Pain in the tongue
introduction
The tongue is formed by a very flexible interplay of muscle cords in the oral cavity, which is the Chopping up food, of the Language education, the Food transport and the Taste perception serves.
But what if that big muscle hurts and causes problems?
The oral cavity is the place of many diseases and often also a reflection of the overall condition of the organism.

The pain of the tongue is medically referred to as "Glossalgia" guided. Burning tongue is called "Glossodynia"Or"Burning mouth syndrome“.
An inflammation of the tongue is called "Glossitis“.
It is estimated that around two to three percent of the German population suffer from burning tongues each year.
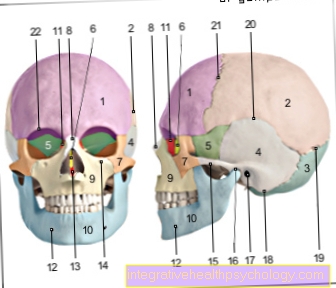
Figure pain on the tongue

Pain in the tongue
Glossalgia
Burning tongue -
Glossodynia
(Burning Mouth Syndrome)
Inflammation of the tongue -
Glossitis
- Underside of tongue -
Facies inferior linguae - Tongue base -
Radix linguae - Tongue almond -
Lingual tonsil - Tongue edge
- Tip of tongue -
Apex linguae - Hyoid bone -
Os hyoideum - Tongue root
An overview of all figsDr-Gumpert applications can be found at: medical illustrations
Causes of tongue pain
The causes of pain, swelling, or burning of the tongue extend over a wide area. Often there are mechanical causes. Pain in the tongue can also be related to other diseases or drugs. Oral hygiene and nutrition also play a role.
Mechanical causes of pain in the tongue
The easiest way that causes tongue pain is through minor mechanical injuries. The tongue is often irritated, for example by a sharp edge or an incorrectly fitting denture. Even a full or partial denture that does not fit well can permanently irritate the tongue. A piercing can also injure the tongue.
When eating, you can easily burn yourself with food that is too hot or accidentally bite your tongue while chewing.
Pain on the tongue as a symptom of other diseases
Inflammatory changes in the tongue are a common side effect of other diseases. These include as examples Syphilis, diphtheria, AIDS or Scarlet fever (Raspberry tongue).
But also the suffering diabetes, Herpes or liver disease Cirrhosis of the liver falls into this category.
Furthermore, one may be allergic to certain foods, often Nuts, special types of fruit, cheese etc .. The body can also lack vitamins A, B, C or iron. The vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to anemia, should be mentioned in particular. The technical term for this is "Pernicious Anemia", which can be fatal if left untreated. The tongue is reddened, very smooth, has fiery red spots surrounded by light or grayish areas. The tongue papillae can be completely lost, this is called Mirror tongue.
Antidepressants or ACE inhibitors have a burning tongue as a side effect. The tongue can be affected due to radiation to head and neck cancer.
Other causes of tongue pain
Psychological causes are often reflected on the tongue, especially a burning sensation is typical. If the soul is suffering, there is excessive stress in everyday life, serious problems are unresolved deeply hidden or one is accompanied by depression, the burning of the tongue can be an indication of such a problem.
The tongue can also burn due to the backflow of stomach contents and thus stomach acid into the esophagus. If the body is given toxic substances in the form of medication, drugs or tobacco consumption, this can also cause problems with the tongue.
Also known is the so-called map tongue, which, as the name suggests, got its name from reddened islands with a white border. However, this is benign, the trigger for it is likely hereditary, but not yet known.
Read more on the subject at: Red spots on the tongue.
In addition to daily dental care, the care of the tongue is essential, because bacteria on it can also lead to inflammation and thus to pain. A tongue scraper, special mouthwashes or a soft toothbrush that you use to clean your tongue quickly reduce this risk.
A sore tongue can also result from an inflamed wisdom tooth. A sign that this needs to be dealt with.
Are you interested in this topic? Read our next article on this below: Big tongue
Symptoms
The complaints can either only appear briefly or extend over a longer period of time. As the day draws towards evening, the pain usually increases.
