Desensitization
definition
The desensitization represents a causal (causal) therapy, i.e. it interferes with the cause of the allergy. In the case of desensitization, also known as “specific immunotherapy”, or SIT for short, the principle is to restore the balance between inflammation-promoting and anti-inflammatory messenger substances, which has been shifted in allergy sufferers. A desensitization is mainly carried out in the case of allergies to house dust mites, pollen or insect poisons.

Causes of Hay Fever and Other Allergies
Certain immune cells belonging to the group of Th2 cells are responsible for the inflammation-promoting messenger substances formed in excess after allergen stimulation. A second type of immune cell, the Th1 cells, naturally downregulates the Th2 cells in the body and other messenger substances are produced. This relationship between the immune cells normally represents a finely regulated equilibrium in the body. If this equilibrium is upset, allergies such as Hay fever.
The reaction also recommends you: hay fever and Hay fever in children
Implementation of the desensitization
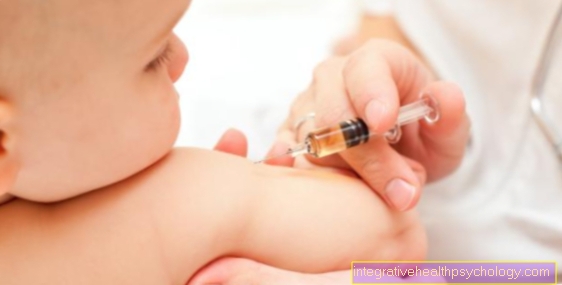
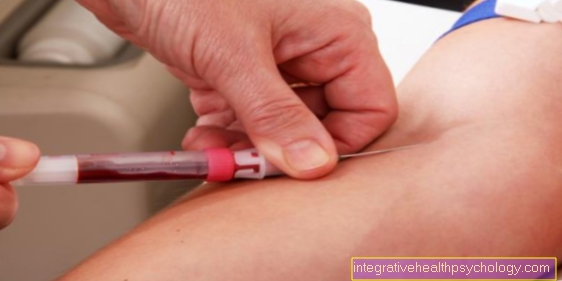
In order to restore the above-mentioned equilibrium, patients are injected under the skin with increasing amounts of the allergen at variable intervals. As a result, more Th1 cells and their specific range of messenger substances are formed, which leads to the regression of the allergic symptoms.
After the injections have been carried out, the patient must be monitored for 30 minutes, as serious side effects with symptoms corresponding to the allergic symptoms, up to and including a shock requiring resuscitation, can occur (this is very rare, however).
Read more on the subject at: Allergic shock
The treatment is usually carried out after a period of pollen count until the acute symptoms have subsided somewhat. The time until the maximum amount of allergen is reached is often up to 3 years.
Which doctor does this?
The desensitization is partly carried out by general practitioners, ENT doctors or also by specialists in allergies, the so-called allergologists.
The first point of contact for allergies is often the general practitioner. If this does not offer specific immunotherapies, those affected can ask their family doctor about allergists, or search the Internet for doctors who offer hyposensitization in their area.
How long does a desensitization take?
The classic desensitization or specific immunotherapy usually takes place over a period of 3 years.
At the beginning of the therapy, the so-called dosing phase, the patient receives a syringe once a week, the allergen concentration of which is continuously increased (the dose is therefore continuously increased). The dosing phase is over after about 16 weeks and the patient is given an allergen injection once a month in the further course of treatment until the 36 months are reached.
In addition to the classic form, there is also short-term desensitization. The concentration of the allergen is increased more quickly in the initial phase and the maintenance dose is reached earlier. Thereafter, as with the classic form, the therapy is continued with a monthly allergen injection. Short-term hyposensitization is mainly used for insect allergies.
There is also the Rush or Ultrarush desensitization. Translated into German, the term “rush” or “ultra rush” means something like, fast or very fast desensitization. With this type of desensitization, the allergen is dosed very quickly. Patients often receive several injections a day and are in-patient during the initial phase. As with the other variants of the desensitization, another monthly allergen injection is planned for the remaining period of 3 years.
What does a desensitization cost?
The costs of desensitization can vary, depending on the type of therapy and the allergy present. One can assume costs of around 3000 € over the entire treatment period of three years.
