Numbness of the head or scalp
definition
A feeling of numbness in the head or on the scalp is a sensory disorder in this area.The medical term for this clinical picture is hypesthesia. The feeling in the corresponding skin areas is reduced. Sometimes there is also an uncomfortable tingling sensation. It is comparable to the sensitivity disturbance after an injection at the dentist. Often the numbness is temporary, but in some cases it is permanent. It depends on the cause.

Causes of numbness in the head
There are numerous causes of numbness in the head and scalp area. First and foremost, numbness in the head makes you think of a nerve disorder. The feeling in the skin is conveyed by sensitive nerves that transmit information to the brain via their nerve fibers. If these nerves are damaged anywhere along their course, there is a feeling of numbness in the corresponding skin area. The cause can be, for example, a stroke or an accident. In this case, the symptoms often appear on only one side of the body.
But circulatory disorders can also cause numbness. If the blood circulation is poor, the nerves are not adequately supplied with nutrients and can then no longer fully perceive their function, the transmission of stimuli. This also applies to inflammatory processes.
Also read the article on the topic: Numbness of the face
psychosomatic causes
But psychosomatic causes can also play a role in head numbness. Psychosomatic illnesses are physical complaints that are caused by psychological stress factors. In short, when the soul suffers, the body also suffers. The causes of numbness are often false or pathological nerve irritation; this over-excitability of the nervous system can be explained well by an increased level of stress. However, you should always consult a doctor if you have numbness in the head, as there can be other causes.
Accident or fall as a cause of numbness in the head
An accident with a fall on the head can also lead to numbness in this area. It is conceivable that in the event of a fall, the sensitive nerve endings in the skin are injured. These can then no longer properly forward the relevant information to the brain. The skin feels “numb” in this area. Most of the time these complaints are only temporary; as a result of the fall, the function of the nerves, as in the case of a bruise, is only temporarily disturbed. When they have recovered, the numbness will also go away. If the numbness does not subside, a doctor should be consulted, since in rare cases it can also be serious damage.
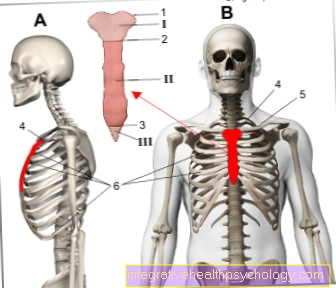
Can the numbness also come from the cervical spine (Cervical spine)?
You can answer this question clearly with yes. Numbness on the head or scalp can be caused by discomfort in the cervical spine. The back of the head and the skin around the ear in particular receive sensitive supplies from nerves from the cervical plexus. These nerve fibers emanate from the spinal cord in the area of the cervical spine. If the nerve fibers in this area are e.g. Damaged by a herniated disc or a narrow bony (spinal stenosis), this leads to a feeling of numbness in the head.
Read more on the subject at: This is how I recognize a herniated disc or symptoms of spinal stenosis
Thyroid problems as a cause of sensitivity disorders
Thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto's disease, which is a type of underactive thyroid, cause many symptoms. However, these do not occur in all those affected. But there are definitely patients who complain of numbness in the head. Usually these occur in connection with other symptoms such as concentration and memory disorders, lack of drive and depression. The good news is that these symptoms usually resolve completely with adequate treatment for thyroid disease.
Migraines can also cause numbness
In addition to the regular form of migraines, there are also patients who suffer from migraines with aura. Here, numbness of the head is a typical symptom. The aura is understood to be the neurological symptoms that precede the headache. A classic example is visual impairment (flashes of light or flickering in front of the eyes). But numbness or a tingling sensation in the head or in the limbs also occur. However, these disorders are all temporary. With the end of the migraine attack, they recede completely.
Also read: Migraine attacks
Sinus infection as a cause of numbness of the face
Sinus infections can also cause sensory disturbances in the head area. Large parts of the skin on the face are supplied by fibers of the fifth cranial nerve, the trigeminal nerve. This arises in the brain and then divides into its three branches. Some of these run in very close proximity to the paranasal sinuses. These nerves can be damaged as part of an inflammatory process in the area of the sinuses. The result is numbness in the head. The symptoms usually go away as the sinus infection subsides.
Otitis media
An otitis media can also lead to numbness in the head. Compared to sinus infections, however, otitis media is much less likely to damage nerves. Since there are usually no large sensitive nerves in the middle ear area. Nevertheless, it is also conceivable that the inflammation could spread to surrounding structures. This can damage sensitive nerves that innervate parts of the skin on the head. This would explain the numbness in these areas.
Concomitant symptoms
In most cases, numbness in the head is only temporary and therefore harmless. However, it can also be a sign of a threatening illness. This mainly depends on the accompanying symptoms. Alarm signs are numbness that occurs together with speech or vision disorders, or those that spread to one side of the body next to the head. Sudden symptoms of paralysis and severe headaches are also warm signals.
If the numbness occurs together with toothache or earache, it is usually an underlying disease from this area. Since the causes of numbness are very diverse, a wide variety of accompanying symptoms are also conceivable.
You might also be interested in that: Numbness in the ear - what's behind it?
Numbness and pain in the head
Patients often find numbness in the head uncomfortable. Some described it as painful, for others it was "just" a tingling sensation. In addition, headaches can occur as an accompanying symptom. This is the case, for example, with a migraine with aura. Painful muscle tension in the cervical spine also leads to numbness in the head and, in addition, to pain radiating there.
Any numbness should be seen as a warning sign that can indicate an undersupply of the tissue. Find out more about this topic at: Numbness of the tongue
Diagnosis for numbness in the head
In order to be able to diagnose numbness on the head or in the area of the scalp quickly and reliably, a medical consultation and a physical examination are most important. The conversation itself often provides the first clues as to the cause of the sensitivity disorder. A physical examination may reveal other accompanying neurological symptoms that have not yet been noticed.
This then also decides which further diagnostic measures should be taken (e.g. laboratory examination, measurement of the nerve conduction velocity, sectional imaging using CT or MRT).
Find out all about the topic here: The sensitivity disorder.
Therapy for numbness of the head or scalp
Treatment for numbness of the head or scalp depends on the underlying cause.
- In the event of a stroke, the person affected is immediately taken to a neurological clinic as an emergency and treated accordingly.
- In the case of migraines as the cause of the numbness, this does not have to be explicitly treated, as it is only an accompanying symptom and it resolves itself after the attack. The headaches typical of migraine should be treated with pain relievers.
- If the numbness has a psychosomatic cause, it is advisable to treat it. Stress reduction, relaxation procedures or psychotherapy are useful.
- If the numbness is caused by inflammation in the sinuses or the ear, this infection must be treated as soon as possible. This is done with antibiotics and, if necessary, with an operation.
- An orthopedic surgeon treats diseases of the cervical spine with pain relievers, acupuncture, or injection therapy.
Ultimately, the treatment of numbness is very complex, so it is important to know the exact cause, otherwise treatment is rarely effective.
Duration of numbness
How long head numbness persists and whether it persists depends on its cause. Most of the time, numbness in the head is temporary and short-lived. Very often they disappear again completely, as there are often harmless causes behind them.
However, if a stroke is the cause, it depends on how quickly and adequately the patient is treated, whether the symptoms resolve completely or not.
forecast
In most cases, the cause of numbness in the head is rather harmless and the prognosis is therefore very good. The unpleasant sensation often disappears without treatment. With psychosomatic causes, stress reduction, relaxation procedures and psychotherapy have a positive effect on the prognosis. If more serious illnesses such as a stroke or an inflammation are behind it, it depends on how quickly and consistently these illnesses are recognized and treated.