Women are more likely to have a problem with their tongue. Research has shown that these symptoms are particularly common during menopause. Why this is the case has not yet been determined exactly, it may have something to do with the estrogen level.
Not all symptoms appear together, but mostly individual ones that are indicative of a certain disease. The tongue may be burning, swollen and / or inflamed, and may have blisters or pimples.
- Burning of the tongue is particularly noticeable at the tip and sides of the tongue, which does not have to show any changes in appearance. The burning sensation can also occur in other areas of the mouth, such as the roof of the mouth or the lips. The feeling of pain itself is sometimes very painful and rather dull. Side effects, in addition to burning, are not uncommon. The mouth can be dry and taste can be impaired. In addition, there is usually a kind of furry feeling and an unpleasant bad breath. In addition, the flow of saliva may be increased.
- The sensitivity to cold or hot food is increased
- Swallowing and speaking cause problems.
- White deposits are usually lost through daily mouth cleaning. If they persist, however, a coating in the back third indicates problems with the intestine, in the middle it is more likely to be an inflammation of the mucous membranes and in the front third of a possible gastric mucosal inflammation.
- Removable coverings indicate a fungal disease, usually with Candida albicans, to.
- If you have a swollen tongue, a possible option is a thyroid problem and associated hormonal imbalances.
- If the veins on the underside of the tongue can be seen particularly clearly and may have sack-like enlargements, this may indicate a problem with the heart. The heart may not pump hard enough for the blood to build up in the veins.
- Side effects of medication can manifest themselves in the fact that the papillae turn black or brown.
Some of the accompanying symptoms are taken up and explained again below.
In most cases, symptoms usually go away after a few days. If it doesn't, it indicates a more serious condition that should be investigated by the doctor.
Pain in certain areas of the tongue
The pain can affect all or part of the tongue. The localization is very important in order to be able to infer the correct cause. Sometimes only the tip or side of the tongue is affected, the back / base of the tongue or other areas.
Pain under the tongue
In most cases, pain under the tongue is accompanied by severe swelling, reddening or localized warming. The reasons for this can be varied. A lack of minerals and vitamins is often the reason for a sore tongue. Furthermore, injuries, infections, canker sores, general diseases or even oral cancer can be the causes.
Read more on the topic: canker sores on the tongue
Another common case is a blocked duct in one of the salivary glands. The paired salivary glands on the ears, under the tongue and on the lower jaw produce most of the saliva per day. They open into the oral cavity via an outlet duct. If this is blocked, it comes to swelling and back pressure. The skin around the salivary gland is often red and swollen and is painful, especially when it is pressure. A doctor should be consulted to clear the blockage.
Allergies, neuralgia (nerve pain), smoking or even dental problems can also affect the tongue and lead to pain.
Read more on the subject at: Pain under the tongue
Pain at the tip of the tongue
If the pain is only at the tip of the tongue, the cause is usually mechanical stimuli. These include bruises or injuries due to sharp edges, for example on prosthetic fittings or on a glass while drinking. If, for example, you have bitten your tongue or burned yourself on something hot, the pain in the tip of the tongue can persist for a few days after the injury without you being able to see anything outwardly.
Read more on the topic: Burned tongue - what to do?
Another possible cause of the pain in the tip of the tongue is the presence of one or more small canker sores in the area of the tip of the tongue. These are small blisters that are particularly painful to the touch. The canker sores are visible to the naked eye. In this case, non-prescription ointments and creams will help to relieve a little of the pain.
The front 2/3 of the tongue become sensitive to the Lingual nerve, a branch of Trigeminal nerve, provided. An irritation of this nerve when there is pain in the front part of the tongue is therefore possible. If the pain in the tip of the tongue persists, it is advisable to consult a doctor who can find out the cause.
Read more about this under Pain at the tip of the tongue
Pain on the edge of the tongue
Pain at the edge of the tongue is often caused by mechanical stimuli such as bruises or sharp-edged prosthetic restorations. The constant rubbing on the restorations results in small, barely visible injuries, which can sometimes cause severe pain.
