Pain in the abdomen
General
Are you female and looking for a possible cause of your abdominal pain? Then you will find helpful information in our following article.
Abdominal pain is a common problem, especially for women. However, the causes are varied and sometimes difficult to find.
In the woman's abdomen there are, among other things:
- Urinary bladder with urethra
- Uterus,
- part of the intestine,
- the appendix
- Nerves, vessels and lymph nodes
If you are one of our male readers, visit our page: Abdominal pain in men
In principle, in addition to normal menstrual pain, any organ can cause the pain. A thorough medical history is therefore important to make the diagnosis.
Particular attention is paid to:
- Pain quality (stabbing, dull),
- Localization,
- Radiation of pain,
- Duration and intensity.
Since the diagnosis is easier to make when the exact location is known, the causes are classified here according to the location.

Right lower abdomen pain
- Appendicitis
Appendicitis often manifests itself in the lower right quadrant. Sometimes the pain is also described next to the navel.
Possible symptoms are: loss of appetite, vomiting, nausea, fever and diarrhea. Appendicitis should be treated as quickly as possible, as the appendix can burst in the worst case.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder
Although the gallbladder is located in the right upper abdomen, it can also radiate painfully into the right lower abdomen if it is inflamed. Patients particularly complain of pain after eating, especially after consuming fatty foods or coffee. Gallbladder inflammation often triggers nausea, as well as nausea and fever.
Read more on the topic: Right abdominal pain
Pain in the left lower abdomen
- Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a disease in which there is inflammation of intestinal protrusions. The pain of diverticulitis often manifests itself on the left side, since mostly the rectum (Sigmoid colon) is affected. The pain often occurs suddenly and also radiates to the back. Diarrhea, vomiting, mucus and blood in the stool can occur. Changes in urine behavior can also occur. Patients with diverticulitis often complain of problems urinating.
You can find further information under our topic: Abdominal pain on the left side
Pain in the right or left abdomen
- Pelvic inflammation
Urinary tract infections often precede this. Renal pelvic inflammation manifests itself with fever, increased urge to urinate, flank pain, chills, nausea, vomiting, blood in the urine and pain when urinating.
- Kidney stone
Depending on the location of the stone, the pain is higher or lower and can occur on both sides. If the stone is in the ureter, the pain is often not constant, but occurs in waves. Often there is excretion of blood in the urine and, depending on the size of the stone, urine congestion and inflammation of the kidney.
- Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infections lead to pain and burning when urinating, bloody urine, frequent urination, burning in the vagina and, depending on the severity of the inflammation, flank pain, nausea and vomiting.
- Ectopic pregnancy
The symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are: missed periods, vaginal bleeding, dull to sharp pain in the right or left lower abdomen, breast tenderness, nausea, and vomiting.
- Egg ladder inflammation
The symptoms of fallopian tube inflammation are often similar to symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy. These include: fever, sharp or dull pain, increased discharge, nausea and vomiting.
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease:
These two conditions are inflammatory bowel disease and often cause pain.They differ in the localization of the infestation.
Ulcerative colitis is restricted to the large intestine, while Crohn's disease can affect anything from the onset of the oral cavity to the anus. However, the symptoms are similar. Both cause pain in the lower abdomen and frequent diarrhea. There may also be blood in the stool. The patient often complains of fever, night sweats and severe weight loss.
- Ileus
The word ileus in medicine means intestinal obstruction. A bowel obstruction can be mechanical or functional. Adhesions caused by operations in the abdominal cavity can pinch the bowel and lead to closure. The main symptoms are: Excessively bloated stomach, wind and stool retention, vomiting and severe stabbing pain.
- Intussusception
Intussusception describes the invagination of the intestine. In adults, the symptoms often start slowly and resemble those of an intestinal obstruction. An indicative symptom can be a jelly-like stool.
- Volvulus:
The volvulus describes the twisting of intestinal loops. The symptoms are: bloated stomach, nausea, vomiting, stool retention and fever.
- Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the lining of the uterus is not only inside the uterus but also outside of it. Usually it is only dispersed in the basin. Endometriosis can cause very severe pain in the abdomen, regardless of the amount of mucous membrane that is scattered. However, this pain usually only occurs during your period. In addition to back pain, vomiting and diarrhea can be symptoms. In addition, the pain can also occur during sexual intercourse.

