleed easily from time to time.
Find out more: Spinalioma
Basalioma
Basalioma is a slowly growing form of skin cancer and is particularly noticeable due to the following types of skin changes:
- Ulcerous
- Nodular
- Flat
- Scar-like
- Often they have a pearl-like border
Their color is predominantly skin-colored or reddish.
Read more about this:
- Initial stage of basalioma
- Prognosis in basalioma
Actinic keratosis
A preliminary stage of skin cancer is actinic keratosis, which manifests itself through the following symptoms:
- It usually only emerges at an advanced age ( > 50 years)
- Piled in places that are exposed to a lot of the sun (Face, forehead, bald or thin hair on the head, forearms)
- The first signs are small reddish spots
- These later develop into reddish nodules (5-10mm)
- The skin on the affected areas feels rough
- Cornification can occur, as well as small skin horns
Bowen's disease
Bowen's disease is another preliminary stage of skin cancer.
Here there are irregularly shaped eczema-like changes in the skin. These are mostly reddish and covered with scales, so they can easily be mistaken for psoriasis.
itching
Itching alone is not a clear sign of skin cancer; what is also important here is the change in the appearance of the skin and its texture.
For birthmarks that are in places where they are exposed to more friction, e.g. On the bra or waistband, inflammation can occur, which also causes severe itching. But this is nothing bad or evil.
However, if there is severe itching and abnormalities or changes in the appearance of a birthmark, plus possibly bleeding, a specialist should be consulted and further clarification should take place.
If you notice reddening, flaking and itching on the skin, you should definitely see a specialist, especially if these are on parts of the body that are exposed to a lot of solar radiation.
Small wounds that ooze, do not want to heal and keep itching should also be clarified.
Read more on the subject at: How do you recognize skin cancer?
Pathogenesis of skin cancer
In order to be able to recognize skin cancer, knowledge of the course is necessary. What all forms of skin cancer have in common is that they develop from a single degenerate cell that reproduces in an uncontrolled manner. The result is skin cancer, consisting of many clones of this single cell.
- Basalioma: Basaliomas arise from so-called basal cells in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis). The epidermis consists of several layers of cells, the lowest of which is made up of the basal cells. If one of these cells degenerates, it reproduces uncontrollably and also loses its ability to keratinize. As a result, this skin cancer develops.
- Spinalioma: A spinalioma arises from epithelium. This is understood to be tissue that lines the inner and outer surfaces of the body.
- Malignant melanoma: Malignant melanomas develop from pigment cells (Melanocytes). This skin cancer can develop on normal skin or on pre-existing changes (Nevus cell nevus = Mole, Lentigo maligna = Precancerous disease).
Causes of skin cancer
Cause for all 3 types of skin cancer (Basalioma, spinalioma and malignant Melanoma) may be a genetic predisposition (e.g. DNA repair disorders). However, there are also numerous risk factors for Skin cancer.
Basalioma: In skin cancer "Basalioma" belong UV radiation (sunlight), chemical and physical noxae (arsenic, X-rays, Burns) as well as suppression of the Immune system (e.g. through Medication, Diseases).
Spinalioma: Even with skin cancer "Spinalioma"UV light is one of the most important risk factors. In addition, there is an increased risk of this skin cancer in light skin types (Type 1 and 2) and when infected with certain viruses (HPV = Humane Papilloma-Viren). Furthermore, scars or lesions caused by chronic skin diseases (e.g. Lupus vulgaris, Lichen) viciously degenerate. Also called "precancerous" Skin changes exist, by which one understands to a certain extent "pre-tumor forms".
Malignant melanoma: There are also such precancerous risks as risk factors for malignant melanoma. Furthermore, nevi (Mole) to the Skin cancer develop. Acquired factors that promote melanoma are severe, frequent sunburns, a high socio-economic status and immunodeficiency.