Causes of Petechiae
What are petechiae?
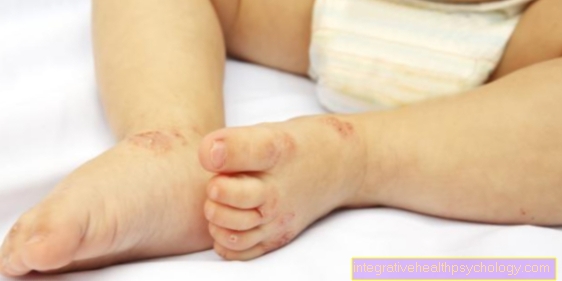
Petechiae are small punctiform hemorrhages that can occur in all organs.
Typically, petechiae become noticeable when they are in the skin.
In contrast to other punctiform changes in the skin, petechiae cannot be pushed away.
If you press the petechiae with a glass spatula, they do not go away, because it is bleeding and not malformation of blood vessels.
Petechiae are mainly caused by blood clotting disorders.
Tiny injuries in small blood vessels can no longer be adequately closed by thrombocytes (blood platelets), which are very important for hemostasis. Either the number of thrombocytes is too low (thrombocytopenia) or the thrombocytes are not fully functional (thrombocytopathy).
Another cause of the small bleeding is excessive injury to the blood vessels. An example of this is inflammation of the blood vessels called vasculitis.

The most common causes:
-
Thrombocytopenia (lack of platelets)
-
Thrombocytopathy (platelet dysfunction)
-
Small vessel vasculitis
-
Autoimmune diseases
-
Vitamin deficiency
-
Infectious diseases
-
Strenuous sport
-
stress
-
leukemia
-
Drug overdoses
-
Drug side effects
Cause thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia means that there is a lack of platelets.
Platelets are also known as platelets.
The main function of platelets is what is known as primary blood clotting, i.e. the first and rapid closure of large and small wounds.
Thrombocytopenia can go through on one hand
- decreased production of platelets or
- cause increased degradation.
The decreased production is due to a disruption of the bone marrow, in which the blood cells are produced.
Production there can be disrupted by various processes:
- These include malignant processes such as leukemia or the absorption of substances that damage the bone marrow.
- A vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency also means that fewer platelets are produced.
Reasons for an increased turnover of platelets can be autoimmune diseases, in which case antibodies against platelets are formed.
These antibodies bind to the platelets and ensure that they are recognized and destroyed by the immune system.
Cause vasculitis
There are a variety of different types of vasculitis.
What these diseases have in common is that they are autoimmune diseases.
The body actually recognizes the body's own cell components as foreign and triggers an immune reaction against them.
The result of this reaction is inflammation.
Vasculitis is divided into large, medium and small vessel vasculitis.
Vasculitis of the small vessels in particular can trigger petechiae, as the smallest vessels, the capillaries, are damaged and blood leaks into the surrounding tissue.
Often, however, vasculitides are not only associated with bleeding in the skin, they can affect every organ of the body with blood.
Please also read the article: Symptoms of vasculitis
Treatment for vasculitis often includes immunosuppressive therapy with glucorticoids such as dexamethasone or other immunosuppressive drugs.
Immunosuppression means that the immune system is weakened and thus the reaction to the body's own structures is reduced.
However, immunosuppressive treatment is associated with many side effects.
Find out more about this in our article: Immunosuppressants
Cause vitamin deficiency
Vitamins are essential substances for the body that must be taken in with food.
The body cannot produce vitamins by itself.
In the case of malnutrition or a disturbance in the absorption of vitamins, a variety of diseases can occur.
A deficiency that rarely occurs nowadays is the vitamin C deficiency, which not only leads to tooth and hair loss but also to petechiae.
The combination of the various symptoms is called scurvy and was once very common among seafarers.
The reason for the pronounced symptoms is a disruption in collagen synthesis, as vitamin C is required for this. Collagen is an important part of connective tissue. The result is a generalized weakness of the connective tissue.
Other vitamins that can trigger petechiae in the event of a deficiency are vitamin B12 and folic acid.
These are very important for DNA production. If this is disturbed, cells can no longer divide as well.
As a result, blood production is reduced. This also affects the platelets, which can then no longer fulfill their hemostatic function. This may also lead to petechiae.
Cause stress
Petechiae are usually triggered by damage to the small blood vessels or impaired blood clotting.
If the cause of petechiae cannot be found, other possible causes are discussed.
An increased level of stress may be a contributing factor to petechiae.
The body's basal metabolic rate is increased during stress, but petechiae are not a typical consequence of stress.
If you discover petechiae on your body and suffer from constant stress, there may be a disease causing these symptoms.
A detailed evaluation and a synopsis of all symptoms is important in order to identify an underlying disease.
Cause strenuous exercise
Regular exercise is primarily beneficial for cardiovascular health. The load should be chosen so that it is strenuous, but does not lead to pain or overload.
Petechiae do not occur in a healthy person during strenuous exercise.
If you discover petechiae after doing very strenuous sport, you should consult a doctor.