Pain in the root of the tongue
The thickest and rearmost part of the tongue, which is located in the back third of the mouth, is called the root of the tongue or also Radix linguae designated. In this area is the tongue tonsil (Lingual tonsil). This is part of the immune system and can be swollen and red in the case of inflammation. Tonsillitis is very common.
Read also: Swollen tongue
In this case, there may be pain in the area of the root of the tongue. Herbal medicines are suitable for mild inflammation, while an antibiotic should be prescribed by a doctor for more severe inflammation. Pain in the root of the tongue is usually accompanied by difficulty swallowing or pain in the throat and pharynx.
Read more on the topic: difficulties swallowing
Hormone fluctuations or a tumor in the area of the root of the tongue can also cause pain in the tongue, throat and throat area. In general, however, in most cases it is tonsillitis. Nevertheless, it is advisable to consult an ENT doctor who can make a clear diagnosis. Furthermore, it can be tested whether an irritation of the Glossopharyngeal nerve present. This supplies the back third of the tongue sensitively.
Pain at the base of the tongue
The tongue base is the rearmost fixed part of the tongue. It is between the epiglottis (the epiglottis) and the mobile part of the tongue. The tongue tonsil is also in this area, the inflammation of which can also cause pain here. The original organs for squamous cell carcinoma or tumors in the oral cavity are the tonsils and the base of the tongue. So if pain occurs in these areas, it is very important to see a doctor. Tumors are usually not painful, but early diagnosis is very important.
Read more on the topic: Tongue cancer
Smoking and alcohol consumption are the main causes of this disease. Care should always be taken to minimize the risk factors. Often there are pain in the area of the base of the tongue with further symptoms. These include Difficulty swallowing, breathing, feeling hot, scratchy throat and feeling of inflammation. Often these symptoms can also be an indication of a basic tongue hyperplasia. This means that the base of the tongue is greatly enlarged, as the number of cells has risen sharply due to the increased division rate. Hyperplasia can cause shortness of breath. Therefore, a doctor must assess whether the hyperplasia needs treatment or not.
Hyoid bone pain
The hyoid bone (Os hyoideum or Hyoid) is a small bone spanned by ligaments and muscles that lies between the larynx and the lower jaw below the tongue. It is essential for breathing, swallowing and speaking. Hyoid bone diseases are rather rare.
The pain in this area could be caused by inflammation or growth. Since the bones are spanned by muscles and ligaments and attached to them, there may be muscle tension, which can lead to pain, restricted mobility and difficulty swallowing.
Difficulty swallowing and tongue pain
Difficulty swallowing can have a variety of causes. These include allergies, organic causes, neuralgia, psychological factors or infectious diseases. Swallowing difficulties usually arise due to swollen tissue. Depending on where the swelling is, it can lead to life-threatening breathing problems if left untreated. One example is that Basic tongue hyperplasia. Depending on the severity, this swelling with increased cells must be treated surgically.
Aphthae can also cause pain on the tongue. These are usually accompanied by difficulty swallowing and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Read more on the topic: difficulties swallowing
Symptoms accompanying tongue pain
It is important to keep a close eye on the complaint area and to be able to describe to the doctor how you are feeling. Often the tongue burns heavily or whitish deposits can be found. If swallowing problems occur, you should definitely have this clarified so that there is no risk of life-threatening shortness of breath.
White spots and tongue pain
White spots on the tongue are harmless in most cases. They are a sign of dehydration, inadequate fluid intake and poor oral hygiene. You should therefore first carry out extensive oral hygiene and clean the tongue with a tongue cleaner. It is recommended that you drink plenty of water to wash away the white particles.
The white spots can also be caused by a fungal infection Candida albicans yeast be evoked. One then speaks of oral thrush. Especially when taking antibiotics, the fungus that is naturally present in the mouth takes over, so that an infection develops.
Read more on the topic: Oral thrush
If the white spots have not disappeared on their own after about two weeks, a doctor should be consulted.
Burning tongue pain
Often there is pain in the tongue that can be described as burning tongue. Most patients experience burning, itching, and stinging of the tongue. Usually an irritation in the mouth together with an inflammation of the tongue is the cause of the burning sensation. These can also be mechanical stimuli, such as rubbing a prosthesis on a pressure point or an allergic reaction.
