Visual disturbance after a stroke
introduction
A stroke describes a circulatory disorder in the brain. This can be triggered by calcification of the vessel walls or by a blood clot that clogs the vessels. A cerebral haemorrhage can also lead to an insufficient supply of the brain. As a result, the cells die and the tissue perishes.
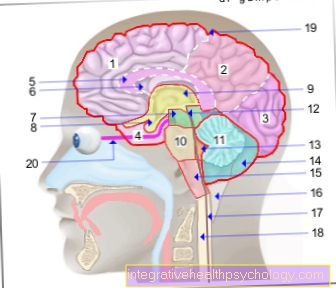
The stroke can affect different areas of the brain. If the visual center is damaged, a visual disturbance results that can even lead to blindness.

The accompanying symptoms
A visual impairment can be caused by damage to the so-called occipital lobe. In this area, visual stimuli are processed and vision is only possible. This area is supplied by the posterior cerebral artery (arteria cerebri posterior). If the artery closes on one side, there is a loss of visual field. The field of vision can only be perceived to a limited extent. A bilateral closure leads to complete blindness.
Learn more about that Scotoma.
If the posterior cerebral artery is severely occluded, the thalamus is damaged. The thalamus is part of the diencephalon and is used to process information. Here the stimuli are received, processed and then passed on to the cerebrum. The damage results in a loss of consciousness and a contralateral hemihypesthesia. This means that, not on the side of the damaged thalamus, but on the opposite side, there is a reduced sense of touch or pain. Furthermore, memory disorders and problems with learning can arise. Psychological changes, such as depressive behavior with exhaustion, can also be observed frequently.
Read more about this at: Dizziness and blurred vision
General information on the topic can be found here: Visual disturbances
The balance disorder after a stroke
If the posterior cerebral artery closes early on, arteries leading to the cerebellum may also be affected. Functionally, the cerebellum has different tasks. This includes the coordination and fine-tuning of movement sequences and the maintenance of balance. The muscle tone is also regulated by the cerebellum.
With a stroke, the tissue in the cerebellum is no longer supplied with blood and the nerve cells perish. As a result, neurological deficits such as balance disorders arise. The affected patients walk uncoordinated and very shaky.
Also read the article: The cerebellar infarction.
The dizziness after a stroke
The dizziness can also be caused by damage to the cerebellum. If the stroke affects the posterior cerebral artery early on, the cerebellar nerve cells perish. In addition to coordinating movement sequences, the cerebellum also regulates the fine motor skills of the eye muscles. As a result, the view can no longer be stabilized. The combination of these functional failures leads to uncoordinated eye movements and an unsteady gait pattern. The body no longer knows what position it is in. This loss of information creates dizziness.
Another cause can be the faulty blood pressure regulation. The blood pressure is lowered too much, which is especially noticeable when moving.
Find out more about the topic here: Dizziness after a stroke.
The healing of a visual disorder after a stroke
The healing process for a stroke varies greatly from person to person. It depends on the extent of the damaged area, the start of therapy and the rehabilitation measures. In addition, each person has a different reserve capacity. The less the brain is damaged by small micro-infarcts or trauma, the higher the reserve capacity. Because of this, younger patients also have a better prognosis.
In addition, the brain exhibits neural plasticity. This means that nerve cells from other brain regions can partially take over the function of the dead cells. This may improve the symptoms clinically. Progress can be observed, especially with visual field defects. A cure for blindness, however, is unlikely.
The healing process can be positively influenced by early rehabilitation. The neural plasticity or the reorganization of the brain mainly takes place in the first 6 months after a stroke. For this reason, rehabilitation measures should be initiated as early as possible.
Find out all about the topic here: The cure after a stroke.
You can do this yourself to improve healing
To improve healing, the first step would be self-motivation. The affected patients should take rehabilitation and physiotherapy seriously and, if necessary, perform the exercises independently at home. You should also avoid risk factors such as nicotine and alcohol. If there is no physical limitation, it is advisable to go for a walk regularly to promote the circulation and blood circulation. Swimming or yoga are also suitable sports. In addition, a balanced diet can be ensured. Mediterranean food, with lots of vegetables, olive oil and fish is particularly suitable for this. It protects the vessels from calcification and prevents the progression of calcifications.
Since the stroke not only causes physical symptoms, but also represents an emotional burden, it should be dealt with openly. Support from relatives or psychological support can be a considerable relief.
The long-term consequences
The long-term consequences can vary. They depend on the location and the extent of the damaged area. It also depends on the healing. If the brain was slightly damaged, it can recover from the stroke more quickly. Reorganization also plays a role here - nerve cells from other areas are able to partially take over the function of the dead cells. Because of this, some symptoms may improve clinically or even go away completely. For example, mild visual disturbances, dizziness, and gait disorders may improve over time as the body gets used to them and develops other strategies to deal with them.
However, the prognosis for complete blindness is not particularly good. This symptom usually persists. Affected patients must try to adapt to everyday life with suitable aids. Other long-term consequences can be changes in personality. Some patients become particularly aggressive, while others lose their drive and suffer from depression.
In general, however, it can be said that symptoms that persist after 6 months are more likely to persist.