In this case, the petechiae are most likely to be the cause of a vitamin deficiency or a disorder of blood clotting.
Drug overdose
Petechiae can occur when certain drugs are given in too high a dose.
Platelet aggregation inhibitors are particularly predestined for this.
The best-known substance in this group is acetylsalicylic acid, or ASA for short - the active ingredient in aspirin.
This causes a certain enzyme in the platelets to be inhibited. This makes it harder for platelets to accumulate together and prevents blood clots from forming.
If the dose is chosen too high, petechiae develop, as minimal damage to the vessel wall can no longer be adequately closed.
Other active substances in this class are clopidogrel or ticagrelor.
Cause drug side effect
If drug side effects come into question as a cause of petechiae, so-called HIT (heparin-induced thrombocytopenia) is the most common.
Heparin is the drug of choice if you want to prevent thrombosis from developing.
It is used for longer periods of immobilization.
It is also used in heart attacks and other heart diseases to prevent further vascular occlusions.
The most feared side effect of heparin is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
It is now reasonable to suspect that this side effect will result in increased bleeding because the platelet count is reduced.
However, the opposite is true.
There are more and more thromboembolic events, i.e. blood clots that can be life-threatening.
The cause of this side effect is an autoimmune-mediated reaction to a complex of heparin and a protein produced by platelets.
The resulting immune complexes of heparin, protein and antibodies can bind to thrombocytes and thus cause the thrombocytes to aggregate and thus to clot.
Cause cough / vomiting
Coughing and vomiting both primarily cause increased intra-abdominal pressure, i.e. an increase in pressure in the abdomen.
Coughing and vomiting can certainly lead to bleeding, but more on the affected organs.
- When coughing, the lining of the airways can become irritated and bleed.
- If vomiting is very severe, it may cause slight bleeding of the lining of the stomach and esophagus.
- Heavy bleeding occurs particularly in the context of alcohol addiction.
However, if petechiae occur with coughing or vomiting, there is probably another cause.
Cause Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a vasculitis of the small arteries that is particularly common in children.
The affected children often had an upper respiratory tract infection in their recent history.
Vasculitis usually results in bleeding into the skin in the form of petechiae.
The cause is probably antibodies that are formed as part of the infection.
The prognosis of the disease is very good, those affected usually recover quickly and healing without consequences can be expected.
Cause leukemia
Leukemia (white blood cancer) is a malignant disease in which there is a strong increase in white blood cells (leukocytes).
The formation of blood cells takes place in the bone marrow.
As the cancer cells multiply in the bone marrow, normal blood cells are displaced.
The result is anemia, i.e. an insufficient number of red blood cells (erythrocytes), and thrombocytopenia.
The lack of platelets then leads to an increased tendency to bleeding and petechiae.
In addition to this bleeding, leukemia can quickly become fatigued.
This article might also interest you: How do you recognize leukemia?
Cause blood poisoning
Blood poisoning is the spread of pathogens through the blood.
The technical term for blood poisoning is sepsis.
Sepsis is a very serious clinical picture and can be associated with petechiae.
The petechiae in sepsis are triggered by toxins from the bacteria that have entered the blood.
These so-called endotoxins lead to excessive activation of the coagulation system.
This activation leads to thrombosis and embolism on the one hand, and bleeding on the other.
The bleeding can appear as petechiae, but extensive bleeding can also occur.
This complication of sepsis is called Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome.
You might also be interested in: Symptoms of blood poisoning
Cause meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the skin that surrounds the brain (meninges).
The disease can be triggered by viruses, bacteria or, less often, other microorganisms.
In the case of diseases caused by viruses, a milder course of the disease can often be observed, while bacterial meningitis is severe and, if left untreated, can quickly lead to death.
Petechiae occur particularly with a certain pathogen, the meningococci.
These trigger meningococcal meningitis which, as a serious complication, can trigger Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome.
In this complication, petechiae occur due to the activation of blood coagulation, and multiple thrombi and embolisms can also lead to multiple organ failure.
You might also be interested in: Signs of meningitis
Cause "hickey"
Changes in pressure due to external pressure can lead to bleeding.
Basically, the bleeding that occurs is rather extensive and a typical bruise forms.
Sucking on a very thin area of the skin, such as the neck, causes the blood vessels supplying the skin to tear through a strong negative pressure.
However, these bleeds are not petechiae, but hematomas, i.e. typical bruises.
You might also be interested in: Blue spot won't go away - what can I do?
Cause poor circulation
A lack of blood flow causes an undersupply of the tissue and results in damage to the tissue with poor blood flow.
Depending on the severity of the lack of blood flow, there may only be a slight restriction in function.
However, there can also be such a severe lack of blood flow that the tissue dies.
If there is insufficient blood flow, the affected tissue appears lighter because there is less blood.
Petechial skin hemorrhages tend not to be observed if there is a lack of blood flow.
Read more about this under our category: Circulatory disorders
Recommendations from the editorial team
You might also be interested in these topics:
- Red spots on the face
- Red spots on the arms
- Red spots on the body
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- meningitis