Who pays the costs?
The costs of a desensitization are usually borne by the statutory health insurance. In the case of privately insured patients, the reimbursement of costs depends on the contractually agreed health services. Depending on the contractual arrangement, both complete and partial cost assumption can be provided. In order to avoid unforeseen costs, private patients should get in touch with their health insurance fund before starting immunotherapy.
Contraindications to desensitization
A desensitization treatment must not be carried out
- malignant / malignant cancers
- Autoimmune diseases
- Pregnancy before the start of desensitization
- acute infection
- and inflammatory bowel disease, as it is an intolerable intervention in the immune system in such cases.
Other severe acute and chronic diseases, e.g. Tuberculosis or purulent inflammation of the bone (osteomyelitis) and coronary heart disease (CHD) are contraindications (contraindications).
Desensitization is also carried out in the case of severe hypersensitivity reactions to insect stings from bees, wasps, rarely also bumblebees or hornets, as well as allergies to house dust mites, some molds and exfoliating products from the skin of cats (epithelia).
Are there any side effects to be expected?
In the case of desensitization, which is carried out by administering allergens in the form of syringes, a local allergic reaction can occur at the injection site. This manifests itself as itching, reddening of the skin and swelling. The local symptoms usually subside after a few days. In order to counteract a local skin reaction, the injection site can be cooled after the allergens have been administered or an alternating injection can be made into the right or left arm.
Read more on the subject at: Allergic reaction on the skin
In rare cases, the administration of allergens can also lead to a general allergic reaction. This can manifest itself in the form of asthma or hives, which are the formation of small red pustules on the skin. Another serious side effect is allergic shock, also known by medical professionals as anaphylactic shock. It is an allergic reaction of the body, which is very rare but acutely life threatening.
To make sure that there are no serious allergic reactions, patients are usually monitored for some time by medical staff or the doctor after the injection of allergens.
Even if allergens are given in drop form, allergic reactions can occur. Because of this, the first dose should also be taken in the presence of a doctor
What is the success rate of a desensitization?
The success of a specific immunotherapy or desensitization depends on various factors. These include the duration of the illness, the type of allergy, the type of allergen administration, the age of the patient and, among other things, one of the most important influencing factors - the cooperation of those affected or the allergy sufferer.
With continuous specific immunotherapy, studies in many age groups have shown a clear reduction in symptoms in the case of an allergic runny nose, pollen allergy, house dust mite allergy or wasp or bee allergy. In the case of other forms of allergy, including allergic asthma, the study situations are partly ambiguous and statements about the chances of success are therefore only rarely or only partially possible.
Is it possible to hyposensitize against house dust mites?
Desensitization or specific immunotherapy can also be used if there is a pronounced dust mite allergy. The therapy is usually 3 years and shows the greatest prospect of success in children from the age of 6, only recently existing allergies to house dust mites or otherwise few to no further existing allergies.
In addition to the administration of syringes that contain specific allergens, allergen preparations in the form of drops can also be taken in the case of house dust mite allergies. This procedure is an attractive alternative, especially for children or sensitive patients.
Read more on the subject at: House dust mite allergy
Can you hyposensitize during pregnancy?
To date, there is no evidence of a harmful effect of desensitization during pregnancy. Doctors assume that treatment with allergens, unlike medication, poses no danger to the newborn.
However, specific immunotherapy can be associated with side effects, such as a severe allergic reaction. For the safety of mother and child, experts therefore recommend the following procedure: If therapy has already started “before pregnancy” and without any side effects, the therapy can be continued. However, the dose of the allergen should not be increased any further.
If no desensitization was carried out before the onset of pregnancy, the start of this should be postponed until after the pregnancy in order to protect against side effects such as a severe allergic reaction in the mother.
Is that also possible with animals?
Desensitization is also possible in animals, especially dogs and cats. As with humans, specific allergens are injected for this. The allergens are mostly proteins that are part of substances or materials to which the animal has an allergic reaction. They are administered in a modified form to the animal for desensitization. This is usually done at the vet at certain time intervals or is sometimes carried out by the owners themselves (as instructed by the vet).
The chances of success for an improvement in the allergy are around 50-60%. In 30% of them there is a remission, i.e. there are no more allergy-related symptoms.