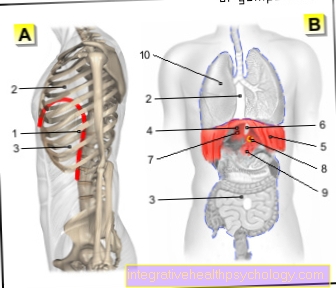
Abdominal pain - woman
- Gallbladder - Vesica biliaris
- Kidney - Ren
- Ureter - Ureter
- Small intestine -
Intestine tenue - Rectum - Rectum
- Appendix - Caecum
with appendix
Appendix vermiformis - Uterus - uterus
- Urinary bladder - Vesica urinaria
- Urethra - urethra
- Sheath - vagina
- Large intestine, descending part -
Descending colon - Fallopian tubes - Tuba uterina
- Ovary - Ovary
A - kidney stones (nephrolites),
Ureteral stones, bladder stones
(Uroliths) and urethral stones
B - inflammation of the appendix
of the cecum (appendicitis)
is also called appendicitis
designated
C - diverticulum (protuberances of the
Mucous membrane) - preliminary stage of diverticulitis
D - diverticulitis (disease of
Colon and rectum)
Inflammation of intestinal protuberances
E - ovarian cyst (ovarian cyst) -
liquid-filled cavity
F - endometriosis - overgrowth of
Tissues of the uterine lining
(Endometrium) outside the uterus
G - Myomas - Benign adhesions
the uterine muscles
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Pain in the bladder area
Cystitis, in which pathogens rise through the urethra and into the bladder, causing inflammation of the bladder lining, can also cause pain in the abdomen. Due to the anatomical proximity, these can pull into the back. Symptoms such as frequent, painful urination in small amounts of urine suggest a cystitis.
Bladder inflammation can be promoted by pregnancy, diabetes, immune deficiency, urinary stones, tumors, bladder dysfunction in certain nerve diseases or reflux of urine from the bladder back to the kidney.
If the symptoms do not go away after a day or two, you should consult a doctor. If left untreated, the infection of the bladder can ascend via the ureters to the kidneys, where it can trigger a very painful pelvic inflammation, often accompanied by fever.
A so-called irritable bladder, which is associated with symptoms similar to cystitis, can also cause sharp pain in the abdomen and back. The reason for this has not been sufficiently clarified. One suspects a psychological component. The patients are also often prone to infections and tension.
Urinary stones and mineral salts, which are normally dissolved in the urine and are easily excreted, can precipitate in the form of small crystals in the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra in metabolic disorders such as gout or diabetes. If the crystalline deposits are deposited on top of one another and thus become larger, they can cause cramp-like pain in the abdomen, which can radiate from the genitals to the back. The therapy depends on the size of the stones and ranges from drug dissolution to shock wave destruction to surgery for very large urinary stones.
You may also be interested in this topic: Burning in the abdomen
Menstrual pain
Women often experience cramping abdominal pain during their menstrual period, which is completely natural and harmless.
During your period, the lining of the uterus and its vaginal discharge become detached and contracted. The abdominal pain that this triggers often extends to the lower back. Hot water bottles, relaxation baths or a massage can counteract the pulling pelvic pain. Under certain circumstances, the monk's pepper used in naturopathy can help to stabilize the hormone balance and thus possibly reduce pain.
Pain during pregnancy
If abdominal pain occurs during pregnancy, this can be very worrying for the expectant mother. Not all ailments in the lower abdomen are dangerous, many are natural and normal. Especially in the first and second trimester of pregnancy, up to about the 20th week, pregnant women often complain of pain in the abdomen. To make room for the growing baby, the uterus enlarges under the influence of pregnancy hormones. The surrounding connective tissue and the associated ligaments and muscles are stretched and loosened. They lead to the typical abdominal pain in early pregnancy. Try to counteract the symptoms by, for example, relaxation exercises or a warm bath.
If, however, in the so-called critical phase, the first twelve weeks of pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman's body decides whether the embryo is viable or not, abdominal pain accompanied by bleeding and severe cramps occur, this can also be an indication of an impending miscarriage .
If, in addition to abdominal pain, there is a tight, hard abdominal wall, it may be a so-called ectopic pregnancy. The fertilized egg has incorrectly lodged in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. Such a fallopian tube can rupture and cause internal bleeding due to the increase in the size of the unborn child. Both cases, the threatened miscarriage and the ectopic pregnancy, represent medical emergencies. Therefore, one should consult a doctor immediately.
In late pregnancy, around the 20th week of pregnancy, there are different reasons for abdominal pain. In the 23rd to 37th week of pregnancy, the pain, possibly accompanied by bleeding, can indicate that the mother-to-be is preparing too quickly for the birth and thus the impending premature birth. See a doctor urgently!
A few days before the planned birth, the cervix dilates and the abdominal pain is associated with it. These are the first contractions and the discharge of the amniotic fluid. It is a natural process that heralds the impending birth of your child.
In any case, seek medical advice if you experience abdominal pain during pregnancy that you cannot properly classify for yourself. On the one hand it can be a completely harmless cause of the abdominal pain, but on the other hand it can also be a serious problem for your unborn child.
Read more about the topic here: Abdominal pain during pregnancy
Diagnosis
The diagnosis can be extremely difficult as the pain is often radiated or diffuse and an exact localization cannot be determined.
Nevertheless, a precise anamnesis is essential as it can provide important information about a serious illness. Particularly important in the anamnesis are:
- Pain quality (stabbing, dull, pressing),
- Localization,
- Intensity (pain scale 0-10),
- Spread and time of occurrence are important (sudden, breath-dependent).
Different tests may be necessary depending on the suspicion of the disease. For gynecological diseases, the examination includes speculum adjustment, smear and ultrasound.
If a stomach disease is suspected, it may be necessary to do a gastroscopy. In the case of intestinal diseases, a colonoscopy can be helpful for diagnosis. CTs, MRIs, X-rays or blood tests can also provide information about the disease.
Therapy options are based on the individual diagnosis.








.jpg)