Read more on the topic: Burning tongue
Another possible cause of the burning sensation in the tongue can be other general illnesses in which burning tongue can occur as a symptom. These include, for example. Diabetes mellitus, vitamin deficiency, anemia or infections in the mouth. Externally, the tongue is usually not visible. If there is inflammation of the tongue, the doctor often recommends mouthwashes in addition to antibacterial or antiviral treatment. General thorough oral hygiene is essential here.
Read more on the topic: Burning at the tip of the tongue
Tongue hurts like a sore muscles
If the tongue feels heavy or if movements of the tongue cause difficulty and possibly pain, this uncomfortable feeling can be described as a kind of sore muscles. The reasons for this cannot be precisely determined. In general, excessive movement of the tongue can also overload the muscles. In this case, it is advisable to have the oral cavity examined carefully by a doctor.
White coating in the rear area
A light, light-colored coating on the tongue is normal. It arises in the course of everyday food residues and bacteria and can be easily removed during daily oral hygiene. However, a white coating on the tongue can also be a sign of illness. White, persistent coating on the tongue can be a sign of a cold or gastrointestinal disease.
White coatings on the edges of the tongue and in the back third of the tongue, on the other hand, are an indication of scarlet fever. Furthermore, a white coating on the tongue can be a sign of cirrhosis of the liver or precancerous disease. A doctor should be consulted if the white coating has not disappeared after two weeks despite your own treatment measures or if swelling and pain occur in the affected areas.
Diagnosis
In the event of uncertainty or symptoms that do not subside, a visit to the doctor is advisable.
Delaying can make the situation worse and a serious illness goes undetected. A possible infection could spread, it could become difficult to swallow, the pain could become chronic, or shortness of breath could occur.
Often the first point of contact is a dentist, as many suspect a problem with their teeth or with a denture. However, the causes listed above show that the cause can be completely different.
The treating dentist or family doctor examines the oral cavity and analyzes possible previous illnesses and the general course of the disease. A broad anamnesis (medical history) is necessary because a lot has to be considered, from psychological factors to a skin disease.
A swab from the tongue can reveal a fungal infection, or an allergy test can reveal possible intolerances. A referral to a specialist is normal in this case.
therapy
With a slight inflammation of the tongue, therapy is not very difficult if there is no major illness behind it. The pain can be relieved by drinking sage tea or rinsing with a saline solution.
If a fungal infection has been diagnosed, a Antifungal agent administered or the appropriate antibiotic to fight bacteria.
Yoghurt should be suitable as a home remedy, which should have a soothing effect on a sore tongue.
If you have a psychological problem, it is certainly advisable to see a therapist, but this will be discussed in detail by the attending physician.
Once the cause of the tongue pain is found, it should go away quickly after starting the appropriate treatment.
Building the tongue
The tongue (lat. lingua) is made up of different muscles and is divided into three sections. These are the root of the tongue (Radix linguae), the tongue body (Corpus linguae) and the tip of the tongue (Apex linguae).
The smooth underside of the tongue body is over a ribbon (Frenulum linguae) grown together with the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth.
Through a furrow (Sulcus medianus) the tongue is divided into a right and left half. This runs backwards until another furrow (Sulcus terminalis) divided the body from the root. The muscle body consists of inner (for self-deformability) and outer tongue muscles (for freedom of movement).
The tongue papillae and glands sit on the mucous membrane of the back of the tongue. Some of the different papillae are responsible for the sense of taste, others for the sensation of warmth or for an enlargement effect when we feel structures with the tongue, as when eating. It is supplied by branches of the lingual artery and branches of cranial nerves.
The task of the tongue is, in addition to the different sensations, also to participate in the formation of sounds or to support the immune system.
Recommendations from our editorial team
- Burned tongue - what to do?
- Canker sores on the tongue - what does that mean?
- How to recognize inflammation of the tongue
- Causes of a Chapped Tongue
- Burning Tongue - This Can Be Done










.jpg)