Torem®
Synonyms in a broader sense
Torasemide, diuretic, diuretic, loop diuretic, furosemide
also read:
- Diuretics
- Furosemide
introduction
The drug Torem® contains the active pharmaceutical ingredient torasemide. This belongs to the group of diuretic drugs (Diuretics). The point of attack of the drug lies with a certain ion transporter, which is located in a certain section of the tubular system of the kidney, the loop of Henle (Loop diuretic). The drug is mainly used for water retention in tissues (edema). As a "new loop diuretic", the derivative (Descendant) Torasemide of the main substance of the loop diuretics furosemide only in the secondary properties such as dosage and kinetics of action.
Mode of action
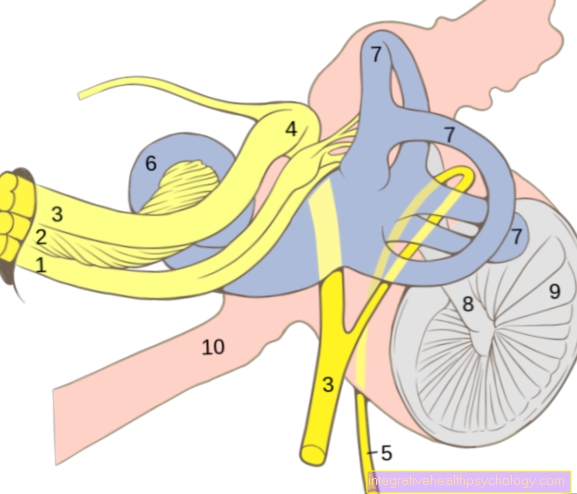
As a so-called Loop diuretic is the point of attack of the in Torem® contained active ingredient torasemide in one specialized transporter in the kidney. This specialized transporter conveys the ions in the thick section of the ascending leg of the Henle loop of the tubular system sodium, potassium and chloride against a slope from the tubular lumen. A stream of water follows these ions. This way it becomes this Primary urine of approx. 180 liters per day on 1.5 - 2 liters per day reduced. This terminal urine is excreted. Will the transporter through Torasemid inhibited, less water-attracting particles are transported out of the tubular lumen (the osmolarity decreases) and thus the water reabsorption is reduced. There is an increased amount in the urine excretion.
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability
In contrast to the lead substance Furosemide, has the Torasemid a more stable bioavailabilitywhat especially with a Heart failure (Heart failure) matters. If the bioavailability varies greatly with furosemide, it is relatively stable with torasemide at over 80%. The effect sets in relatively quickly, but lasts longer than with furosemide and enables one more efficient urination (Diuresis).
The substance is filtered from the bloodstream at the kidney filter into the primary urine and partly also actively released into the tube lumen by the cells of the tube system.
The substance can be used as Tablet or infusion administered. The onset of action occurs after oral ingestion (as with furosemide too) quite fast (30 - 60 minutes). To 12 hours the maximum effect is reached. But torasemide has a longer duration of action than furosemide (approx. 6 hours).
Note: drug allergy
In addition, the general rule is that drugs to which the patient has had an allergic reaction should not be prescribed again! The danger of an extended allergic reaction is too big and should not be entered.
application
The substance is used when water accumulates in the tissue (Edema). Especially through Heart, kidney and liver diseases caused water retention can through Loop diuretics like Torem® be washed out. Torasemid acts just as quickly and powerfully as the lead substance Furosemide. The specialty compared to furosemide is that it works longer and is therefore more efficient. Especially with through Heart failure conditional water retention Torem® particularly well suited.
Loop diuretics are also used when other diuretics are due advanced (kidney) diseases no longer work and the filtration capacity of the kidneys is significantly reduced.
To treat high blood pressure Loop diuretics such as furosemide or torasemide are only used when other diuretics such as Thiazides show a loss of effectiveness.
dosage
The drug is usually taken as a tablet. The dose is included 20-40 mg. Due to the longer effectiveness (Half-life approx. 4 hours) versus furosemide (Half-life) 1 to 2 tablets a day are usually sufficient. In the hospital, the gift can be given via a infusion be displayed.
Side effects

Loop diuretics lead to an increased Water, sodium and potassium excretion. This can be up to one Derailment of the water and electrolyte balance pass. There is a risk of thickening of the blood Blood clots (thrombosis). If the clot or parts of the clot come off, they are carried away with the bloodstream and then get stuck in other blood vessels (Thromboembolism). A dreaded complication is that Pulmonary embolism.
A Loss of potassium can be life-threatening Cardiac arrhythmias to lead.
Besides that, there can sometimes be a Hearing impairment come. This is because im ear a similar transporter occurs, the function of which may be impaired when taking Torem®. However, this is usually reversible and occurs more when high doses are given.
Torem also results in a loss of calcium and magnesium. Here you can Muscle tension and Muscle spasms occur. Long-term use without substitution of Electrolytes increases the risk for one osteoporosis.
Furthermore you can Gastrointestinal complaints and with prolonged use an increase in the Uric acid level (gout) occur.
Contraindications
Care should be taken with diseases such as Diabetes mellitus and gout. Also at liver and Kidney dysfunction Torem® may be contraindicated. On a comedication with ear-damaging (ototoxic) Antibiotics should be omitted.
Drug interactions
When consuming e.g. liquorice leads to the simultaneous intake of Torem® to an increased Loss of potassium. In addition, the simultaneous administration of Torem® and Methotrexate delayed excretion of methotrexate, a drug that responds to the immune system works.








.jpg)





.jpg)